Definition of Reproduction – Introduction to fundamental concepts of Biological Science including the organization and common characteristics of living matters, cell structures and functions, food production by photosynthesis, harvesting energy, mechanism of cells reproduction, genetics, evolutions, and Human Biology. Introduction to general chemistry including basic concepts about matter, atomic structure, chemical bonds, gases, liquid, and solids, solutions, chemical reactions, acid, bases, and salt;
organic and biochemistry including hydrocarbons and their derivatives, carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, enzymes, vitamins, and minerals, nucleic acids; principles of physics and applications to nursing including gravity and mechanics, pressure, heat and electricity; nuclear chemistry and nuclear physics, effects of radiation on human beings, and protection and disposal. The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills in general biological science, general chemistry and physics.
Definition of Reproduction
It is a biological process that includes copulation, fertilization, growth and development of a new individual of the same species.
or
Sexual reproduction is the process of producing offspring for the survival of the species, and passing on hereditary traits from one generation to the next.
Child Bearing Age of a Woman:
Women’s reproductive age is called child bearing age.
- It is roughly from 15 to 45 years.
- Period of time (45-15, years):30 years.
Definition of Reproductive Organ:
The reproductive organs are those organs both in male and female those are concerned with reproduction.
Reproductive Organs of Female:
The reproductive organs of the female can be classified into two groups. These are
A. External genital organ
B. Internal genital organs
A. External genital organs:
These are also known as external genitalia or vulva. They are –
- Mons pubis
- Labia majora
- Labia minora
- Clitoris
- Vestibule of the vagina
- Bulbs of the vestibule
- Greater vestibular glands
B. Internal genital organs:
