Definition of Tonsillitis – Health of the children has been considered as the vital importance to all societies because children are the basic resource for the future of humankind. Nursing care of children is concerned for both the health of the children and for the illnesses that affect their growth and development. The increasing complexity of medical and nursing science has created a need for special area of child care, i.e. pediatric nursing.
Pediatric nursing is the specialized area of nursing practice concerning the care of children during wellness and illness. It includes preventive, promotive, curative and rehabilitative care of children. It emphasizes on all round development of body, mind and spirit of the growing individual. Thus, pediatric nursing involves in giving assistance, care and support to the growing and developing children to achieve their individual potential for functioning with fullest capacity.
Definition of Tonsillitis
Tonsils are the two lymph nodes located on each side of the back of your throat. They function as a defense mechanism. They help prevent your body from infection. When the tonsils become infected, the condition is called tonsillitis.
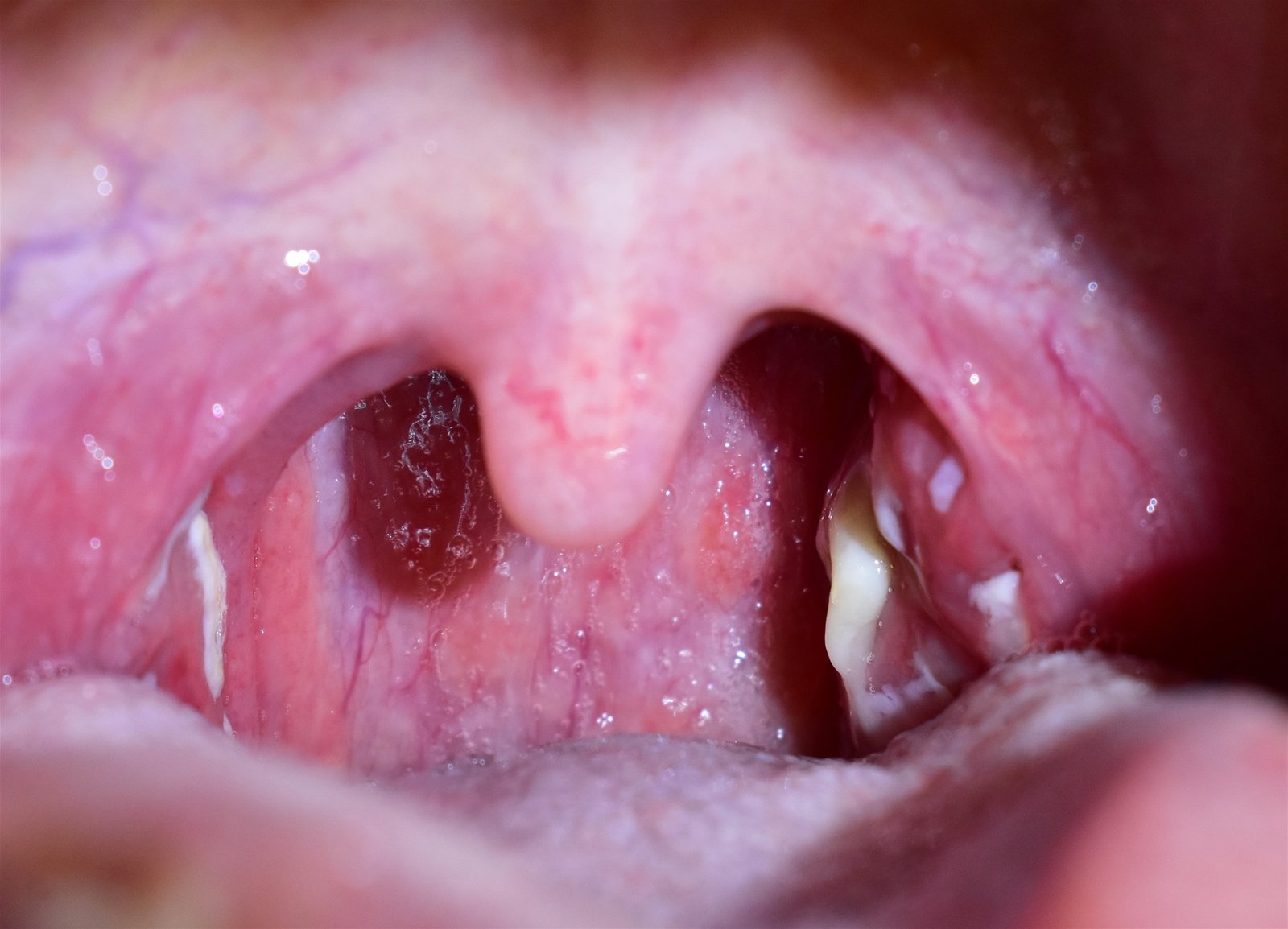
Tonsillitis can occur at any age and is a common childhood infection. It is most often diagnosed in children from preschool age through their mid-teens. Symptoms include a sore throat, swollen tonsils, and fever.
