Definition of Hyperthyroidism – This course is designed to understand the care of pregnant women and newborn: antenatal, intra-natal and postnatal; breast feeding, family planning, newborn care and ethical issues, The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and develop competencies regarding midwifery, complicated labour and newborn care including family planning.
Definition of Hyperthyroidism
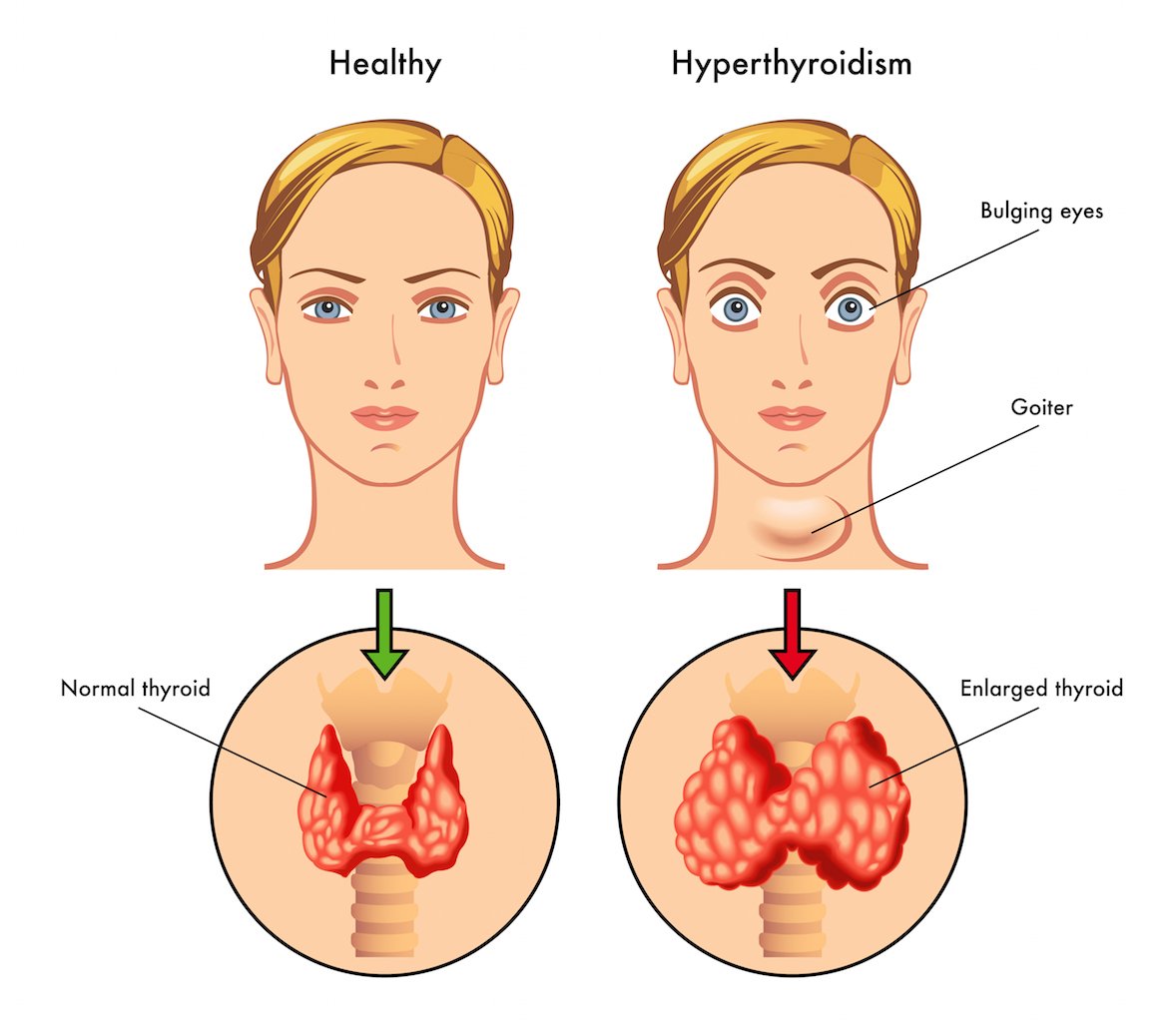
Hyperthyroidism:
The disease should be suspected on any woman who fails to gain weight satisfactorily despite a good appetite. Other symptoms include exophthalmos, eyelid lag and persistent tachycardia. Clinical diagnosis is difficult as the physiological signs and symptoms pregnant women normally exhibit, such as heat intolerance,
palpitations, and mood lability may mask this condition, Hyperthyroidism when poorly controlled is associated with an increase in preterm delivery, low birth weight and fetal death (Mestman, 1980). Thyroid autoimmunity is related to abortion and chromosomal abnormality with increased fetal loss. Thyroid stimulating immunoglobulins can cross the placenta and produce neonatal thyrotoxicosis with increased neonatal death.
Diagnosis:
Clinical diagnosis is confirmed by measuring free T4 and T3 levels along with TSH. Radioactive iodine uptake and scans should not be done during pregnancy as it will cross the placenta and damage the fetal thyroid gland permanently.
Treatment
♦ The main form of treatment for hyperthyroidism is by means of antithyroid drugs (Carbi- mazole, methimazole and Propylthiouracil).
♦ Carbimazole is given wally with a daily dose of 20 to 60 mg and maiinained at this dose until the woman becomes euthjroid.
♦ Then it is progressively reduced to maintenance of between 5 to 15 mg daily.
♦ Propylthiouracil is given at a daily dose of 300 to 450 mg and continued until the patient becomes euthyroid the maintenance dose being, 50 to 150 mg daily.
♦ Both the drugs may cause fetal goiter and hypothyroidism.
♦ Methimazole has been linked to a scalp defect-aplasia cutis of the neonate.
♦ Patients having marked tachycardia or arrhythmias should also have proponolol (p blocking agent). The drugs are not contraindicated during breastfeeding provided the dose is kept relatively low and close monitoring of the neonatal thyroid functions is carried out.
♦ Propylthiouracil is the drug of choice as it crosses into the breast milk to a lesser extent Cord blood should be taken for TSH and free T, at the time of delivery to detect neonatal hyperthyroidism.
Preconceptional Counseling
♦ Considering the hazards during pregnancy, preconceptional counseling is important.
♦ Adequate treatment should be initiated to bring down the thyroid function profile to normal. Radioactive iodine therapy should not be given to women wanting pregnancy within one year.
♦ If pregnancy occurs inadvertently, terminationshould be done. Oral pill is to be withheld because of accelerated metabolism and disturbed liver function.
