Definition of Cyanosis – Nursing is a profession within the healthcare sector focused on the care of individuals, families, and communities so they may attain, maintain, or recover optimal health and quality of life. Nurses may be differentiated from other healthcare providers by their approach to patient care, training, and scope of practice. Nurses practice in many specialisms with differing levels of prescriber authority.
Many nurses provide care within the ordering scope of physicians, and this traditional role has shaped the public image of nurses as care providers. However, nurses are permitted by most jurisdictions to practice independently in a variety of settings depending on training level. In the postwar period, nurse education has undergone a process of diversification towards advanced and specialized credentials, and many of the traditional regulations and provider roles are changing.
Nurses develop a plan of care, working collaboratively with physicians, therapists, the patient, the patient’s family, and other team members, that focus on treating illness to improve quality of life. Nurses may help coordinate the patient care performed by other members of an interdisciplinary healthcare team such as therapists, medical practitioners, and dietitians. Nurses provide care both interdependently, for example, with physicians, and independently as nursing professionals.
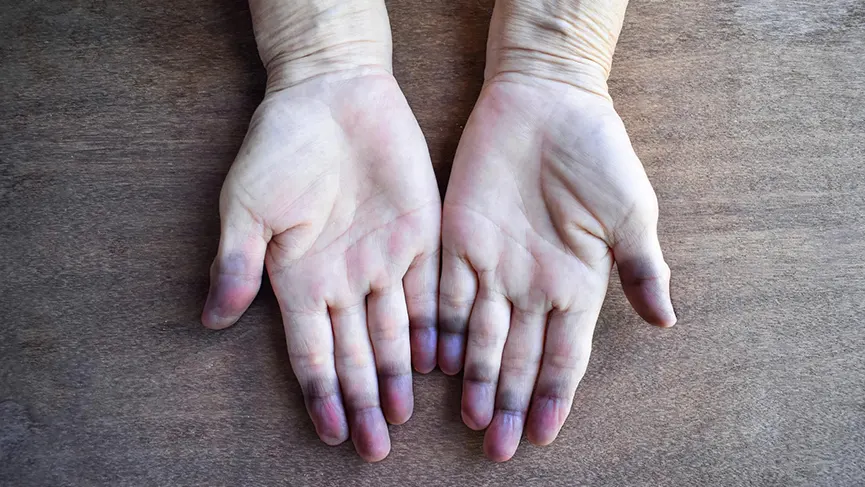
Definition of Cyanosis
Cyanosis is a clinical condition characterized by dusky bluish discoloration of skin & mucous membrane due to increased deoxygenated Hb more than 5 gm/dl in the blood.
Site of Observation:
- Tip of tongue
- Tip of Nose
- Ear lobule
- Lips & mucous membrane of oral cavity,
- Nail bed & Sole.
- Finger
- Whole skin
Types of Cyanosis:
1. Central cyanosis.
2. Peripheral cyanosis -Tongue is spared in peripheral cyanosis.
A. Central cyanosis: Bluish discoloration of skin & mucous membrane as a result of increased deoxygenated haemoglobin (More than 5 gm/dl) in blood due to defective O2 saturation or imperfect mixture of venous & arterial blood.
Site of Observation:
- Tip of tongue (Mainly) levodyissa tina tetines de Mucous membrane of mouth.
- Causes of central cyanosis:
| A. Lung diseases: |
|
| B. Heart diseases |
Tetralogy of Fallot. Transposition of great vessels Tricuspid atresia.
