Definition of Partograph – This course is designed to understand the care of pregnant women and newborn: antenatal, intra-natal and postnatal; breast feeding, family planning, newborn care and ethical issues, The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and develop competencies regarding midwifery, complicated labour and newborn care including family planning.
Definition of Partograph
Definition of Partograph:
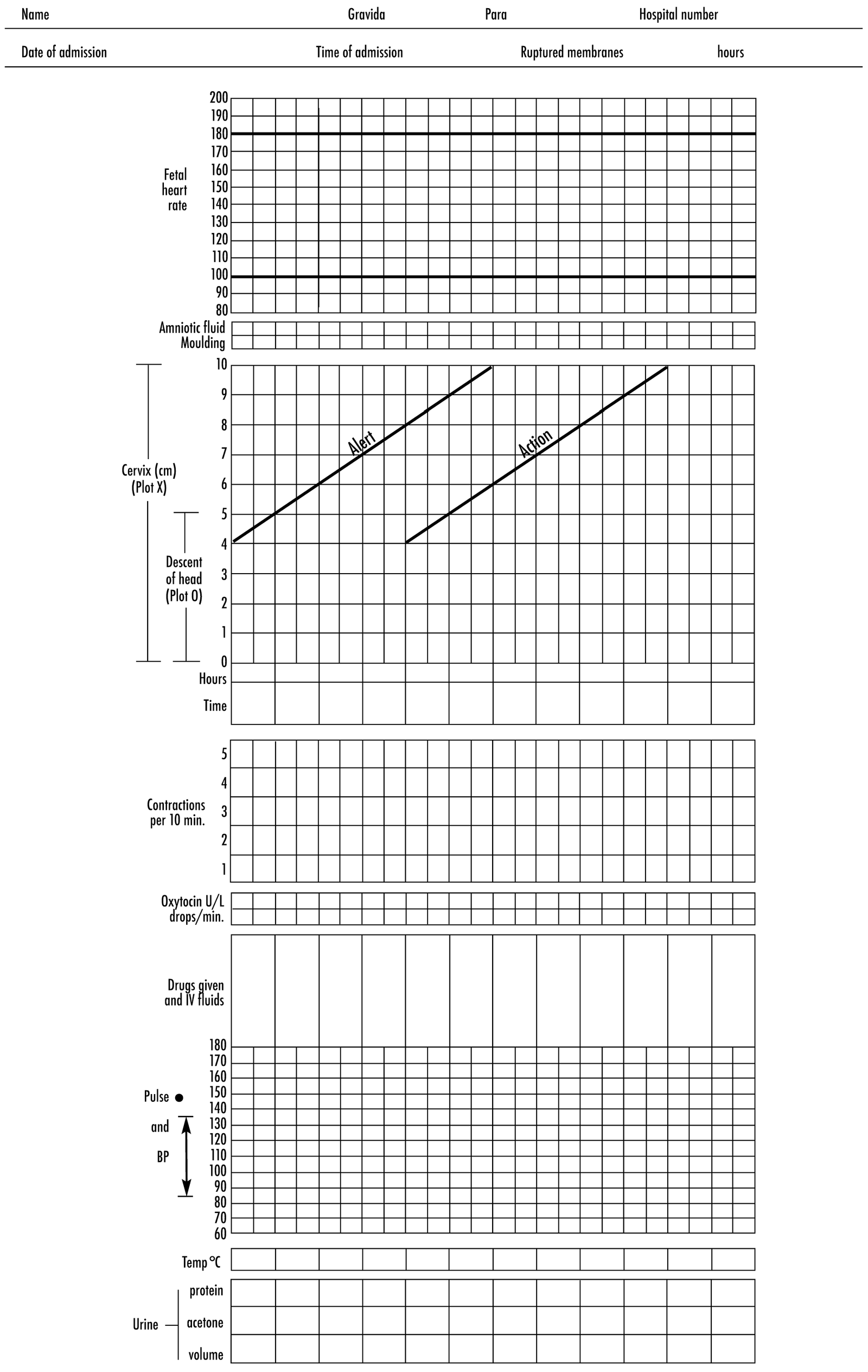
It is a composite graphical record of cervical dilatation and descent of head against duration of labour in hours. It also gives information about fetal and maternal condition, which are all recorded on a single sheet of paper.
Or
Partograph is the complete graphic representation of the events of labour plotted against the during of labour in hour
Friedman (1954) first devised partograph.
