Definition of Bandaging – Nursing is a profession within the healthcare sector focused on the care of individuals, families, and communities so they may attain, maintain, or recover optimal health and quality of life. Nurses may be differentiated from other healthcare providers by their approach to patient care, training, and scope of practice. Nurses practice in many specialisms with differing levels of prescriber authority.
Many nurses provide care within the ordering scope of physicians, and this traditional role has shaped the public image of nurses as care providers. However, nurses are permitted by most jurisdictions to practice independently in a variety of settings depending on training level. In the postwar period, nurse education has undergone a process of diversification towards advanced and specialized credentials, and many of the traditional regulations and provider roles are changing.
Nurses develop a plan of care, working collaboratively with physicians, therapists, the patient, the patient’s family, and other team members, that focus on treating illness to improve quality of life. Nurses may help coordinate the patient care performed by other members of an interdisciplinary healthcare team such as therapists, medical practitioners, and dietitians. Nurses provide care both interdependently, for example, with physicians, and independently as nursing professionals.
Definition of Bandaging
A bandage is a piece of material used either to support a medical device such as a dressing or splint, or on its own to provide support to or to restrict the movement of a part of the body.
Or.
A Bandage is defined as a piece of gauze or other materials used for wrapping, binding up and Support or immobilized a part of the body.
Commonly a bandage is defined as a material applying to secure a dressing in position.
Bandaging is the process of covering a wound or injured part using various materials such as gauze, elasticized knit, flannel or muslin.
Bandaging is a process which applied to the injured part of the body or to limb for immobilize, binding up and secure to support.
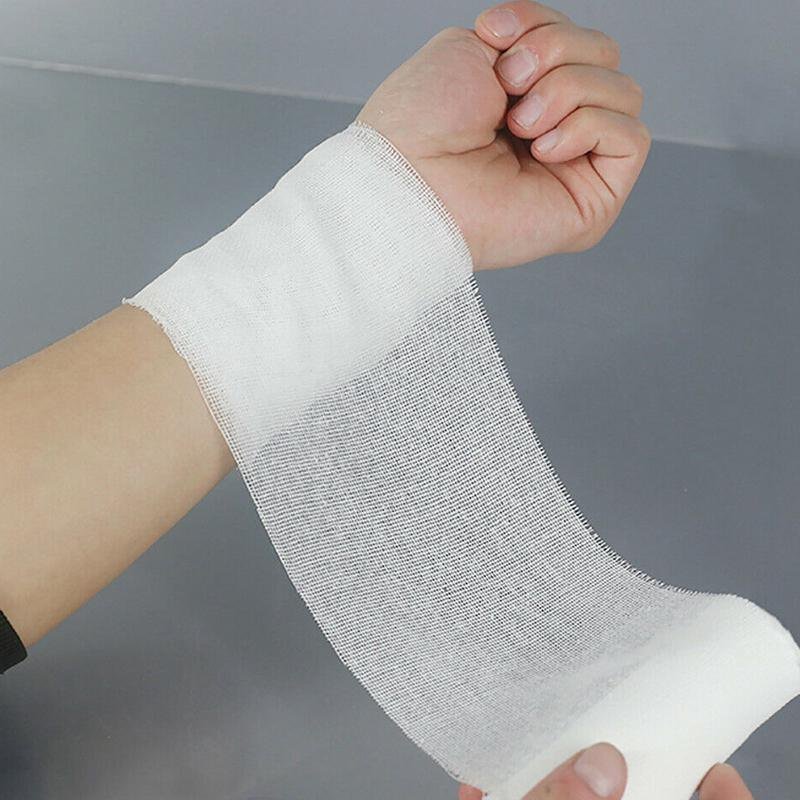
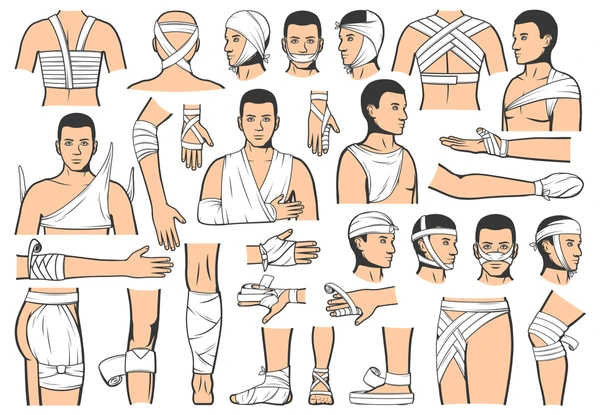
Types of Bandages
A) Triangular bandage: It used for slings.
