Definition of Fertilization – Introduction to fundamental concepts of Biological Science including the organization and common characteristics of living matters, cell structures and functions, food production by photosynthesis, harvesting energy, mechanism of cells reproduction, genetics, evolutions, and Human Biology. Introduction to general chemistry including basic concepts about matter, atomic structure, chemical bonds, gases, liquid, and solids, solutions, chemical reactions, acid, bases, and salt;
organic and biochemistry including hydrocarbons and their derivatives, carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, enzymes, vitamins, and minerals, nucleic acids; principles of physics and applications to nursing including gravity and mechanics, pressure, heat and electricity; nuclear chemistry and nuclear physics, effects of radiation on human beings, and protection and disposal. The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills in general biological science, general chemistry and physics.
Definition of Fertilization
The process of combining the male gamete, or sperm, with the female gamete, or ovum. The product of fertilization is a cell called a zygote.
or
Fertilization is the process by which male and female germ cells fuse to form a zygote.
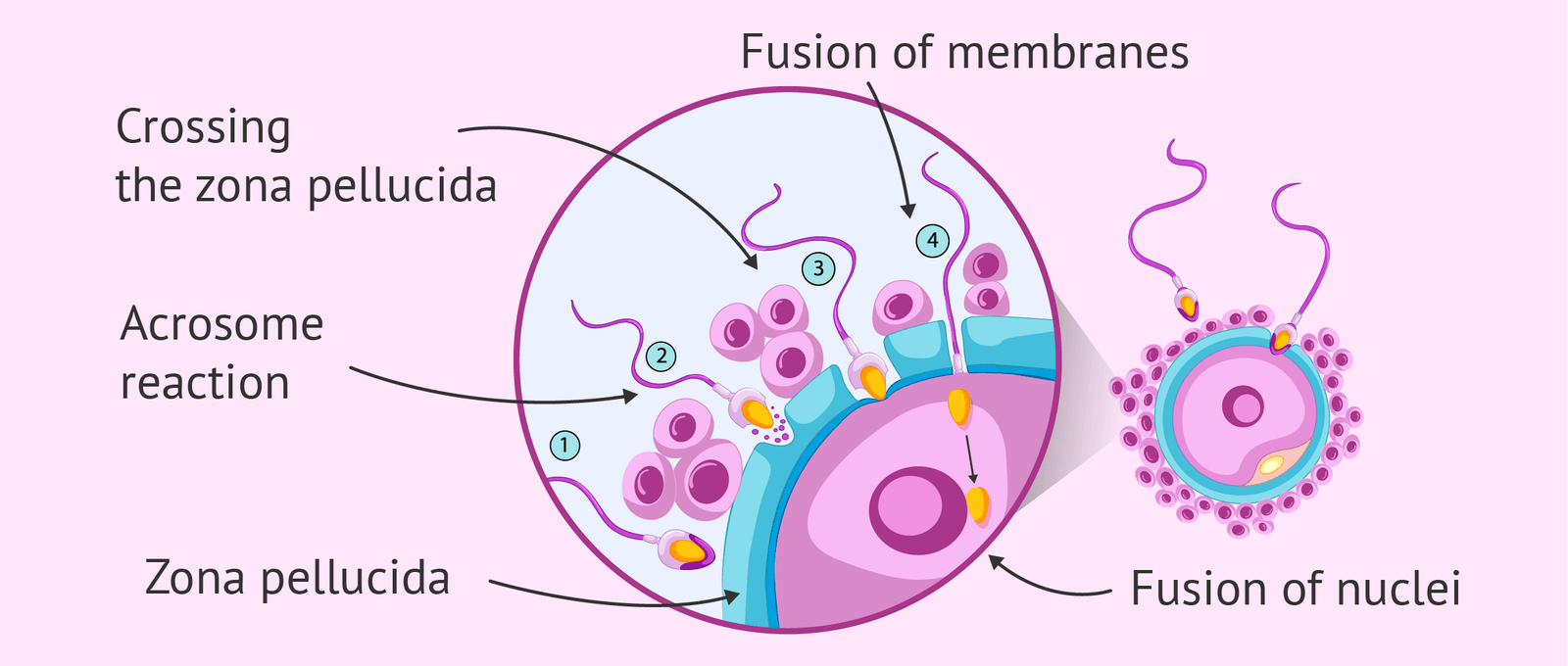
Figure: fertilizations
Phases of Fertilization:
➤ Transport of spermatozoa: 200-300 million of spermatozoa deposit in the female genital tract. Among them 300-500 reach in site of fertilization. Of them only one is needed for fertilization. Other helps in barrier penetration.
