Definition of Conjunctivitis – This course is designed to understand the concept of community health nursing: nurses’ roles and interventions in family health, school health, occupational health, environmental health, elderly health care, gender issues, disaster management and principles and terminology of epidemiology. The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills in community health nursing.
Definition of Conjunctivitis
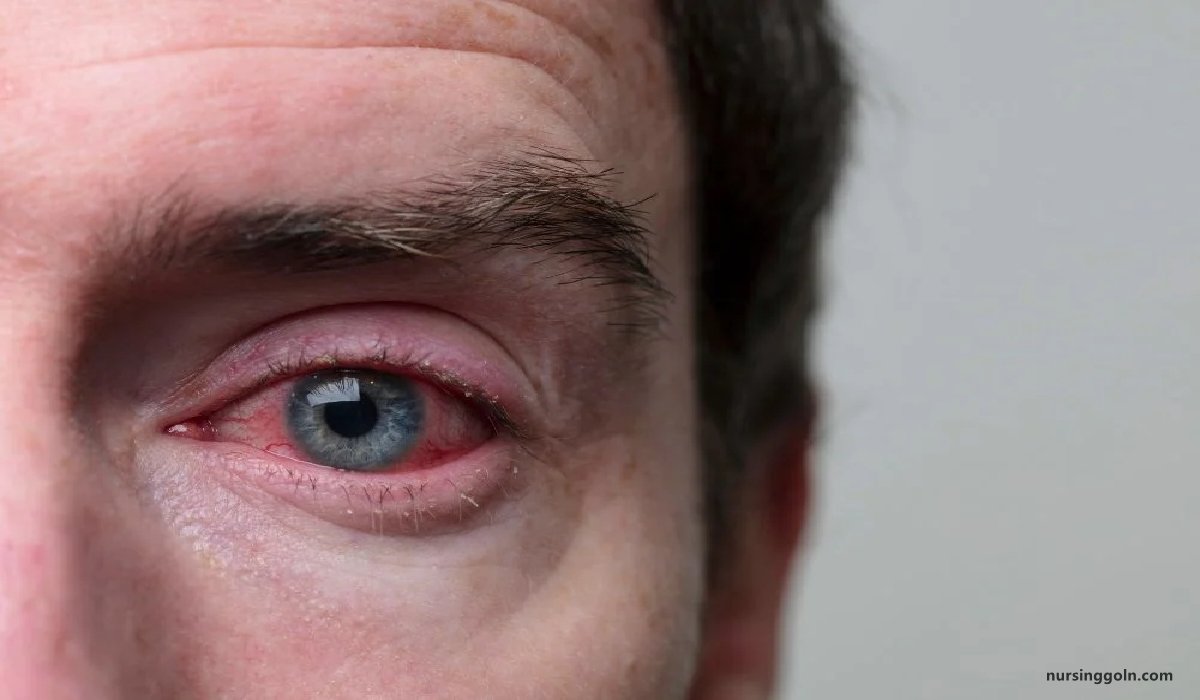
Conjunctivitis is the inflammation of the conjunctiva, characterized by cellular infiltration and exudation.
Or,
Conjunctivitis, also known as pink eye, is inflammation of the outermost layer of the white part of the eye and the inner surface of the eyelid
Or,
Conjunctivitis, also known as pinkeye, is an inflammation of the conjunctiva. The conjunctiva is the thin clear tissue that lies over the white part of the eye and lines the inside of the eyelid.
