Definition of Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) – This course is designed to understand the care of pregnant women and newborn: antenatal, intra-natal and postnatal; breast feeding, family planning, newborn care and ethical issues, The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and develop competencies regarding midwifery, complicated labour and newborn care including family planning.
Definition of Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
UTI in pregnancy
Urinary tract infection (UTI):
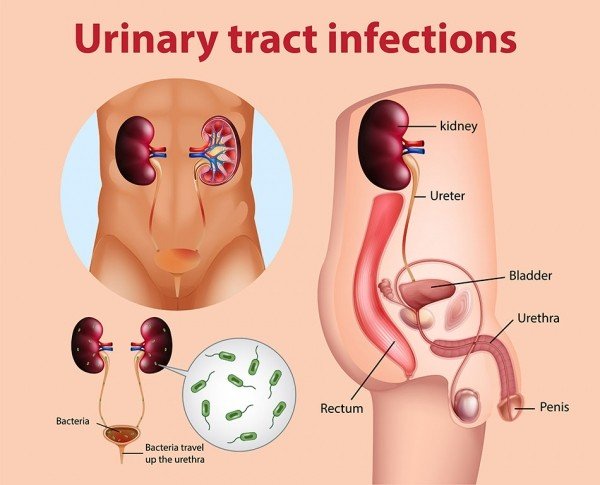
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection in any part of urinary system-kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra. Most infectiones involve the lower urinary inact the bladder and the urethra. Women are at greater risk of developing a UTI than are men.
Predisposing factors for UTI in pregnancy:
Main factors:
♦ Dilstation of renal pelvis
♦ Stasis of urine
Other factors:
♦ Sexual activity.
♦ Certain types of birth control
♦ Urinary tract abnormalities.
♦ Blockages in the urinary tract.
♦ A suppressed immune system.
♦ Catheter use
♦ A recent urinary procedure.
Management of UTI in pregnancy:
Clinical features:
Symptoms:
- Nausea and vomiting.
- High fever with chill and rigor.
- Frequency of micturition
- Burming sensation during micturition.
- Moderate to severe abdominal pain.
Signs:
- III looking (patient may be toxic).
- High rise of temperature.
- Tachycardin.
- Dry tongue.
- Nonspecific tenderness in the lower abdomen.
Investigations:
- Blood for TC, DC, ESR, Hb%.
- Urine R/M/E.
- Urme CS.
- USG of lower abdomen.
Treatment of UTI:
A. General treatment
- Bed rest
- Plenty of water intakes.
- Maintenance of personal hygiene.
B. Specific treatment:
- Appropriate antibiotic: Cap. Amoxicillin (500 mg tds)
- Anti-spasmodic: Tah. H-N butyl bromide (10 or 20 mg bd or tds)/Tab.
Tiemomium methyl sulphate (50 mg bd er tdi). - Anti-pyretic: Tab. Paracetamol (500 mg tds).
- Anti-emetic (if vomiting is present) Tah ondansetron (8 mg od or bd).
Obstetric management:
1. Careful monitoring of maternal and fetal condition.

Complications of UIT in pregnancy:
- Increase fetal mortality & morbidity Abortion.
- Preterm labour.
- JUD.
- LBW.
- Prematurity.
- Dysmaturity.
Probable causes of retention of urine at 14 weeks of gestation:
- Incarcerated retroverted gravid uterus,
- Impacted pelvic tumours.
- During labour: obstructed labourk uncoordinated uterine action.
- During puerperium Diminished bladder tone, reflex from vulval injury & bruising, & oedema of the bladder neck.
Treatment:
- Catheterization to relief the bladder distension.
- Treatment of the underlying cause.