|
| C. Others: |
|
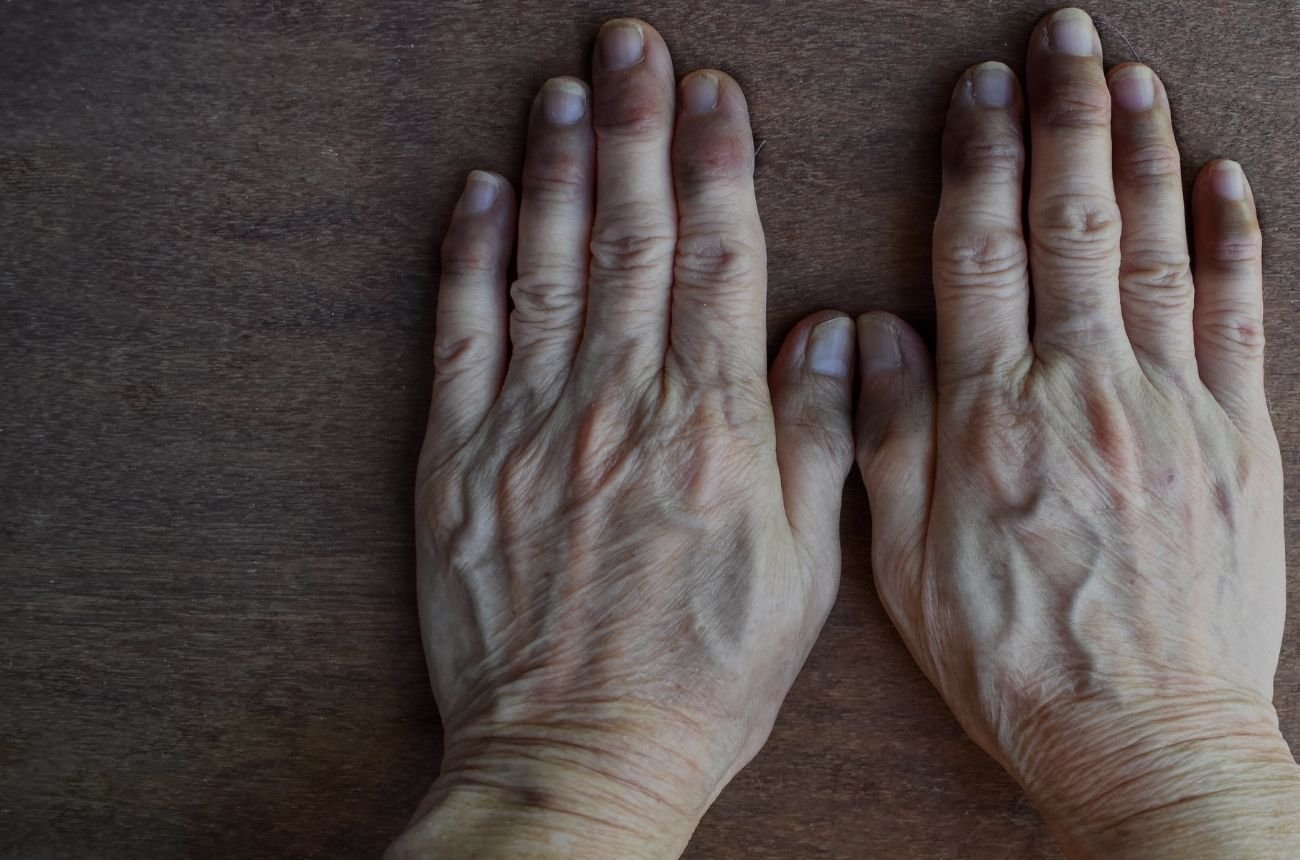
B. Peripheral cyanosis:
Site of observation:-
- Tip & Alae of the nose,
- ear lobules,
- lips,
- fingers & toes
Causes:
- Vasoconstriction, e.g. exposure to cold
- Arterial obstruction, e.g. atheroma.
- Low cardiac output, e.g. heart failure, cardiogenic shock, aortic stenosis (the cyanosis of heart failure is often due to both central and peripheral causes)
(Ref-DMC Lecture +Macleod’s 13th)
Difference between Central and Peripheral Cyanosis:
| Points | Central cyanosis | Peripheral cyanosis |
| i. Mechanism | Due to low arterial 02 saturation & imperfect mixture of venous & arterial blood. | Due to poor peripheral circulation |
| ii. Site | Tip of the tongue | Tip of the nose, lips, ear lobules, tip of the fingers and toes |
| iii. Extremities | Warm | Cold |
| iv. Application of heat | No effect | Cyanosis disappears |
| v. Administration of 02 | Cyanosis disappears | No effect |
| vi. Tongue | Involved | Usually not Involved |
| vii. Type | Generalized | Localized |
Nice to know:
Criteria of central cyanosis:
| Criteria of peripheral cyanosis:
|
Clinical Feature of Cyanosis:
| A. Central cyanosis: |
|
| B. Peripheral cyanosis: |
|
