Definition of Mastoiditis – This course is designed to understand the concept of community health nursing: nurses’ roles and interventions in family health, school health, occupational health, environmental health, elderly health care, gender issues, disaster management and principles and terminology of epidemiology. The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills in community health nursing.
Definition of Mastoiditis
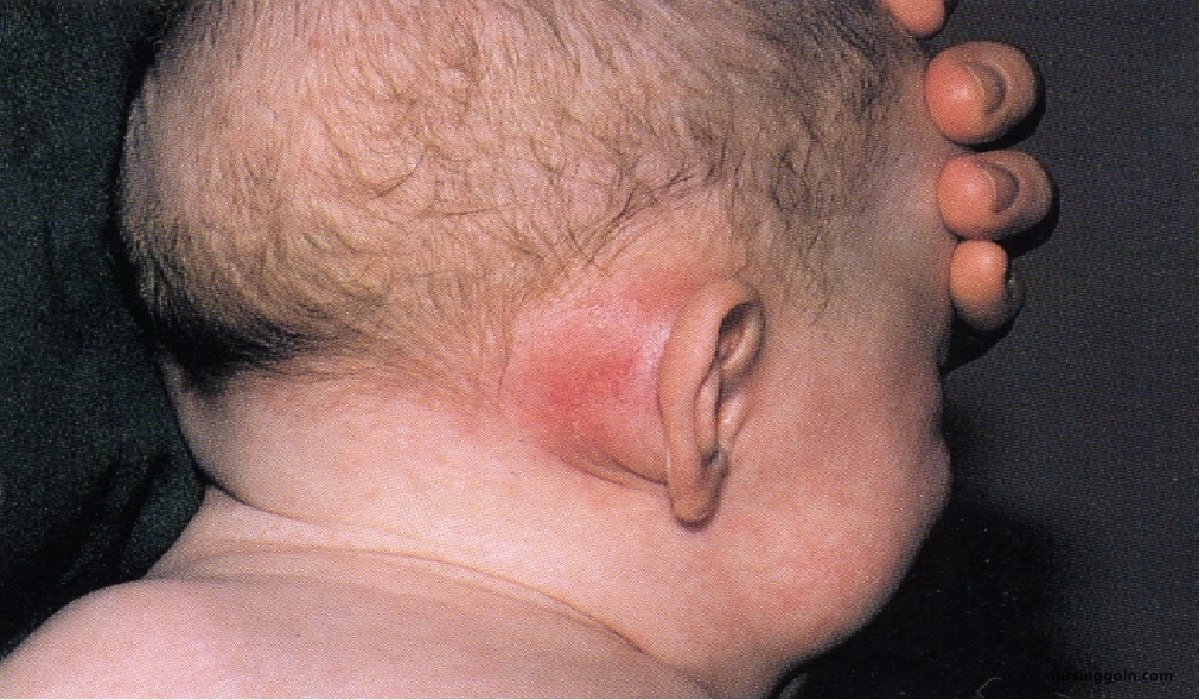
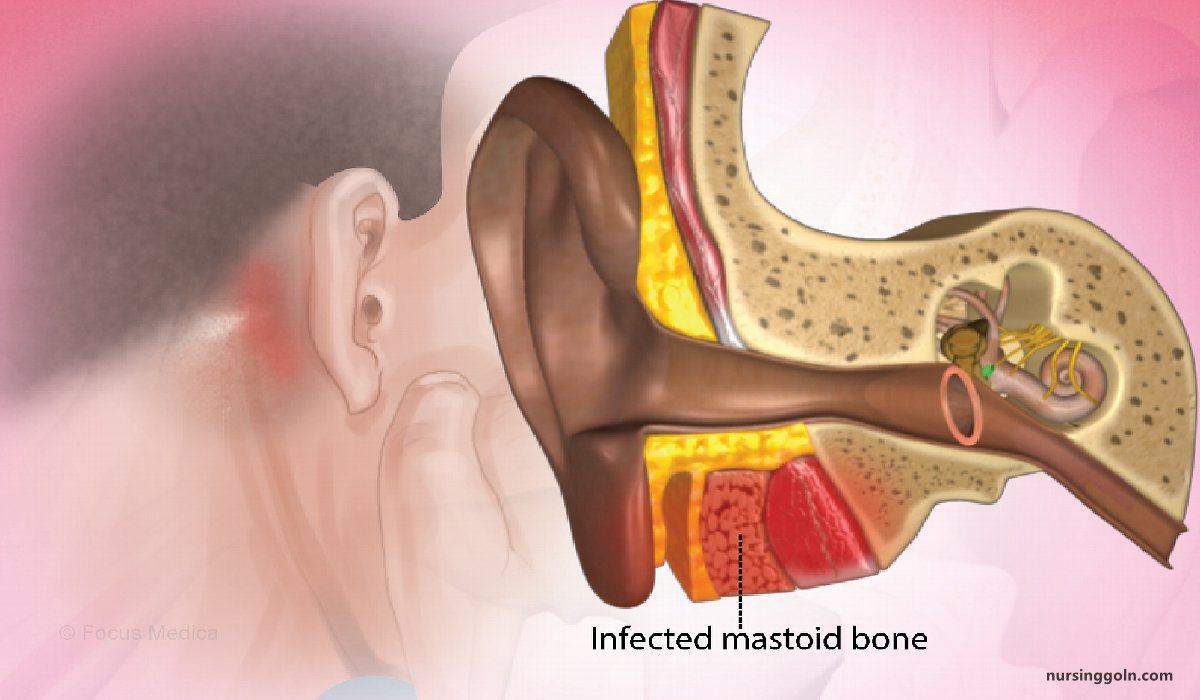
It is a spreading type of infection involving mucosa, lining of mastoid air cells and bony wall of mastoid air cell system.
Management of Acute Mastoiditis:
Clinical features:
Symptoms:
➤ General symptoms:
- Malaise.
- Headache.
- Fever with chill & rigor.
➤ Local symptoms:
- Earache.
- Otorrhoea.
- Deafness.
- Unilateral headache.
- Giddiness.
- Tinnitus.
Signs:
➤ General signs:
- Patient is pale looking.
- III & restless.
- Temperature-101° F to 103° F.
➤ Local signs:
- Discharge from the external auditory canal.
- Sagging of the posterior-superior canal wall – diagnostic.
- Tympanic membrane – posterior-superior part perforation, granulation tissue
- polyp.
- Mastoid tenderness.
- Swelling over the mastoid bone.
➤ Signs of complication:
- Drowsiness.
- Vomiting.
- Vertigo with nystagmus.
Investigations:
➤ Pus for culture & sensitivity.
➤ X-ray mastoid (Town’s view and lateral view):
- Pus in the mastoid air cells.
- Homogenous opacity in mastoid antrum
- Cholesteatoma
➤ Blood count.
Treatment:
➤ Conservative treatment-in cases where sub-periosteal abscess has not formed.
- Systemic broad-spectrum antibiotic by parenteral route.
- Analgesics- paracetamol 500 mg thrice daily after meal till pain & fever subsides.
- Topical antibiotics- when perforation with acute mastoiditis.
- Nasal decongestants: oxymetazoline 3 to 4 drops 8 hourly for 14 days.
➤ If not responds within 48 hours & sub-periosteal abscess in post-auricular region – abscess should be drained first.
➤ Then cortical mastoidectomy should be done.