This condition is contagious and can be caused by a variety of common viruses and bacteria, such as Streptococcal bacteria, which causes strep throat. Tonsillitis caused by strep throat can lead to serious complications if left untreated.
Tonsillitis is easily diagnosed. Symptoms usually go away within 7 to 10 days.
Tonsillitis is inflammation of the tonsils, typically of rapid onset. Symptoms may include sore throat, fever, enlargement of the tonsils, trouble swallowing, and large lymph nodes around the neck
Or
Tonsillitis is inflammation of the tonsils. It’s usually caused by a viral infection or, less commonly, a bacterial infection.
Inflammation of tonsil is called tonsillitis.
Classification of Tonsillitis:
1. Acute Tonsillitis
- Catarrhal tonsillitis
- Follicular tonsillitis
- Parenchytnatous tonsillitis
- Peritonsillar abscess (quinsy)
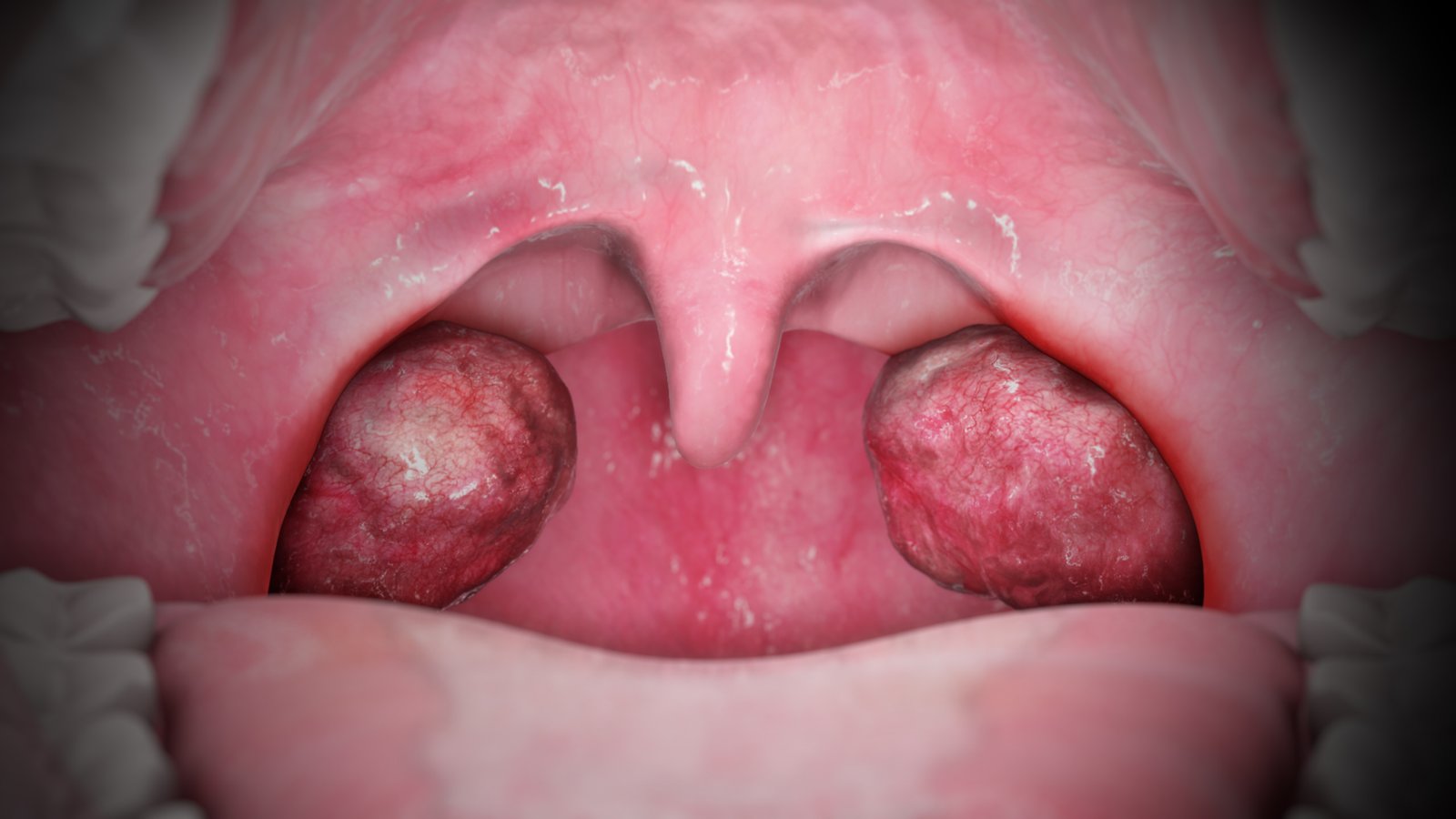
2. Chronic tonsillitis
Causes of Tonsillitis:
The most common cause includes
- Group A beta hemolytic streptococci
- Adenovirus,
- H. Influenzae
- Rhinovirus,
- Coronavirus, and
- Respiratory syncytial virus.