B) Roller bandage: It used for bandaging any part of the body.
C) Special bandages:
a) Many tailed bandages: It used as abdominal binder.
b) Four tailed bandage: It used for bandaging the chin or jow bandage.
c ) T bandage: It used holding dressing over perineum.
d) Crepe and plastic bandages: It used for joints and varicose veins and also used in sprain.
e) Crinoline and plaster of Paris bandages: It used for making casts or for plasting.
Purposes of Bandaging
- To fix and retain dressing or splint in a position.
- To give support to an injured part.
- To apply pressure to stop bleeding/hemorrhage.
- To prevent and reduce swelling.
- To immobilize an injured part so as to relieve pain.
- To prevent contamination of a wound.
- To secure splints in position.
- To retain warmth (e.g. a flannel bandage on a rheumatoid joint).
- To correct hemorrhage by means of pressure.
- To correct deformity.
- To absorb discharge.
- To prevent infection and avoid further injury.htung Basin si baskningslin
- To restrict movement.
- To provide physical comfort.
Common Uses of Bandage
- Roller Bandage- Uses for Hand, Thumb, Palm, Finger Elbow, Eye, Ear, and Capeline bandage for the head.
- Triangular Bandage/ Handkerchief: It is used in the different part of the body. Such as for the scalp, hand, eye, cheek, front or back of the chest, for the shoulder, elbow, knee, foot, hip and groin and for the sling.
- Collar and cuff sling: This is used to support the wrist only.
- Triangular Sling- The sling is used to treating a fracture of the collar bone (Beauty Bone).
- Many Tailed Bandage- Used as chest and abdominal area for the support.band
- Crepe or Elastic Bandage-This is comfortable and give good support. uses in joints, varicose veins and sprains.
- Plaster: It used for fracture in the limbs or long bone of the lower limbs, upper limbs, Femur.
- Rubber Bandage: Used to control and prevent bleeding but should not applied more than 30 minutes at a time,
Materials Used During Bandaging
- Gauze
- Cotton
- Muslin
- Rubber
- Crepe
- Plaster of Paris
- Elastics
- Flannel
- Adhesive,
Principles of Bandaging
- Place the patient and the injured part which is be bandaged in comfortable position.
- Apply Bandages when patient is sitting or lying down position.
- Injured part should be well supported in position.
- Bandaging is never applied directly over wounds.
- Avoid pressure over painful area.
- The bandage should not be very loose or tight.
- Bandage always should neat and clean.
- Never use dirty or wet or unroll bandage.
- Use a tightly roller bandages of the correct width.
- Support the part to be bandaged throughout the procedure.
- Always stand in front of the patient, except when applying a cape-line bandage.
- Bandage a limb in the position in which it is to remain e.g. forearm and hand should be prone.
- Hold the bandage with the head of roll uppermost and apply the outer surface of the bandage to the part, never unroll more than a few inches of bandage at a time.
- Apply bandage from medial outwards and from below upwards maintaining even pressure throughout.
- Begin the bandage with a firm oblique turn to fix it and below each successive turn to cover two thirds of the previous one with the free edges lying parallel.
- Make any reverse or crossing line on the outer side of the limb except, when this brings the bandage over a wound or bony prominence, in which case, it must be on the front of the limb. 17. Pad the axilla or groin when bandaging these parts, so that two surfaces of skin do not touch each other beneath the bandage.
- Finish off with a straight turn above the part, hold the end and fasten with the safety pin.

Rules of Applying Bandage
- Have the patient in a comfortable position either sitting up or lying down.
- Choose the right bandage according to the site.
- Stand opposite the patient and on the same site of the part to be bandaged except in cases of capelin and neck bandages. Be comfortable yourself.
- Place and support the limb in the correct position.
- See that the part is free from perspiration. If necessary wash, dry and apply powder.
- Place the bandage against the skin, seeing that the roll remains upper most.
- Keep skin surfaces apart and allow no turn over bony prominences.
- Bandage from below upward from within outward and over the front of the limb.
- Fix the beginning of the bandage with a circular turn; each succeeding turn should overlap two thirds of the previous turn.
- Keep all margins parallel and let the crossing and reversing be in one line towards the outer aspect of the limb.
- Keep the pressure uniform throughout leave fingers and toes exposed where possible, so the skin of any can be directed.
- Finish by securing the ends nearly with a circular turn.
