Definition of Diverticulitis – This course is designed to understand the concept of community health nursing: nurses’ roles and interventions in family health, school health, occupational health, environmental health, elderly health care, gender issues, disaster management and principles and terminology of epidemiology. The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills in community health nursing.
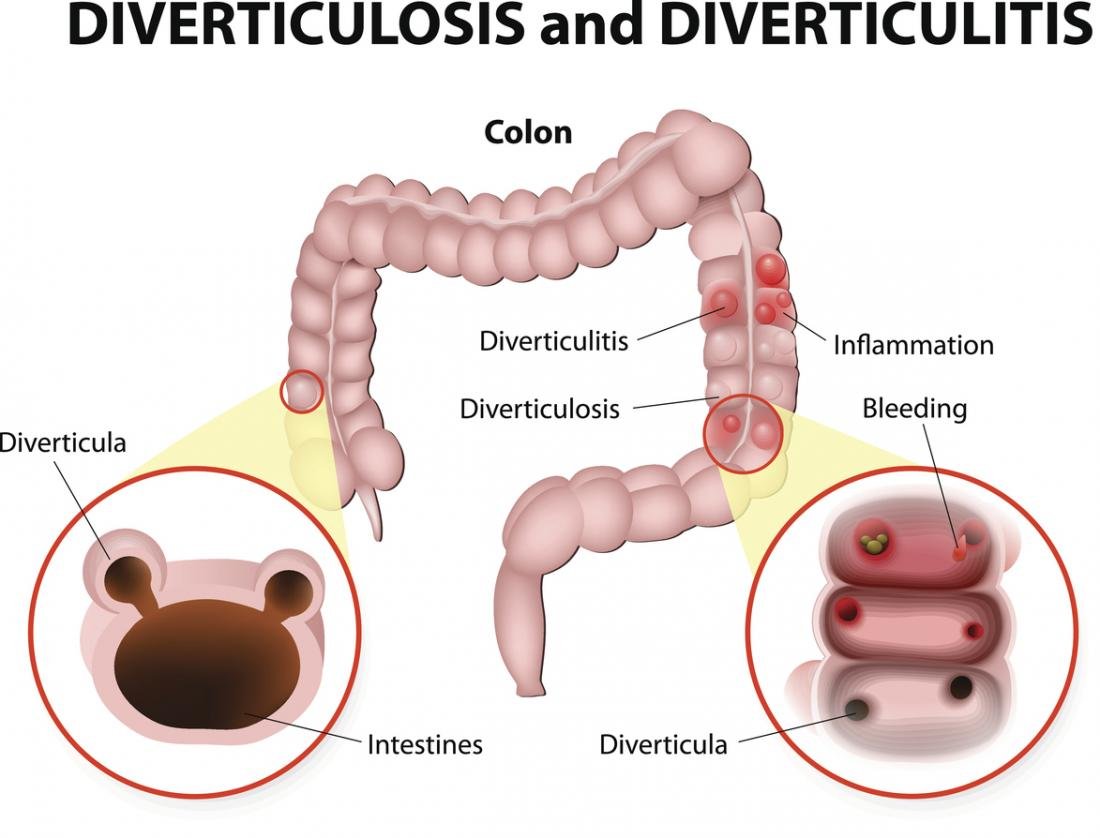
Definition of Diverticulitis
Diverticulitis is inflammation or infection of small pouches called diverticula that develop along the walls of the intestines.
Or,
An inflammatory condition of the colon thought to be caused by perforation of one of the sacs. Several secondary complications can result from a diverticulitis attack. When this occurs, it is called complicated diverticulitis.
Symptoms of Diverticulitis
- Feeling generally unwell (flu-like symptoms)
- High temperature (above 38°C)
- Shivering
- Acute tenderness and pain in the abdomen (tummy)
- Bloating
- Rectal bleeding
- Nausea and vomiting
- Becoming pale and clammy
- Palpitations, feeling that your heart is beating very fast
- Generalized weakness and fatigue
Risk factors
Several factors may increase the risk of developing diverticulitis:
1. Aging: The incidence of diverticulitis increases with age.
2. Obesity.
3. Smoking.
4. Lack of exercise.
5. Diet high in animal fat and low in fiber
6. Certain medications: Several drugs are associated with an increased risk of diverticulitis, including steroids, opiates and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) and naproxen (Aleve)
Complications
About 25 percent of people with acute diverticulitis develop complications, which may include:
- An abscess, which occurs when pus collects in the pouch
- A blockage in the colon or small intestine caused by scarring.
- An abnormal passageway (fistula) between sections of bowel or the bowel and bladder
- Peritonitis, which can occur if the infected or inflamed pouch ruptures, spilling intestinal contents into the abdominal cavity. Peritonitis is a medical emergency and requires immediate care.
Treatment
Treatment depends on the severity of patient signs and symptoms.
A. Uncomplicated diverticulitis
If symptoms are mild, patient may be treated at home. Doctor is likely to recommend:
- Antibiotics, to treat infection.
- A liquid diet for a few days while the bowel heals. Once patient’s symptoms improve, he/she can gradually add solid food to his/her diet.
- An over-the-counter pain reliever, such as acetaminophen (Tylenol, others).
This treatment is successful in 70 to 100 percent of people with uncomplicated diverticulitis.
B. Complicated diverticulitis
If patient have a severe attack or have other health problems, patient will likely need to be hospitalized. Treatment generally involves:
- Intravenous antibiotics
- Insertion of a tube to drain an abscess, if one has formed
C. Surgery
Patient will likely need surgery to treat diverticulitis if:
- He has a complication, such as perforation, abscess, fistula or bowel obstruction He
- has had multiple episodes of uncomplicated diverticulitis
There are two main types of surgery:
- Primary bowel resection.
- Bowel resection with colostomy.
