Definition of Pharyngitis – Health of the children has been considered as the vital importance to all societies because children are the basic resource for the future of humankind. Nursing care of children is concerned for both the health of the children and for the illnesses that affect their growth and development. The increasing complexity of medical and nursing science has created a need for special area of child care, i.e. pediatric nursing.
Pediatric nursing is the specialized area of nursing practice concerning the care of children during wellness and illness. It includes preventive, promotive, curative and rehabilitative care of children. It emphasizes on all round development of body, mind and spirit of the growing individual. Thus, pediatric nursing involves in giving assistance, care and support to the growing and developing children to achieve their individual potential for functioning with fullest capacity.
Definition of Pharyngitis
Pharyngitis is inflammation of the back of the throat, known as the pharynx. It typically results in a sore throat and fever. Other symptoms may include a runny nose, cough, headache, a hoarse voice. Symptoms usually last three to five days. Complications can include sinusitis and acute otitis media. Pharyngitis is typically a type of respiratory tract infection.
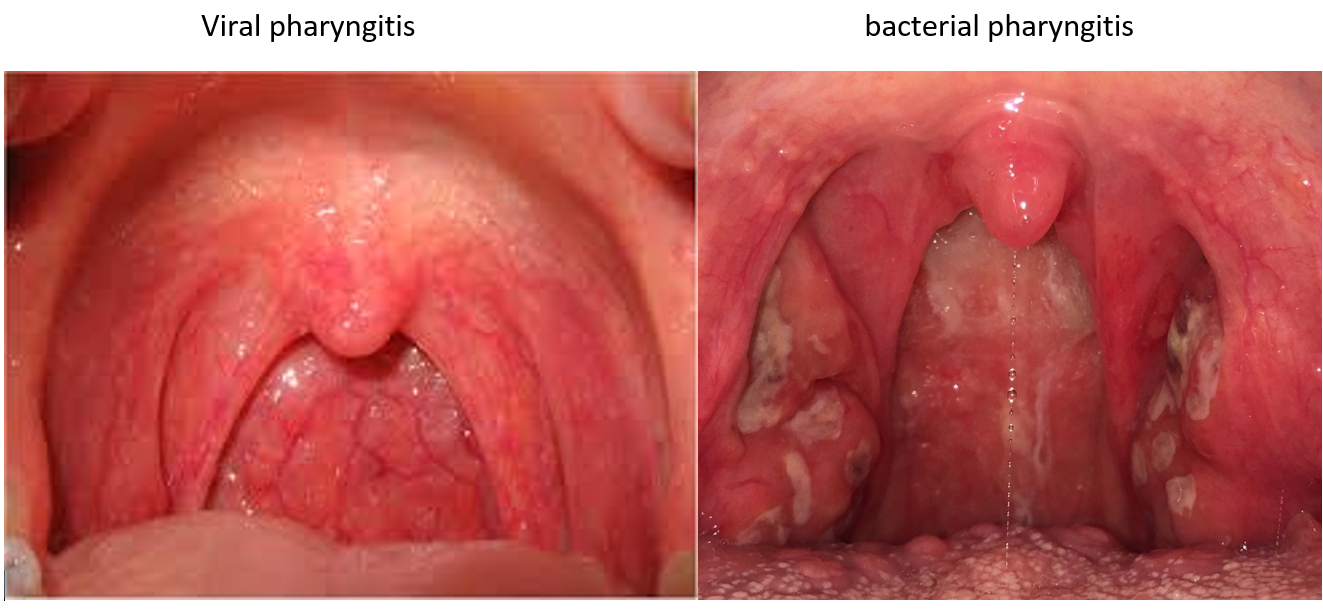
Most cases are caused by a viral infection. Strep throat, a bacterial infection, is the cause in about 25% of children and 10% of adults. Uncommon causes include other bacteria such as gonorrhea, fungus, irritants such as smoke, allergies, and gastro-esophageal reflux disease. Specific testing is not recommended in people who have clear symptoms of a viral infection such as a cold.
Otherwise a rapid antigen detection test (RAPD) or throat swab is recommended. Other conditions that can produce similar symptoms include epiglottitis, thyroiditis, retropharyngeal abscess, and occasionally heart disease.
Definition of Pharyngitis;
Inflammation of pharynx is called pharyngitis
Or
Pharyngitis is commonly termed as sore throat which involves inflammation of pharynx and tonsils.
