Definition ORIF – An orthopedic nurse is a nurse who specializes in treating patients with bone, limb, or musculoskeletal disorders. Nonetheless, because orthopedics and trauma typically follow one another, head injuries and infected wounds are frequently treated by orthopedic nurses.
Ensuring that patients receive the proper pre-and post-operative care following surgery is the responsibility of an orthopedic nurse. They play a critical role in the effort to return patients to baseline before admission. Early detection of complications following surgery, including sepsis, compartment syndrome, and site infections, falls under the purview of orthopedic nurses.
Definition ORIF
O.R.I.F. is an abbreviation for Open Reduction Internal Fixation. Open reduction internal fixation is a method of surgically repairing a fractured bone. Generally, this involves either the use of plates and screws or an intramedullary (IM) rod to stabilize the bone.
Or
An open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) is a type of surgery used to fix broken bones. This is a two-part surgery. First, the broken bone is reduced or put back into place. Next, an internal fixation device is placed on the bone; this can be screws, plates, rods, or pins used to hold the broken bone together.
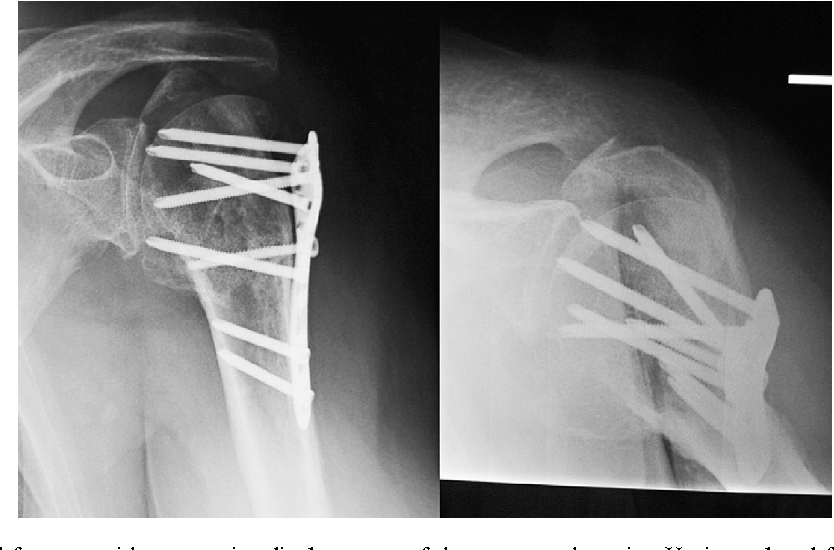
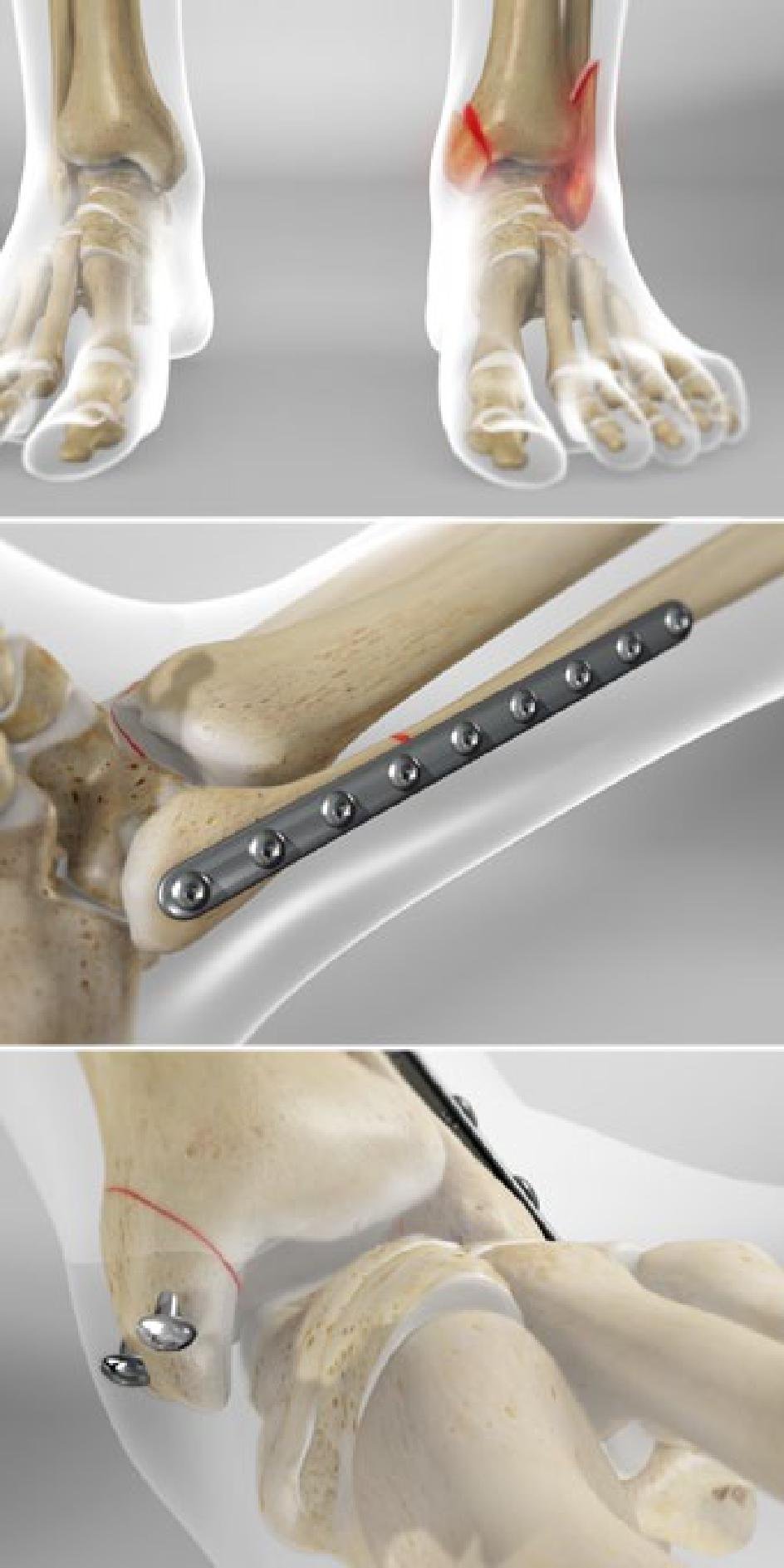
Indications for ORIF:
This surgery is done to repair fractures that would not heal correctly with casting or splinting alone:
- Failure of closed reduction and pecutaneous pin fixation;
- Fractures presenting more than 2 mm of displacement and greater than 15 deg of talometatarsal angulation);
- Young competitive atheletes may require anatomic reduction;
- Disrupted skin and excessive swelling are relative contra-indications for ORIF.
Complications of ORIF:
- Infection.
- Bleeding.
- Reaction to anesthesia.
- Blood clots.
Nursing process of ORIF patients:
A) Assessment: A immediate post operative assessment includes,
1. Assess vital signs
2. Neurovascular assessment: pulse temperature,color, capillary filling, edema and sensory and motor nerve functions.
3. Check that incisional dressing is dry and intact.
4. Check patients level of consciousness and orientation.
5. Assess pain-type, severity, location.
6. Auscultate the lungs sound.
7. Note type of intravenous solution, rate of flow, amounts.
8. Determine the blood loss during surgery and replacement of fluid.
9. Check urinary output.
10. Note any signs and symptoms of shock, pulmonary emboli, deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
B) Nursing diagnosis:
1. Pain and discomfort related to soft tissue trauma.
2. Impaired physical mobility related to instability of the pelvis 3. Risk of impaired skin integrity related to immobility.
4. Constipation related to decrease activity and pain.
5. Ineffective individual copping related to the trauma and rehabilitation process.
6. Increased anxiety related to knowledge deficit.
C) Goal formulation and planning:
