Definition of Nucleus – Introduction to fundamental concepts of Biological Science including the organization and common characteristics of living matters, cell structures and functions, food production by photosynthesis, harvesting energy, mechanism of cells reproduction, genetics, evolutions, and Human Biology. Introduction to general chemistry including basic concepts about matter, atomic structure, chemical bonds, gases, liquid, and solids, solutions, chemical reactions, acid, bases, and salt;
organic and biochemistry including hydrocarbons and their derivatives, carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, enzymes, vitamins, and minerals, nucleic acids; principles of physics and applications to nursing including gravity and mechanics, pressure, heat and electricity; nuclear chemistry and nuclear physics, effects of radiation on human beings, and protection and disposal. The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills in general biological science, general chemistry and physics.
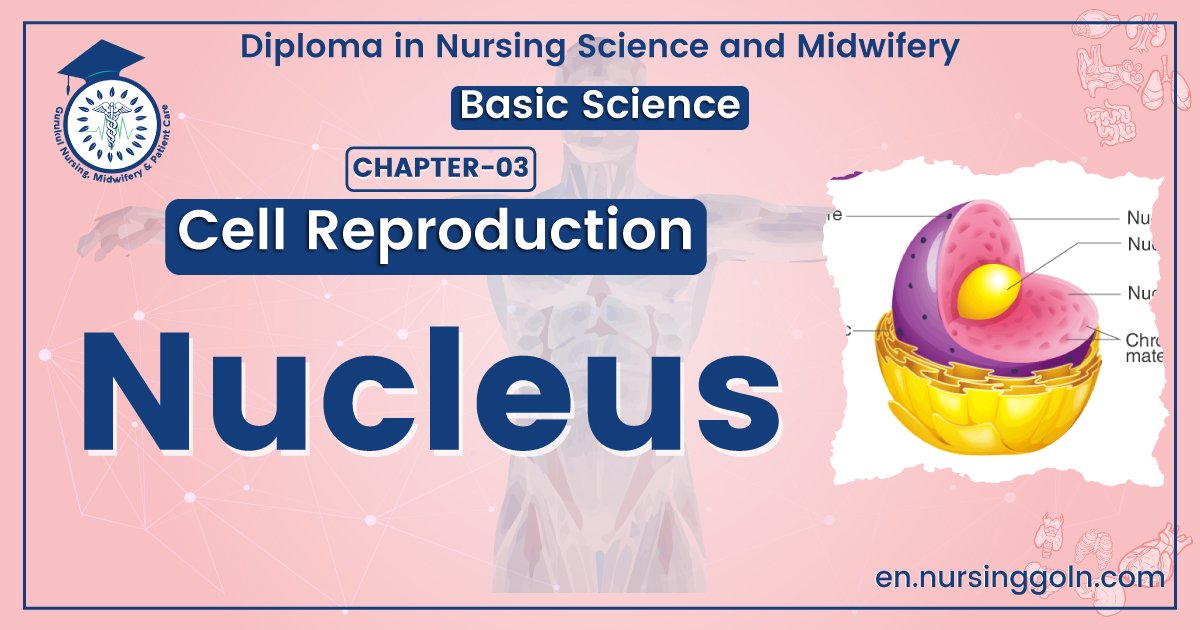
Definition of Nucleus
The cell nucleus is a membrane bound structure that contains the cell’s hereditary information and controls the cell’s growth and reproduction. It is the command center of a eukaryotic cell and is commonly the most prominent organelle in a cell.
Parts/Structure of Nucleus:
1. Nuclear membrane: It surrounds the nuclear material and is perforated through which communication between cytoplasm and nucleus occurs.
2. Chromosome: These are filamentous structures within the nucleus containing DNA and proteins.
3. Nucleolus: Nucleolus is the spherical structure within the nucleus composed of RNA.
4. Nucleoplasm: It is the matrix of nucleus. Nucleolus & chromosomes are floated in the nucleoplasm.

Figure 1.31: Structure of Nucleus
Functions of Nucleus:
- Nucleus stores the genetic entropy necessary for reproduction.
- The nucleus sustains and controls the cell growth.
- Nucleus is the place for DNA transcription in which messenger RNA are produced which synthesize protein.
- The process of energy and nutrient metabolism in the cell is regulated by the nucleus.
- Nucleus is responsible for the secretion of ribosomes.