Definition of K-wire – An orthopedic nurse is a nurse who specializes in treating patients with bone, limb, or musculoskeletal disorders. Nonetheless, because orthopedics and trauma typically follow one another, head injuries and infected wounds are frequently treated by orthopedic nurses.
Ensuring that patients receive the proper pre-and post-operative care following surgery is the responsibility of an orthopedic nurse. They play a critical role in the effort to return patients to baseline before admission. Early detection of complications following surgery, including sepsis, compartment syndrome, and site infections, falls under the purview of orthopedic nurses.
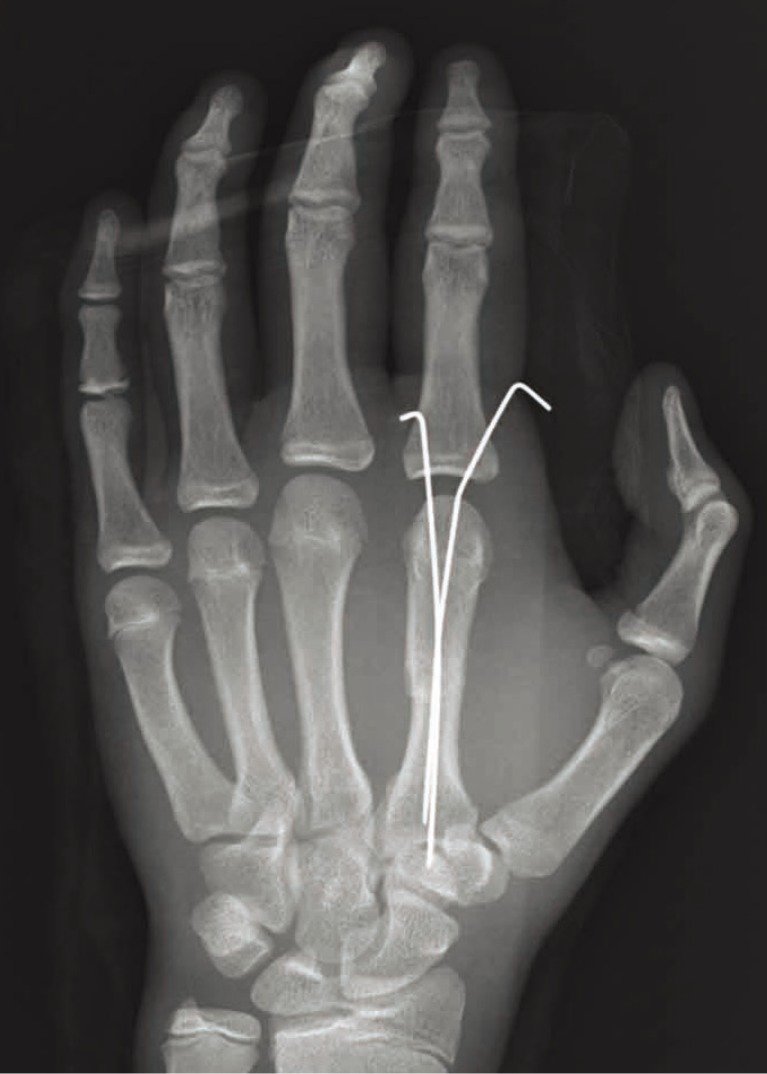
Definition of K-wire
A Kirschner wire (also called a K-wire) is a thin, flexible wire made of stainless a available in various diameters. The wires can be smooth or threaded (the latter arc used in situations in which backing out of the pin is undesirable).
[Ref-Bailey & Love’s, “Short Practice of Surgery”, 25th edition,P-364]
Indications of K-wire insertion:
1. Temporary fixation.
2. Definite fixation – with small fracture fragments (e.g. wrist fracture, hand injuries).
3. Tension band wiring (fractures of the patella and olecranon).
4. Temporary immobilization of a small joint.
5. Avulsion fracture, distal radial fractures.
[Ref-Bailey & Love’s, “Short Practice of Surgery”, 25th edition, P-364]
Advantages of K-wire:
a. Insertion is stress free.
b. Less soft tissue damage.o
c. It allows early exercises after removal.
d. It is done by local anaestesia.
e. Less chance of infection.
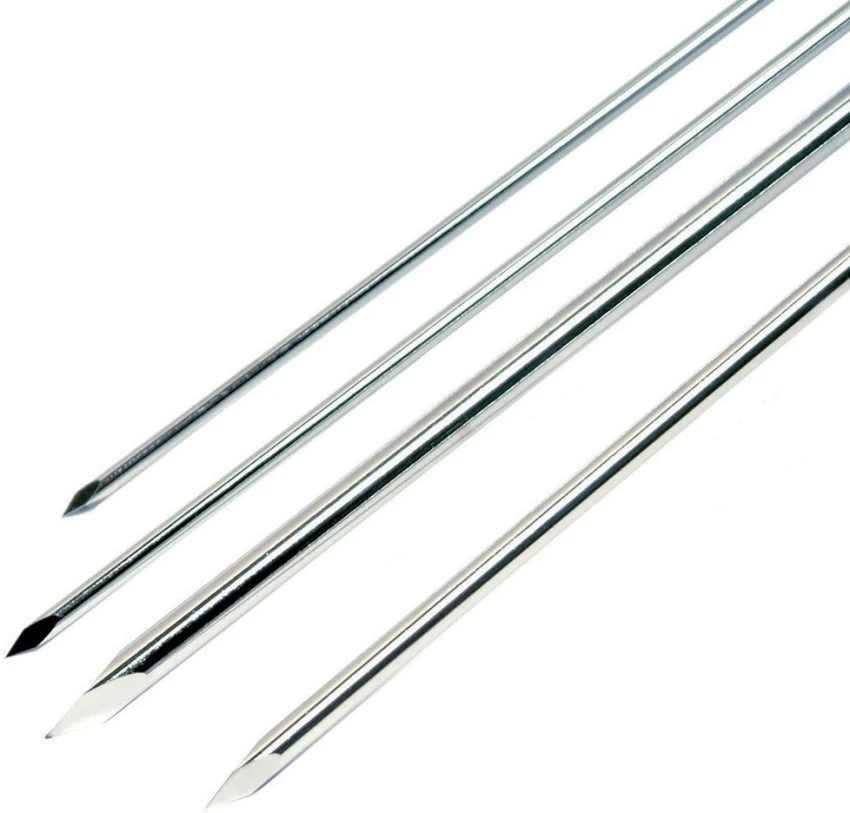

[Ref- John Ebnezar’s, “Textbook of Orthopedics”, 4″ edition, P-601]
1. Pin track infection.
2. Wire breakage.
3. Loss of fixation.
4. Migration of the wire.
[Ref-Bailey & Love’s, “Short Practice of Surgery”, 25 edition, P-365]