It can also be caused by
- Epstein-Barr virus,
- Herpes simplex virus,
- Cytomegalovirus,
Clinical Features of Tonsillitis:
- A. Clinical features of acute tonsillitis:Abrupt onset of pain in the throat which may radiate to the ears
- Painful swallowing with feverso
- Shivering and convulsions may occur especially in younger children.
- Tonsils look markedly red and congested.
- Anterior cervical glands may enlarged and become tender. –
- False membrane may develop in follicular tonsillitis.
B. Clinical features of chronic tonsillitis:
- Recurrent sore throat
- Tiredness
- Poor food intake
- Vomiting
- Bad smell in breadth
- Abdominal pain
- Dryness and irritation in throat
Complications of Tonsillitis:
Inflammation or swelling of the tonsils from frequent or ongoing (chronic) tonsillitis can cause complications such as:
- Difficulty breathing
- Disrupted breathing during sleep (obstructive sleep apnea)
- Infection that spreads deep into surrounding tissue (tonsillar cellulitis)
- Failure of thrive
- Oral thrush
- Diphtheria
- Infection that results in a collection of pus behind a tonsil (peritonsillar abscess)
Risk Factors
Risk factors for tonsillitis include:
| Young age. | Tonsillitis most often occurs in children, but rarely in those younger than age 2. Tonsillitis caused by bacteria is most common in children ages 5 to 15, while viral tonsillitis is more common in younger children. |
| Frequent exposure to germs. | School-age children are in close contact with their peers and frequently exposed to viruses or bacteria that can cause tonsillitis |
Diagnosis:
- The child has been suffering from Tonsillitis.
Nursing Consideration in Case of Tonsillitis:
- Bed rest.
- Isolation from other children to prevent spread of infection.
- Soft or liquid diet.
- Analgesic.
- Antipyretics.
- Systematic antibiotics (penicillin) should be administered parentally for 7 days.
- Other antibiotics (erythromycin, cephalexin) can be given.
- Hot saline gargle or gargles with aspirin in solution may be useful.
- An analgesic lozenge in the early stage is helpful.
Management of Chronic Tonsillitis:
Management of chronic tonsillitis is done with tonsillectomy. It is indicated, if medical treatment is unsuccessful and there is severe hypertrophy of tonsils. It should be advised in more than six significant attacks of tonsillitis in a year for two consecutive years and presence of peritonsillar or retrotonsiliar abscess.
(Ref by: Paediatric Nursing, Parul Datta/3rd/417)
Nursing Management of Tonsillectomy & Adenoidectomy:
Tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy are done under general anesthesia. After surgery –
- The child is placed in a side lying position (tonsillectomy position).
- As bleeding is the main complication of tonsillectomy this position facilitates drainage of any blood and secretions and prevents their aspiration and swallowing.
- Child is closely observed in the post-operative period for swallowing movements of the throat.
- Repeated swallowing movement means that there is bleeding and the child is swallowing it.
- When child becomes conscious, and if permitted by the anesthetist, he may be given cold fluids like fruit Juices or cold drinks.
- Later on soft foods are also started