The internal genital organs are –
- Ovaries
- Vagina
- Fallopian tubes
- Uterus
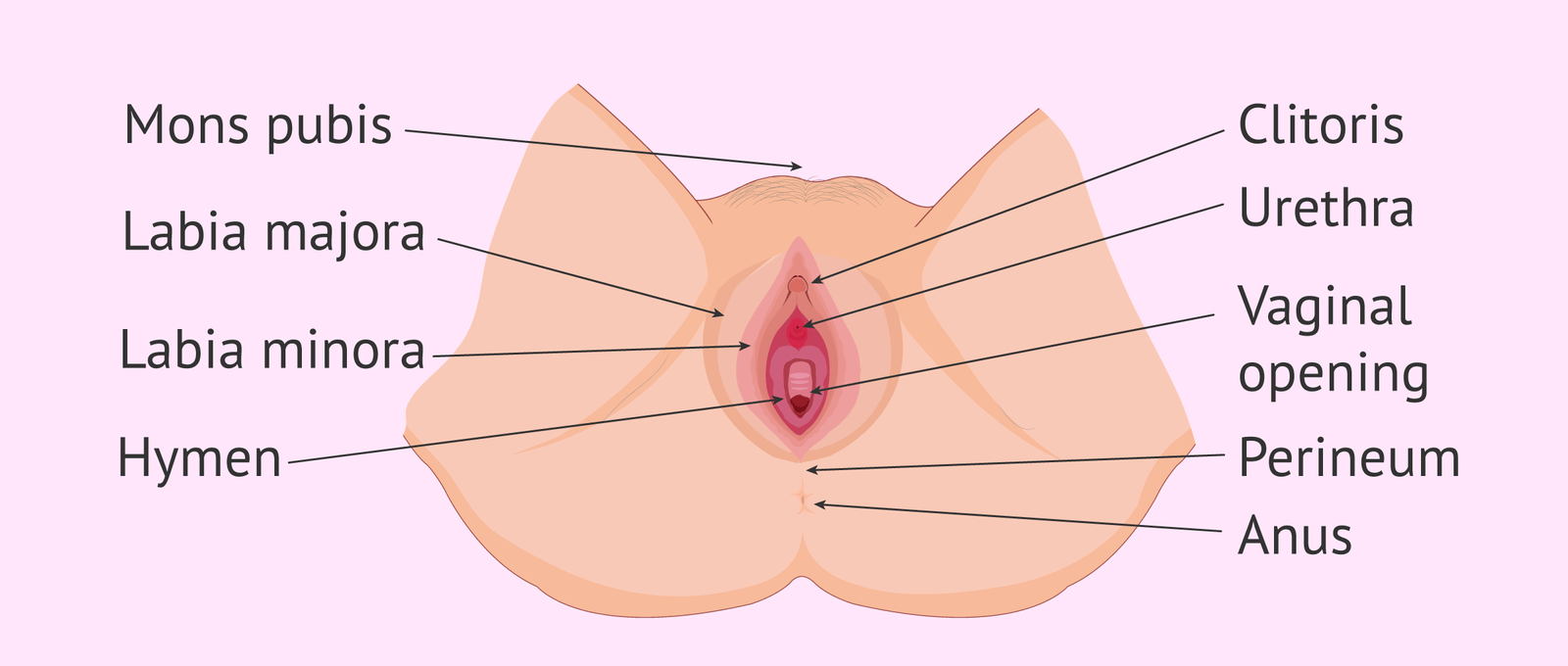
Fig: Female External Genital organ
Male Reproductive Organs:
A. External genitalia:
- Penis
- Scrotum
B. Internal genitalia
- Testes
- Epididymis
- Vas deferens
- Seminal vesicle
- Ejaculatory duct
- Prostate
- Urethra
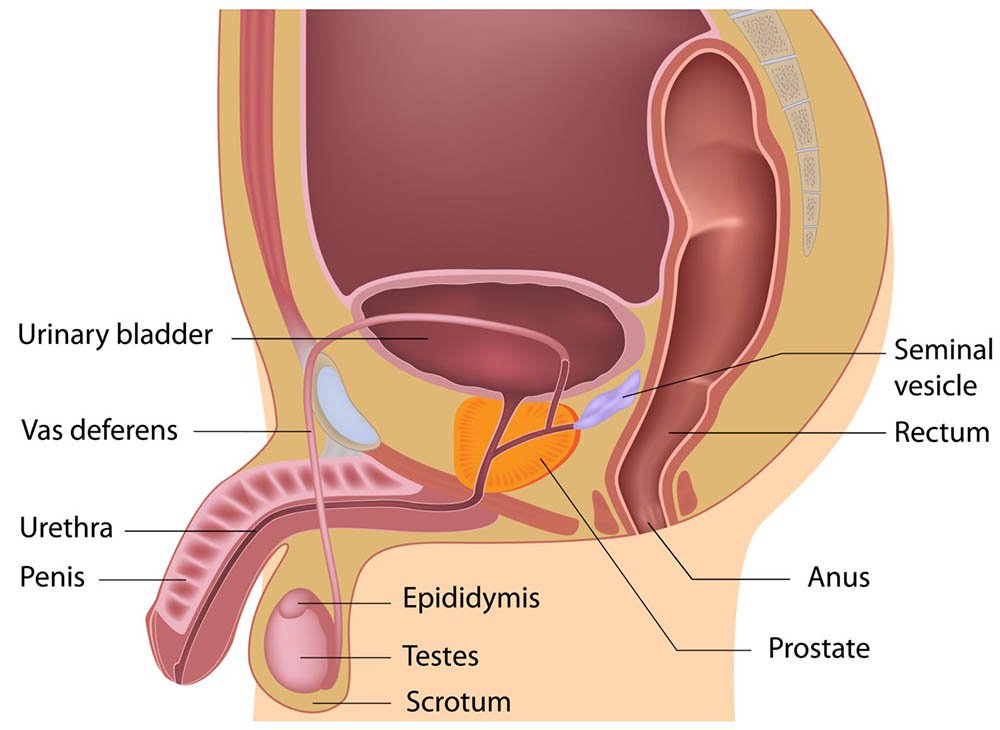
Figure: Male Reproductive Organs
Definition of Secondary Sex Characteristics:
Secondary sex characteristics are features that appear during puberty in humans, and at sexual maturity in other animals. These are particularly evident in the sexually dimorphic phenotypic traits that distinguish the sexes of a species, but unlike the sex organs, are not directly part of the reproductive system.
Secondary Sex Characteristics of Female:
In females, breasts are a manifestation of higher levels of estrogen; estrogen also widens the pelvis and increases the amount of body fat in hips, thighs, buttocks, and breasts. Estrogen also induces growth of the uterus, proliferation of the endometrium, and menses.
1. Enlargement of breasts and erection of nipples.
2. Growth of body hair, most prominently underarm and pubic hair
3. Greater development of thigh muscles behind the femur, rather than in front of it (as is typical in mature males)
4. Change in voice
5. Onset of menstruation
6. Widening of hips; lower waist to hip ratio than adult males
7. Smaller hands and feet than male adults
8. Elbows that hyperextend 5-8° more than male adults
9. Face is more rounded, with softer features
10. Smaller waist
11. Upper arms approximately 2 cm longer, on average, for a given height
(Another Answer)
Female secondary sex characteristics are:
- Onset of menstruation.
- Enlargement of the breast.
- Changes in voice.
- Maturation of female sex organ.
- Appearance of pubic (Femine shaped) and axillary hair
- Changes in voice (High pitched, low frequency)
- Enlargement of pelvis in all diameter (Gynaecoid)
- Feminine distribution of subcutaneous fat.
- Attraction to the opposite sex

