Definition of Otitis media – Health of the children has been considered as the vital importance to all societies because children are the basic resource for the future of humankind. Nursing care of children is concerned for both the health of the children and for the illnesses that affect their growth and development. The increasing complexity of medical and nursing science has created a need for special area of child care, i.e. pediatric nursing.
Pediatric nursing is the specialized area of nursing practice concerning the care of children during wellness and illness. It includes preventive, promotive, curative and rehabilitative care of children. It emphasizes on all round development of body, mind and spirit of the growing individual. Thus, pediatric nursing involves in giving assistance, care and support to the growing and developing children to achieve their individual potential for functioning with fullest capacity.
Definition of Otitis media
A middle ear infection, also called otitis media, occurs when a virus or bacteria cause the area behind the eardrum to become inflamed. The condition is most common in children. According to the Lucile Packard Children’s Hospital at Stanford, middle ear infections occur in 80 percent of children by the time they reach age 3.
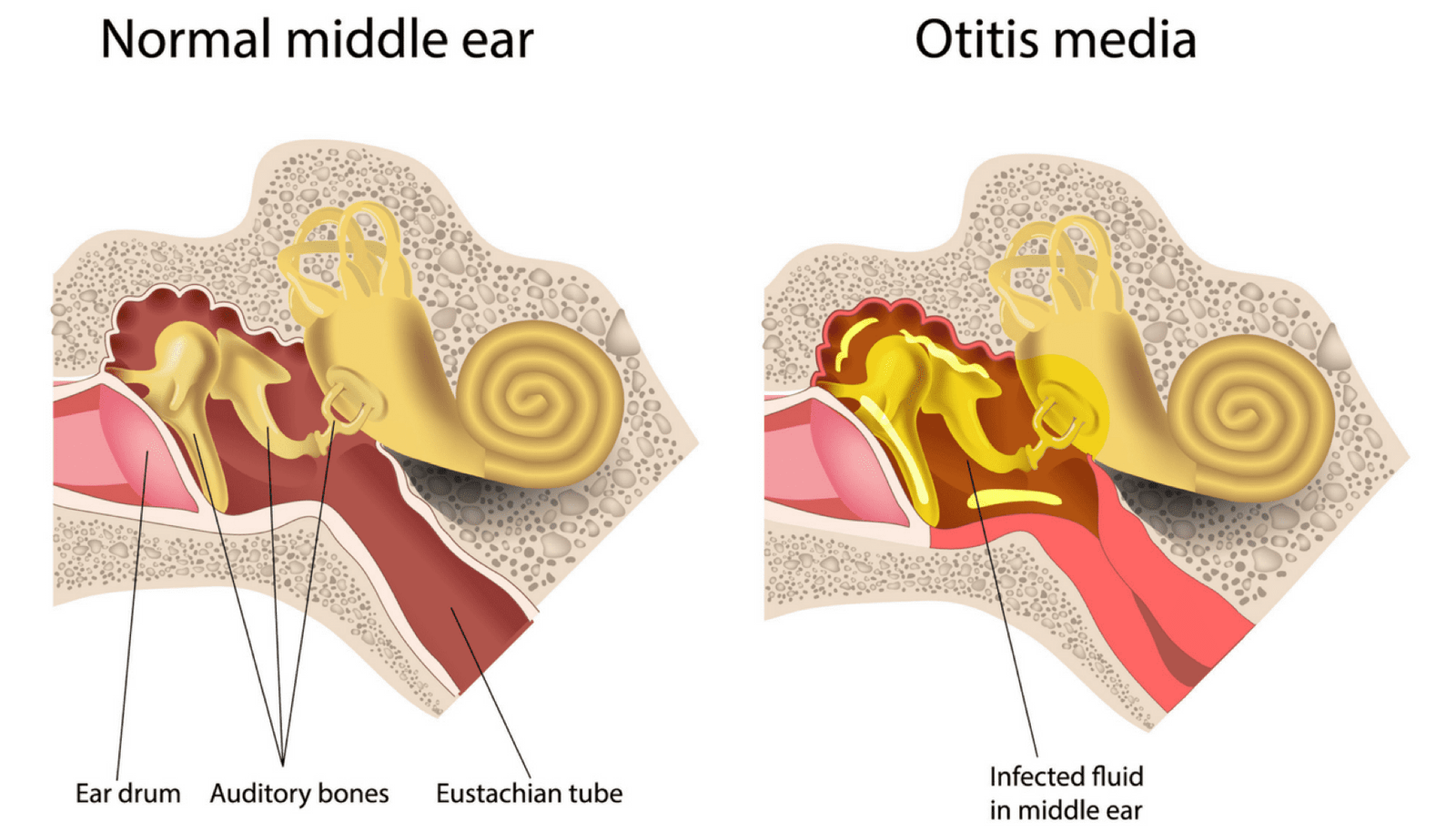
Most middle ear infections occur during the winter and early spring. Often, middle ear infections go away without any medication. However, you should seek medical treatment if pain persists or you have a fever.