➤ Barrier penetration:
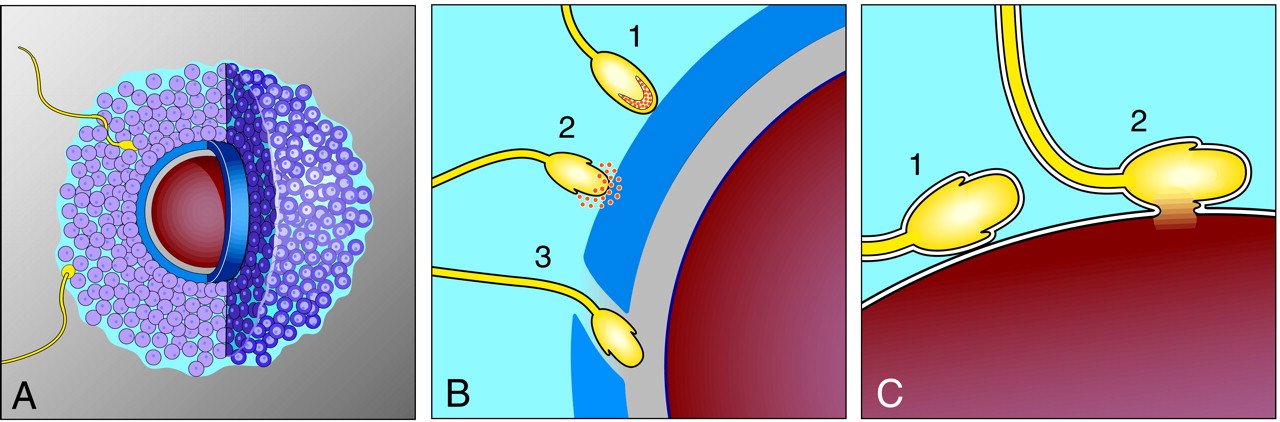
- Penetration of corona radiate: The corona radiata cells are disperse by the combined action of sperm (acrosomal reaction) & sutbal mucosal enzyme.
- Penetration of pellucida: It is penetrated by the sperm with the aid of enzyme (trypsin like substance, acrosin) released from the inner acrosomal membrane. After coming of the 1st sperm in contact with the oocyte surface, zona reaction occurs to prevent further entry of sperm
- Fusion of oocyte and sperm cell membranes: When the sperm touches the oocyte cell membrane, the two plasma membranes fuse. Leaving the plasma membrane behind, the head & tail of sperm enter the cytoplasm of the oocyte.
➤ Pronucleus formation: Now the oocyte completes its 2nd meiotic devision. The daughter cell which receives more cytoplasm forms the female pronucleus. In case of male, nucleus form the head of the sperm becomes, swollen to form male pronucleus.
➤ DNA replication: Replication of DNA occurs in both pronuclei during their formation.
➤ Mitotic division: The pronuclei meet their nuclear membranes disappear and chromosomes are arranged in distinct manner for the normal mitotic division.
Factors Upon Which Fertilization Depends:
1. Time of ovulation.
2. Time by which sperm reaches the uterine tube.
Factors for Successful Fertilization:
1. Sex cells must be matured.
2. Sex cells must have haploid chromosomes
3. Capacitation must occur
4. Union of two different sex cells must their viability.
Results of Fertilization:
1. Restoration of diploid number of chromosome.
2. Determination of sex of new individual.
3. Initiation of cleavage.
4. Completion of second meiotic division of female gamete.
Various Steps/Stages in Fertilization:
- Movement of the sperm towards the egg.
- Capacitation and contact.
- Penetration of sperm into ovum.
- Cortical reaction.
- Activation of the ovum.
- Fusion of male and female pronuclei (amphimixis).
In vitro fertilization:
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is a complex series of procedures used to treat fertility or genetic problems and assist with the conception of a child.
During IVF, mature eggs are collected (retrieved) from ovaries and fertilized by sperm in a lab. Then the fertilized egg (embryo) or eggs are implanted in uterus.
Process of In vitro fertilization:
Follicle growth in the ovary is stimulated by the administration of gonadotropins.
↓
Oocytes are recovered by laparoscopy from ovarian follicles with an aspirator
↓
Oocyte is in the late stage of 1st meiotic division
↓
The egg is planted in a simple culture media
↓
Sperm are added immediately
↓
Fertilized eggs are monitored to the eight cell stage
↓
Placed in the uterus for development till term
IVF
IVF can be used to treat infertility in the following patients:
1. Blocked or damaged fallopian tubes
2. Male factor infertility including decreased sperm count or sperm motility 3. Women with ovulation disorders, premature ovarian failure, uterine fibroids
4. Women who have had their fallopian tubes removed
5. Individuals with a genetic disorder
6. Unexplained infertility
The side effects of -In vitro fertilization
Some side effects after IVF may include:
➤ Passing a small amount of fluid (may be clear or blood-tinged) after the procedure
➤ Mild cramping
➤ Mild bloating
➤ Constipation
➤ Breast tenderness

