Definition of Bronchitis – This course is designed to understand the concept of community health nursing: nurses’ roles and interventions in family health, school health, occupational health, environmental health, elderly health care, gender issues, disaster management and principles and terminology of epidemiology. The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills in community health nursing.
Definition of Bronchitis
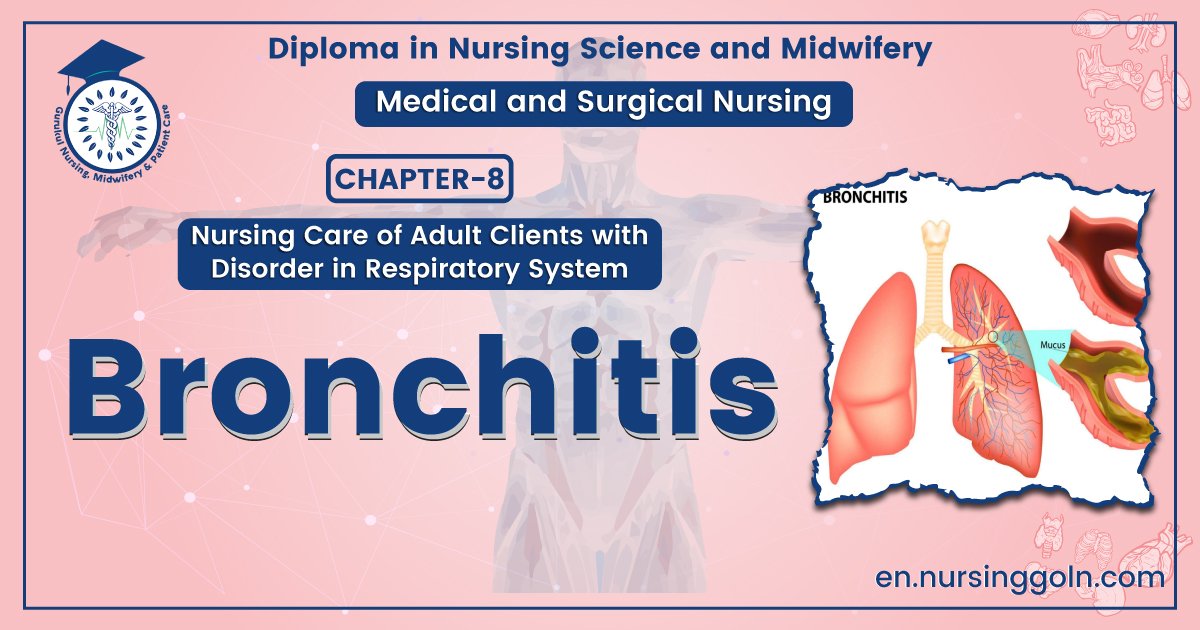
Bronchitis is an inflammation or swelling of the bronchial tubes (bronchi), the air passages between the mouth and nose and the lungs.
Classification of Bronchitis
Bronchitis may be acute or chronic:
1. Acute bronchitis: Acute bronchitis is a shorter illness that commonly follows a cold or viral infection, such as the flu.
2. Chronic bronchitis: Chronic bronchitis is a serious, ongoing illness characterized by a persistent, mucus-producing cough that lasts longer than 3 months out of the year for more than 2 years.
Causes of Bronchitis
Bronchitis is caused by the inflammation of the bronchial tubes, by viruses, bacteria, or other irritant particles.
Causes of acute bronchitis
Acute bronchitis is normally caused by viruses, typically those that also cause colds and flu.
It can also be caused by bacterial infection and exposure to substances that irritate the lungs, such as tobacco smoke, dust, fumes, vapors, and air pollution.
Causes of chronic bronchitis
Chronic bronchitis is caused by repeated irritation and damage of the lung and airway tissue.
Management of Chronic Bronchitis:
Clinical features
Patient profile
- Middle age or late adult life
- Smoker.
Symptoms
- Cough with sputum:
- Mucoid, scanty, tenacious, occasionally streaked with blood.
- Purulent when infected.
- More in morning
- Duration at least 3 consecutive months for more than 2 successive years is suggestive.
- Wheeze, breathlessness, tightness in the chest common in morning
Signs
Physical sign of emphysema may co-exist.
General examination
- Mild dyspnoeic (mild to moderate disease), cyanosed & oedematous
- There may be clubbing
- In advanced case-
- Conjunctional congestion
Respiratory system
- Inspection
• Chest movement symmetrically diminished
• Tracheal tug
• Decreased cricosternal distance
• Features of breathlessness
• Increased respiratory rate
• Intercostals and subcostal recession
• Accessory muscles of respiration in action
- Palpation
•Decreased chest expansion
- Percussion
•May be hyperresonant
•Upper border of liver dullness may be lower downn
- Auscultation
•Breath sound-vesicular with prolonged expiration
•Rhonchi present in both phase
•Crepitations over lower lobes, disappears after cough
•Vesicular breath sound with prolonged expiration.
CVS: (if cor pulmonale present)
- Left ventricular heave.
- Palpable P2.
- Loud P2.
- Pansystolic murmur
CNS
- Flapping tremors (due to hypercapnia)
Treatment
- Smoking cessation
- Bronchodilators: Inhaled route is preferable
•Salbutamol
•Ipratropiumbromide
•Theophylline
- Conticosteroids – Reduce frequency and severity of exacerbation’s (2 or more exaerbations)
- Rx of Respiratory infections: Co-amoxiclav / Macrolide antibiotic
- Pulmonary rehabilitation-Exercise
- 0, therapy: Long term domiciliary 02 therapy
- Other measures:
•Vaccination of influenza & pneumococcus
•Proper nutrition.
•Obesity, social isolation should be identify and if possible, improved
•Mucolytic therapy (acetylcysteine 200 mg orally 8 hrly for 8 weeks.
Complication of chronic bronchitis
- Pulmonary Hypertension
- Corpulmonale
- Respiratory failure-type-2.
- Polycythaemia
- Secondary infections
(Ref by- Kumar & Clark clinical Medicine /8+Harrison’s internal medicine/18)