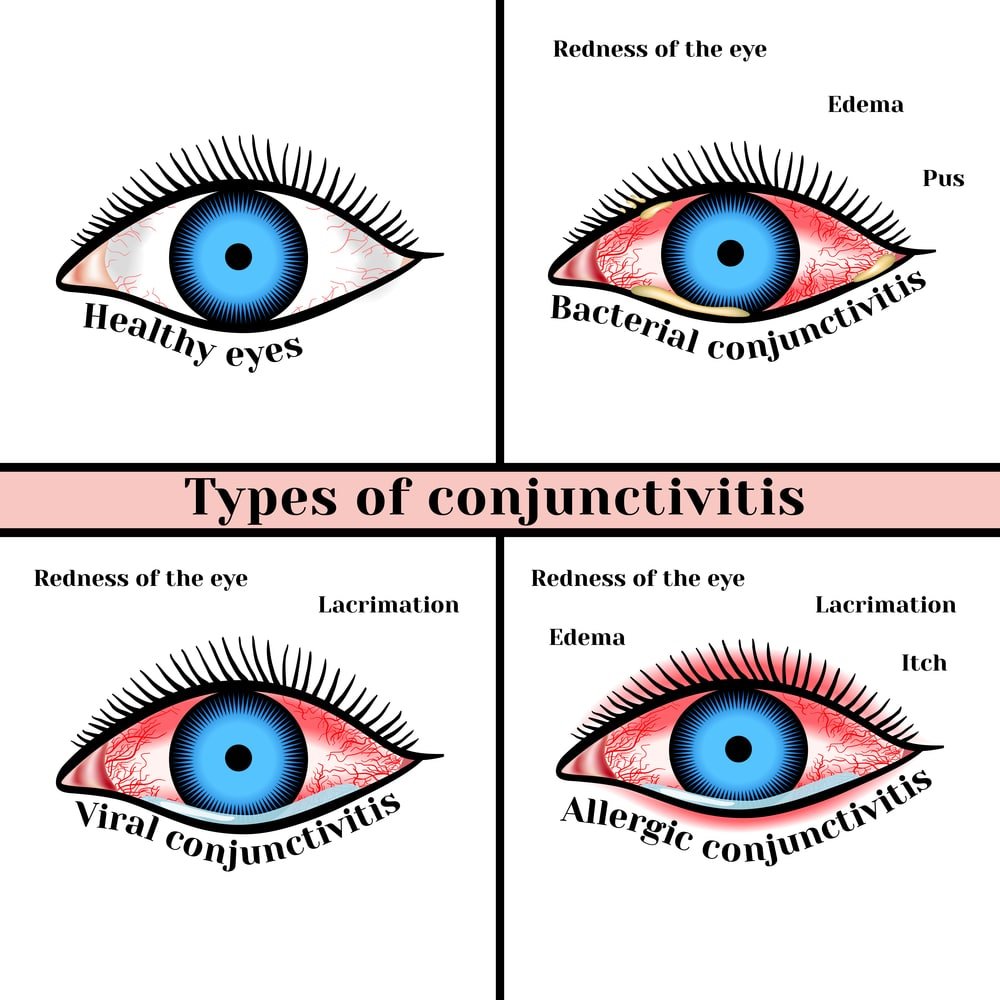
Causes/Classification of Conjunctivitis:
A. Aetiological classification:
a) Infective:
- Bacterial: Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, gonococcus, pneumococcus.
- Viral: Adeno virus, picorno virus, moulluscom contagiosum, HSV, HZV, Measles.
- Protozoal
- Parasites
b) Non-infective:
- Allergic:
✔ Simple allergic: Commonest, exposure to allergens, hay fever, contact with pet animal, drugs, cosmetics, pollen of flowers, foods.
✔ Phlyctenular conjunctivitis
✔ Vernal conjunctivitis
✔Giant papillary conjunctivitis
- Toxic: Drugs.
