Definition of Diarrhea – Nursing is a profession within the healthcare sector focused on the care of individuals, families, and communities so they may attain, maintain, or recover optimal health and quality of life. Nurses may be differentiated from other healthcare providers by their approach to patient care, training, and scope of practice. Nurses practice in many specialisms with differing levels of prescriber authority.
Many nurses provide care within the ordering scope of physicians, and this traditional role has shaped the public image of nurses as care providers. However, nurses are permitted by most jurisdictions to practice independently in a variety of settings depending on training level. In the postwar period, nurse education has undergone a process of diversification towards advanced and specialized credentials, and many of the traditional regulations and provider roles are changing.
Nurses develop a plan of care, working collaboratively with physicians, therapists, the patient, the patient’s family, and other team members, that focus on treating illness to improve quality of life. Nurses may help coordinate the patient care performed by other members of an interdisciplinary healthcare team such as therapists, medical practitioners, and dietitians. Nurses provide care both interdependently, for example, with physicians, and independently as nursing professionals.
Definition of Diarrhea
Diarrhea, also spelled diarrhea, is the condition of having at least three loose or liquid bowel movements each day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration due to fluid loss.
Or,
Diarrhea refers to the passage of liquid / feces and an increased frequency of defecation or it is the discharge of frequent loose stool to the rapid passages of content through the intestines.
Or,
Diarrhea is defined as the passage of loose, liquid or watery stools, more than three times per day.
Or,
Diarrhea is usually defined in epidemiological studies as the passage of three or more loose or watery stools (taking the shape of container) in a 24-hour period.
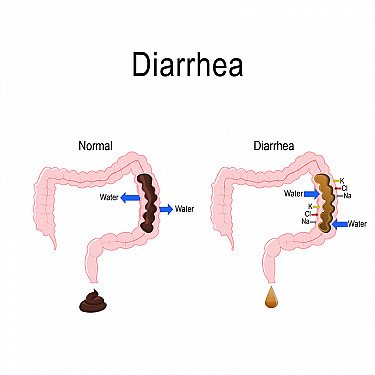
Causes of Diarrhea:
A. Infective causes :
- Viruses:
- Rotaviruses.
- Astro viruses.
- Adenoviruses.
- Coronaviruses.
- Norwalk group viruses.
b) Bacteria:
- Enviroviruses.
- Campylobacter jejuni.
- Escherichia coli.
- Shigella
- Vibrio cholerae.
- Vibrio parahaemolyticus.
- Bacillus cereus.
c) Others:
- Entamoeba histolytica.
- Giardia intestinalis
- Trichuriasis
- Cryptosporidium species.
B. Non-infective causes:
a) Acute diarrhea:
- Food poisoning.
- Drugs antibiotic, NSAID, laxative MgS04.
- Mg04
- Allergic.
b) Chronic diarrhea:
- Intestinal diseases (Inflammatory bowel diseases, Neoplasm)
- Malabsorption (chronic pancreatitis/ celiac disease/ tropical sprue).
- Endocrine: Thyrotoxicosis.
- Metabolic: Pellagra
- Autonomic Neuropathy (DM).
- Spurious disease.
Symptoms of Diarrhea
- Increased frequency, informed and excessive liquid stools.
- Unable to control the urge to defecate.
- At times, piercing abdominal cramps associated with diarrhea.
- Stools with mucus and blood at times
- Nausea and vomiting
- If diarrhea persists, irritation of the anal region.
- Fluid electrolyte loss leading to fatigue, weakness, malaise.
