Definition of Gonorrhea – This course is designed to understand the care of pregnant women and newborn: antenatal, intra-natal and postnatal; breast feeding, family planning, newborn care and ethical issues, The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and develop competencies regarding midwifery, complicated labour and newborn care including family planning.
Definition of Gonorrhea
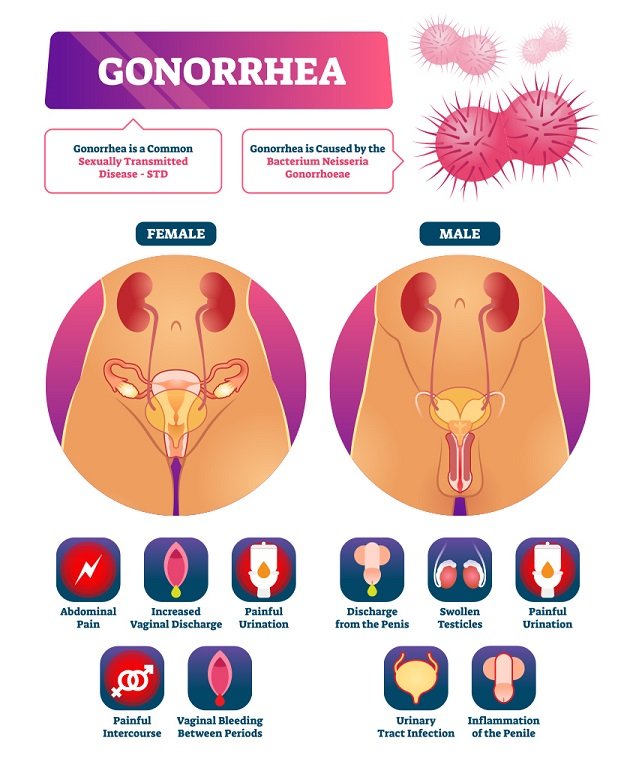
Gonorrhea, also spelled gonorrhoea, is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Many people have no symptoms. Men may have burning with urination, discharge from the penis, or testicular pain, Women may have burning with urination, vaginal discharge, vaginal bleeding between periods, or pelvic pain.
Or
Gonorrhoea is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by bacteria called Neisseria gonorrhoeae or gonococcus.
Management of gonorrhoeae:
Diagnosis:
History:
H/O sexual exposure
Clinical presentation:
Male:
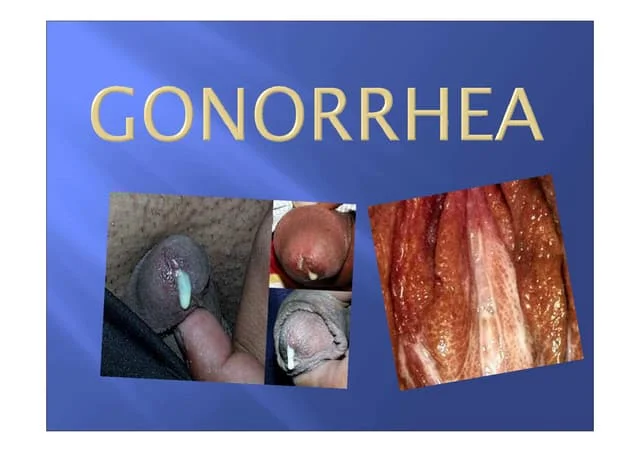
1. Dysuria- painful, burring of frequent micturation.
2. Mucoid urethral discharge within days.
3. Mucopurulent or purulent discharge.
4. Red oedematous everted urethral meatus.
5. Tender swollen & finally formation of abscess in periurethral region.
6. If not treated adequately- acute prostatitis characterized by frequency and perineal & suprapubic discomfort.
7. If not treated adequately- chronic prostates characterized by burning micturition, perineal discomfort.
8. Ascending infection may follow:
- Cystitis
- Trigonitis
- Seminal vesiculitis
- Epididymitis.
- Orchitis
- Epididymo-orchitis.
9. In homosexual men, there may be rectal infection.
Female:
1. Dysuria
2. Slight mucoid urethral discharge.
3. Profuse vaginal discharge.
4. Salphingitis, oophoritis, salphingo- oophoritis.
5. On colposcopy- angry or red looking erosion.
Investigations:
- M/E of urethral discharge, vaginal & cervical swabs-
- Gram staining of specimen- show intra & extracellular Gram negative diplocooci.
- Fermentation test- Gonococcus only ferments glucose.
- Culture for gonococci in chocolate agar media, TM or MNYC media.
- CFT for gonococcus.
Treatment:
- Penicillin sensitive cases: Ampicillin 2-3.5 gm orally & probenecid 1 gm orally single dose.
- Penicillin both sensitive ®istant cases: Ciprofloxacin 250-500 mg orally single dose. Or Ceftriaxone 500 mg IM single dose.
- Pharyngeal gonorrhoea: Co-trimoxazole 5 x 480 mg orally 12 hourly & 3 doses.
- Partner should be notified & treated as same.
Follow up:
- Culture should be made 7 days after the therapy.
- Repeat cultures are made at monthly intervals following mens for three months.
- If the reports are persistently negative the patient is declared cured.
Complications of gonorrhoea in a female patient:
- Bartholinitis
- Salpingitis.
- Tubo-ovarian mass.
- Peritonitis, perihepatitis.
- Bacteraemia, septicaemia.
- Acute gonococcal urethritis.
- Acute purulent conjunctivitis (opthalmia neonatorum).
Patho-physiology of gonococcal salpingitis:
N. gonorrhoea adheres to mucosal surfaces of urethra & other vulnerable sites. But the primary site is uretha Acute uretritis» yellow creamy pus purulent urethral discharge ->> During sexual intercourse, discharge goes to vagina & cervix-> Cervicitis & urethritis (Purulent urethral & vaginal secretion)-> salpingitis.