Definition of Otitis Media:
Otitis media is the inflammation of middle ear. It is very common in infancy and early childhood. It is usually associated with upper respiratory tract infections.
Or
Otitis media is an infection of the middle ear that causes inflammation (redness and swelling) and a build-up of fluid behind the eardrum.
(Ref by: Paediatric Nursing, Parul Datta/34/412)
Classification of Otitis Media:
1. Acute otitis media
2. Otitis media with effusion
3. Acute supportive otitis media (ASOM)
4. Chronic supportive otitis media (CSOM)
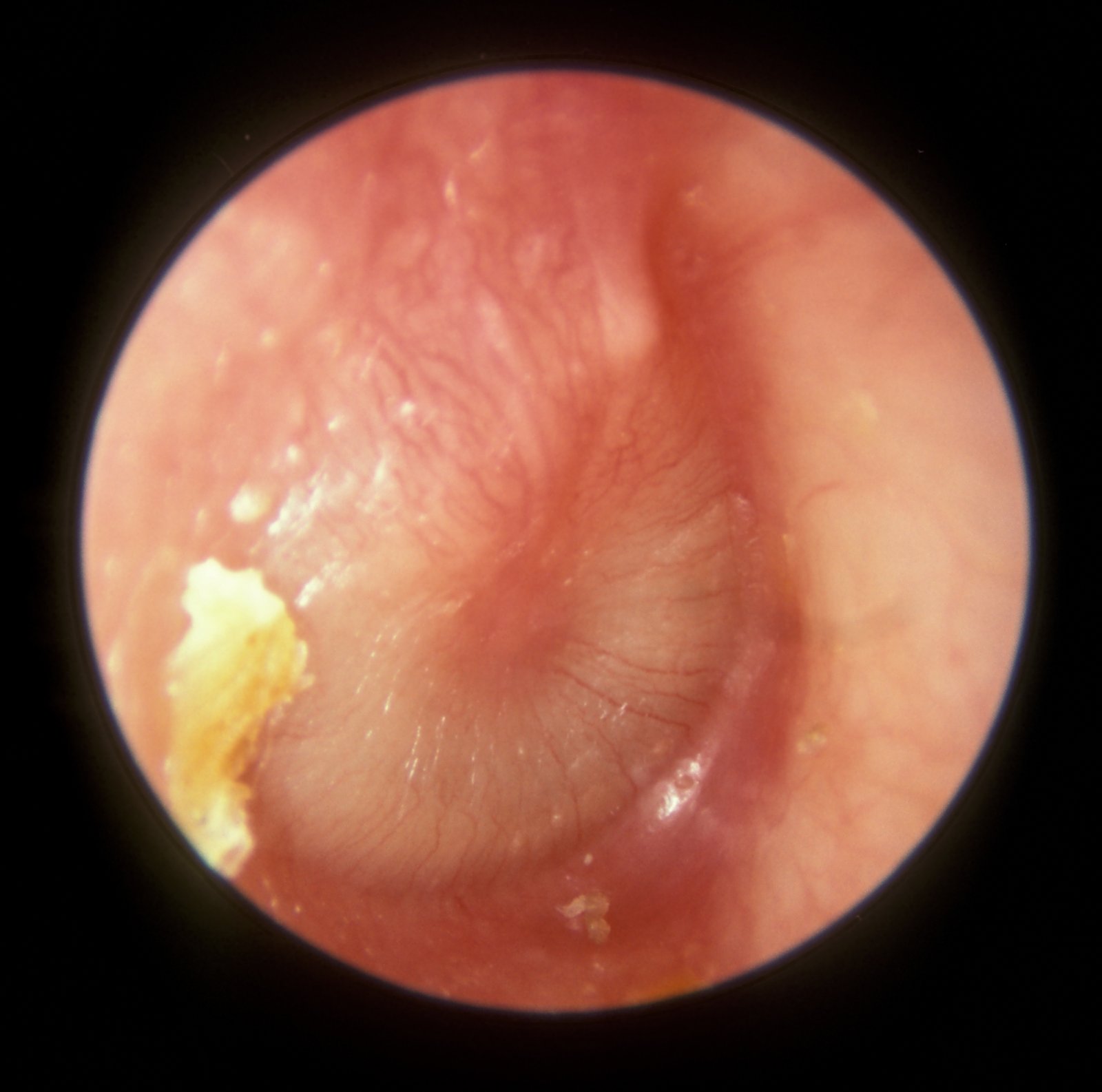
Clinical Features of Otitis Media:
- Pain in the affected ear
- Discomfort
- Irritability
- Restlessness
- Continuous crying and fever.
- Parenteral diarrhea and vomiting
- Pull or rubbing the affected ear
- Discharge and hearing impairment
On examination tympanic membrane looks
- Lusterless
- Rough
- Red and
- Bulging
(Ref: Paediatric Nursing, Parul Datta/3rd/412)
Medical Management of Acute Otitis Media:
- Antibiotic therapy (amoxicillin, erythromycin, cephalosporins) for 10 to 15 days to be given to reduce the chance of complications.
- Dose may vary according to severity of infections.
- Other measures include symptomatic treatment with analgesics, antipyretics decongestants and local heat application.
- Antihistamines and local antibiotic ear drops have little value in the management of AOM,
- Aspiration of middle ear (tympanocentesis) or tympanotomy may be needed in severe pain to drain the middle area collection.