Or
Pharyngitis is inflammation of the back of the throat, known as the pharynx. It typically results in a sore throat and fever. Other symptoms may include a runny nose, cough, headache, a hoarse voice
Clinical Features of Pharyngitis;
| A. Bacterial pharyngitis; |
|
| B. Viral pharyngitis; |
|
Types of Pharyngitis:
| A. Non-exudative | Non-exudative does not produce fluids like pus; this is the most common form of pharyngitis and usually caused by viruses |
| B. Exudative | Exudative produces a body fluid like pus; this usually suggest a bacterial cause |
| C. Ulcerative | Ulcerative production of small ulcers and/or a grayish membrane on parts of the pharynx. Ulcerative pharyngitis (mainly caused by bacteria) is infrequently seen but is considered to be a medical emergency. |
Complications of Pharyngitis:
- Otitis media
- Mastoiditis
- Chronic ulcer in the throat
- Peritonsillar abscess (quinsy)
- Sinusitis
- Meningitis
- Mesenteric adenitis
- Rheumatic fever and
- Acute glomerulonephritis.
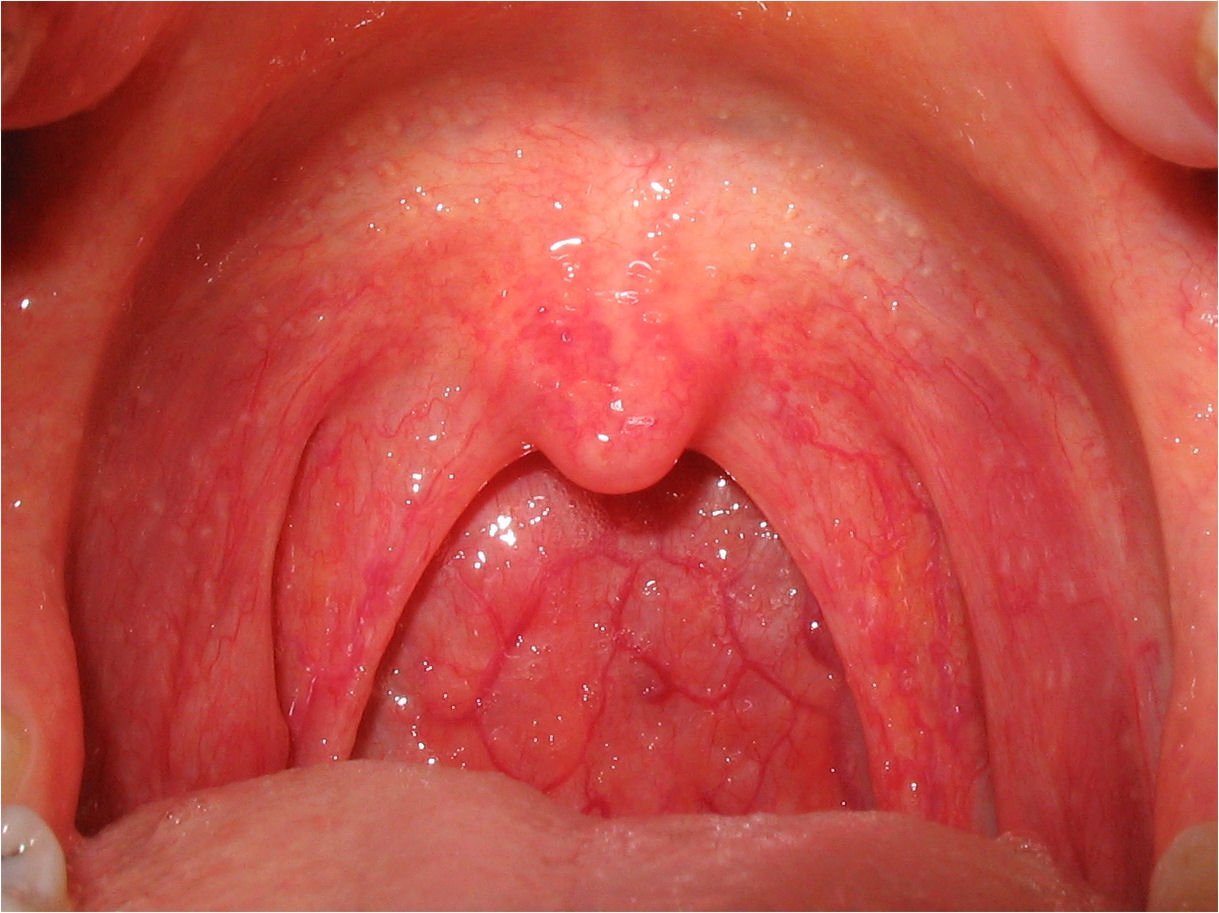
(Ref; Paediatric Nursing, Parul Datta/3rd/417)
Management of Pharyngitis:
- Warm saline gargles (in older children)
- Analgesics
- Antitussive
- Antipyretics
- Steam inhalation
- Extra fluid intake
- Liquid or soil diet
- Oral hygiene.
- Streptococcal pharyngitis should be treated with antibiotics (penicillin, amoxicillin, erythromycin,
- cephalosporin) for 10 to 15 days, and bed rest.
- Nasal decongestant and anti-allergic may be needed for some children.
(Ref by: Paediatric Nursing, Parul Datta/34/417)