- Ocular trauma-Chemical conjunctivitis
B. According to exudates:
a) Purulent
b) Muco-purulent
c) Pseudo membranous
d) Catarrhal
C. According to onset:
a) Hyper acute-Course of onset <24 hours
b) Acute-course of onset hours to days
c) Sub-acute-course of onset hours to days
d) Chronic-Course of onset <4 weeks
D. According to involvement of eye:
a) Unilateral
b) Bilateral
E. Anatomical classification:
a) Simple conjunctivitis
b) Kerato conjunctivitis
c) Blephero-conjunctivitis

Clinical features:
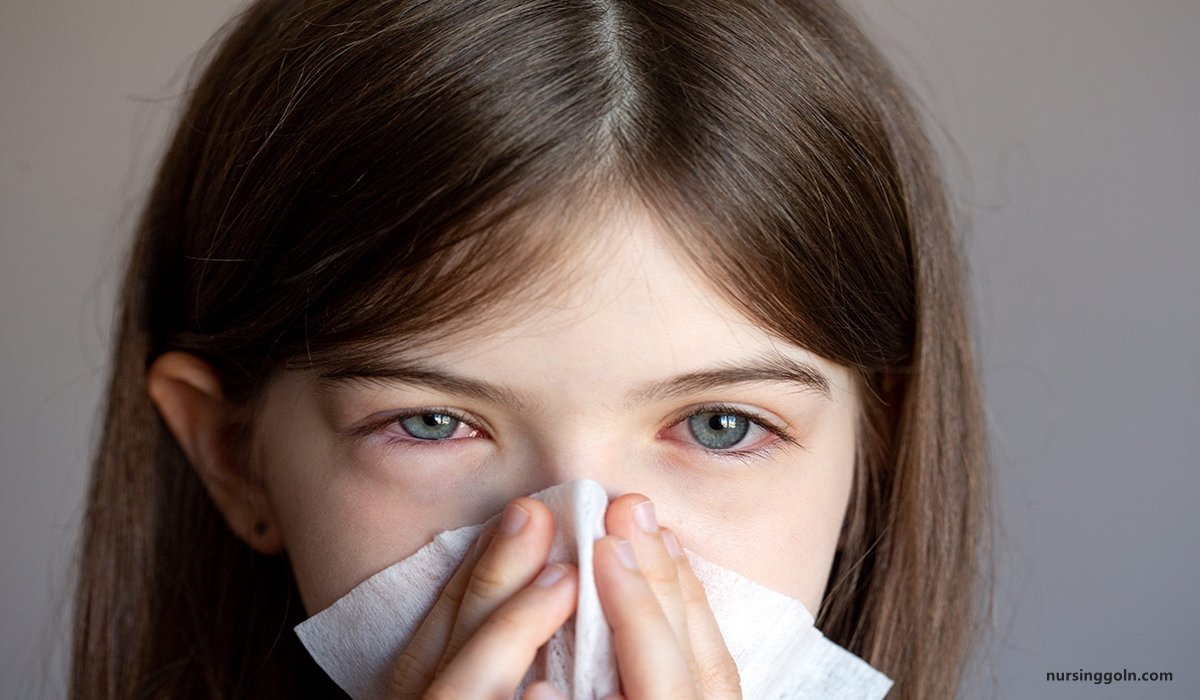
a. Symptoms:
- Discomfort and foreign body sensation
- Redness of the eyes
- Watering of eye
- Slight photophobia
- Rainbow halo around light
- Stickiness of the eyelids
- Color around the light
- Itchy eyes
- Burning eyes
- Blurred vision
b. Signs:
- One eye may be more affected
- Lid edema Congestion of conjunctiva
- Chemosis of conjunctiva
- Presence of muco-purulent discharge in inner and outer canthus
- Sub-conjunctival hemorrhage
- Muco-purulent discharge
Treatment:
a. Curative:
- Washing of conjunctival sac with warm normal saline
- 5% chloramphenicol eye drop – 1 drop hourly or 2 hourly for 5-7 days, or-
- Ciprofloxacin eye drop (0.3%)-4-6 hourly 7-10 days
- Tetracycline (1%) or erythromycin eye ointment 6 hourly
- If marginal corneal ulcer: 1% atropine drop 8 hourly
- Dark glass may be used to prevent photophobia
- If FB (foreign body) sensation present – Artificial tear
b. Prophylactic:
- Protection of unaffected eye from infection by –
✔ 0.5% chloramphenicol 1 drop 6 hourly
✔ Avoid touching with contaminated finger
✔ Advice the patient to lie on affected side
- The family members are advised not to use the towel, handkerchief of the patient.