- Complications should be detected early for appropriate treatment.
- Discharge from the ear should be cleaned aseptically to keep the area dry.
(Ref by: Paediatric Nursing, Parul Datta/3/412)
Nursing Management of Acute Otitis Media:
- Determine pain characteristics through client’s description
- Use pain rating scale appropriate for age
- Monitor skin color and vital signs
- Encourage to increase fluid intake to decrease susceptibility to infection
- Reduce noise in the client environment.
- Look at the client when speaking.
- Speak clearly and firmly on the client without the need to shout.
- Provide good lighting when the client relies on the lips.
- Use the signs of non-verbal (eg facial expressions, pointing, or body movement) and other communications.
- Encourage to listen to music, have focused breathing, socializing to others or other diversional activities
- Administer analgesics as ordered by the physician
- Have the child sit up, raise head on pillows, or lie on unaffected ear. Elevation decreases pressure from fluid.
- Apply heating pad or warm hot water bottle. Heat increases blood supply and reduces discomfort.
- Have the child/patient chew gum or blow on balloon to relieve pressure in ear. Attempts to open the eustachian tube may help aerate the middle ear.
- Instruct family or the people closest to the client on how techniques of effective communication so that they can interact with clients to distract attention and reduce tension towards pain
- If the client wants, the client can use hearing aids.