Aims/Purposes/Objectives of partograph:
1. To observe the progress of labour.
2. To identify the point of deviation from the normal
3. For timely refferel
4. To monitor the well-being of mother as she goes through labour.
5. For timely interference to avoid prolonged labour/obstructed labour/ ruptured uturus.
Or
1. Early detection of abnormal progress of labour
2. Detection & prevention of prolonged & obstructed labour
Benefits/Advantages/Importance of Partograph:
1. A single sheet of paper provides details of necessary information’s at a glance.
2. It gives information about the progress of labour
➤ Cervical dilation
➤ Descent of foetal head
➤ Uterine contraction
3. It also gives information about fetal condition
➤ Foctal heart rate
➤ The membranes & liquor
➤ Moulding
4. It also gives information about maternal condition:
➤ Pulse (half hourly), BP (4 hourly) & temperature (4 hourly or more frequently) is noted.
➤ Urine volume and its protein and acetone levels are estimated at 4 hours interval
➤ Drugs & Iv fluids-these are charted under the uterine contractions
➤ Oxytocin regimen
5. No need to record labour events repeatedly
6. It can predict deviation from normal duration of labour. So appropriate steps could be taken in time
7. It facilitates handover procedure
8. It helps in timely referral
9. It helps to prevent prolonged & obstructed labour
For Viva:
- Fetal heart rate is measured every 1/2 hr. for 1 min
- Amniotic fluid & moulding -every 4 hr.
- Cervical dilatation & descent of heard -every 4 hourly by P/V exam
- Contractions per 10 min -every hourly
Information that can be collect from partograph
1. A single sheet of paper provides details of necessary information’s at a glance.
2. It gives information about the progress of labour
➤ Cervical dilation
➤ Descent of foetal head
➤ Uterine contraction
3. It also gives information about fetal condition
➤ Foetal heart rate
➤ The membranes & liquor
➤ Moulding
4. It also gives information about maternal condition:
➤ Pulse (half hourly), BP (4 hourly) & temperature (4 hourly or more frequently) is noted.
➤ Urine volume and its protein and acetone levels are estimated at 4 hours interval
➤ Drugs & Iv fluids-these are charted under the uterine contractions
➤ Oxytocin regimen
Components of partograph:
1. Patient identification
2. Time-recorded at hourly interval. Zero time for spontaneous labour is the time of admission in the labour ward and for induced labour is the time of induction.
3. Fetal heart rate -recorded hourly
4. State of membranes and color of liquor: To mark-
a. ‘I’ for intact membranes
b. ‘C’ for clear and
c. ‘M’ for meconium stained liquor.
5. Moulding
6. Cervical dilatation and descent of the head
7. Descent of foetal head
8. Uterine contraction
9. Pulse: Every 30 minutes interval
10. BP
11. Temperature is noted
12. Urine volume and its protein and acetone levels are estimated at 4 hours interval
13. Drugs & IV fluids these are charted under the uterine contractions
14. Oxytocin regimen: Conc in the upper box and dose in the lower box.
15. Amniotic fluid.
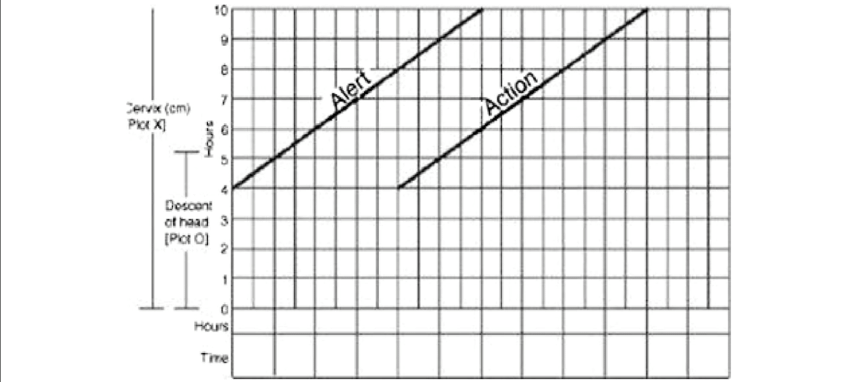
Latent Phase of Labour:
The latent phase means effacement of the cervix and dilations upto 4cm
Duration:
➤ In primigravidae – about 8 hours
➤ In multigavidae- about 4 hours Slow rate of dilation of Cx
➤ Preparatory phase of uterus- no effective contraction
➤ No intervention is required
[NB: At present in modified parograph -latent stage is not shown.]
Time of partograph use
The large multicentre trial of the WHO partograph showed how very important it is that the partograph be started only when a woman is in labour. It is started during active phase when cervical dilatation is 4 cm.
The modified WHO partograph