Definition of Clubbing – Nursing is a profession within the healthcare sector focused on the care of individuals, families, and communities so they may attain, maintain, or recover optimal health and quality of life. Nurses may be differentiated from other healthcare providers by their approach to patient care, training, and scope of practice. Nurses practice in many specialisms with differing levels of prescriber authority.
Many nurses provide care within the ordering scope of physicians, and this traditional role has shaped the public image of nurses as care providers. However, nurses are permitted by most jurisdictions to practice independently in a variety of settings depending on training level. In the postwar period, nurse education has undergone a process of diversification towards advanced and specialized credentials, and many of the traditional regulations and provider roles are changing.
Nurses develop a plan of care, working collaboratively with physicians, therapists, the patient, the patient’s family, and other team members, that focus on treating illness to improve quality of life. Nurses may help coordinate the patient care performed by other members of an interdisciplinary healthcare team such as therapists, medical practitioners, and dietitians. Nurses provide care both interdependently, for example, with physicians, and independently as nursing professionals.
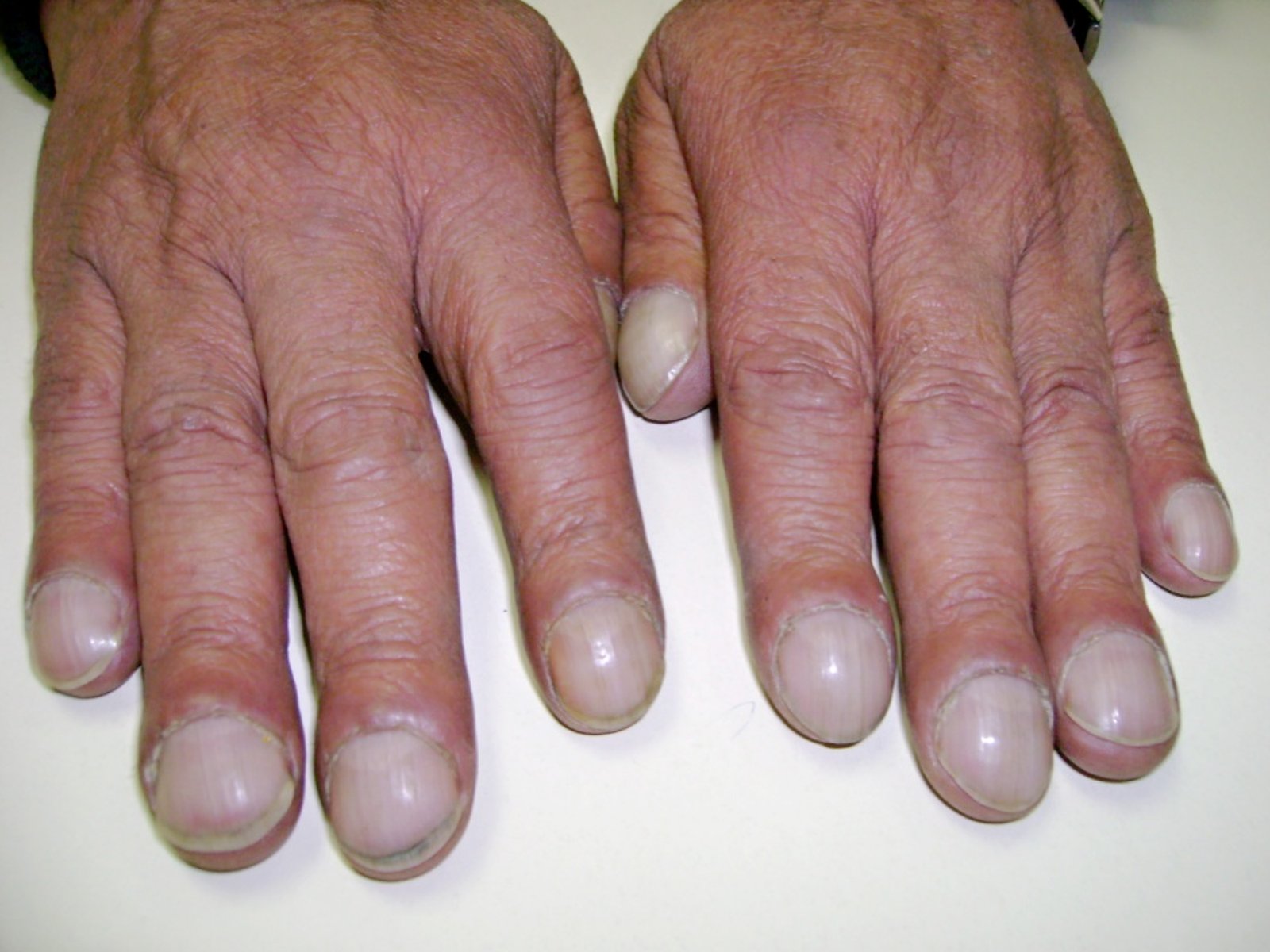
Definition of Clubbing
Definition of Clubbing:
It means selective bulbous swelling of terminal segment of the fingers and toes due to proliferation of connective tissue in distal digit.
Or,
Clubbing refers to the tissue at the base of the nails are thickened and the angle between the nail base and the adjacent skin of the finger is obliterated.
Stages of Clubbing:
1. Stage I: Increased sponginess of soft tissue at the nail base due to proliferation of connective tissue in distal digit so fluctuation is positive
2. Stage II: Obliteration of the angle between the nail base and the adjacent skin.
3. Stage III: Nail lost its longitudinal ridges and become convex from above downwards and from side to side.
4. Stage IV: Drum-stick appearance of the tip of the finger.
5. Stage V: Parrot beak appearance
(Ref-Harrison’s internal medicine/19th)
Causes of Clubbing:
| A. Respiratory: | a. Bronchogenic carcinoma (common in adult) b. Suppurative lung disease:
c. Fibrosing alveolitis (ILD) d. Pleural mesothelioma |
| B. Cardiac: | a. Congenital cyanotic heart disease mostly- Fallot’s tetralogy. b. Sub-acute bacterial endocarditis. |

| C. Alimentary: | a. CLD (cirrhosis of liver) b. Inflammatory bowel diseases
c. Coeliac disease. |
| D. Others: | a. Thyrotoxicosis (thyroid acropachy) b. Familial (rare) c. Idiopathic. |