- Assess motor and language development at each health care visit. Early detection of developmental delays can lead to appropriate intervention
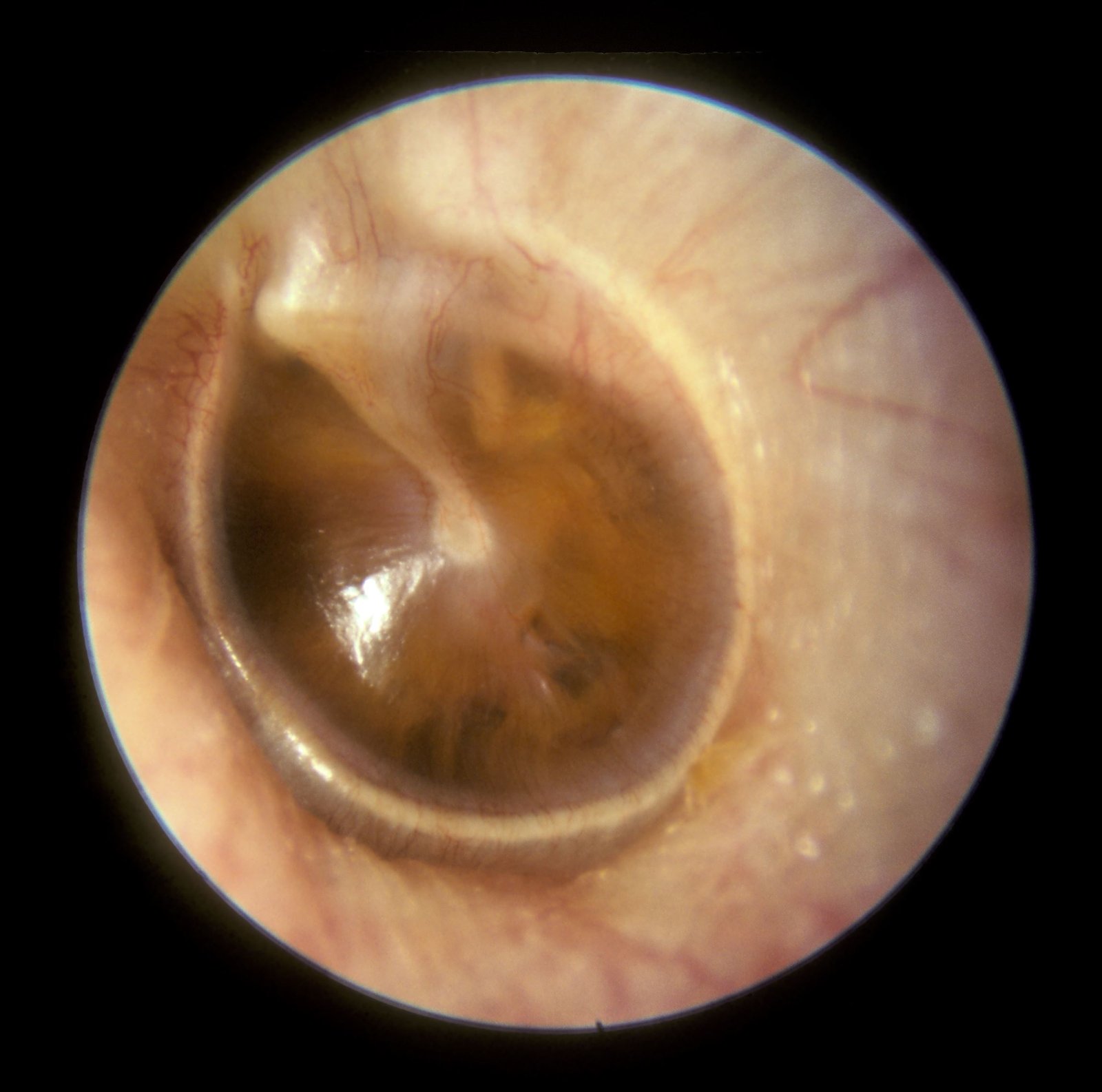
Complications of Otitis Media:
Extra-cranial complications
- Acute mastoiditis
- Chronic and recurrent otitis media
- Facial palsy
- Hearing impairment
- Sub-periosteal abscess and
- Neck abscess.
Intracranial complications
- Meningitis and
- Cerebral abscess