1. To decrease pain through nursing process.
2. An increase mobility with the use of crutches or a walker.
3. To improve skin integrity.
4. Effective copping capability of a patients.
5. To reduce post operative complications.
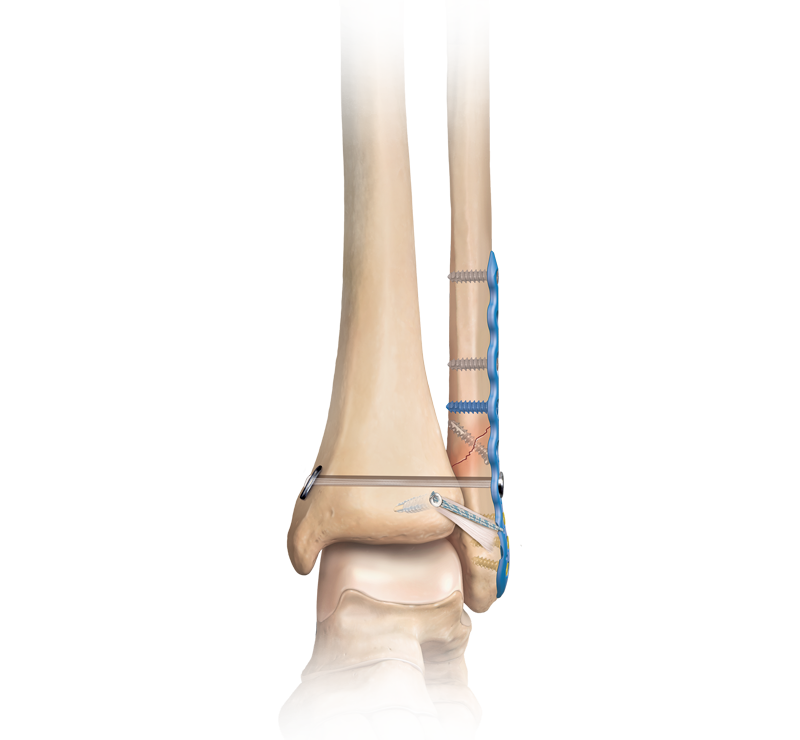
D) Nursing interventions:
1) Alleviating pain:
a. Assess pain for type, severity, locations,
b. Verify that patients is correctly positioned while in bed or in a chair. Teaches the patients about relaxation techniques, e.g. deep breathing, hearing song, watching tv.
c. Give pain medications according to doctors order.
d. Monitor pain reducing symptoms.
e. Verify that correct amount of weight is applied during transfer of a patient.
f. Provide aseptic technique during I/V, I/M procedure.
2) Increase mobility:
i) ii) When patients is in bed, they should be turned and repositioned every 2 hours If the fracture site is only one side, turn the patients on unfracture or non operative side.
a) Positions:
ⅲ) If the patients has bilateral fracture involvement, the patient can be turned from their to either side.
iv) Use long rolling to turn the patients.
b) Exercise:
i) Patients should start muscle setting exercise immediately after surgery. Such as quadriceps, gluteal setting, ankle pumps and range of motion to ankle.
ii) In patients associated with ace tabular fracture, continuous passive motion (CPM) machine may be used to prevent loss of range motions in the hip.
c) Ambulation:
i) Avoid weight bearing in case of acetabular fracture.
ii) Patients with unilateral posterior injuries are permitted early weight bearing in non injured site.
After 12 weeks of postoperative patients with bilateral injuries are allowed to limit weight bearing.
3) Maintain skin integrity:
a. Observe the bony prominence of back.
b. Change the position 2 hourly.
c. Assess signs and symptoms of bed sores.
d. Give back message to improve circulations.
e. Give cotton pad under the bonny prominence to reduce chane of pressure sores.
f. Keep linen dry free of wrinkle s.
g. Keep the bony prominent soft by applying lubricate or powder.
h. Keep the patients well hydrated and maintain well balance diet with adequate protein.
4) Reducing the chance of constipations: Following a pelvic fracture with an ORIF, patients have limited movements, again taking pain medications which put them at risk of constipations,
a) Assess bowel sounds of patients
b) Encourage to take plenty of vegetables.
c) Advice to take plenty of water.
d) Advice to take high fiber containing diet.
e) Give stool softener medication
5) Effective coping mechanisms:
a) Assess the cause of anxiety.
b) Assurance of the patients that he will cure readily.
e) Tell him that nurses and doctors will do the best.
d) Encourage the patients and family to verbalize questions. Encourage to use relaxation technique, such as exercise, deep breathing, listening song, watching movie.
6) Prevention of complications:
a) Maintain personal hygiene.
b) Investigation of TC, De, ESR, HB%, Urine R/M/E, for detection of any abnormality.
c) Assess any signs of hypovolymic shock.
d) Check dressing regularly.
e) Give appropriate antibiotic to prevent secondary infections.
[Ref-Lippincott, Adult Orthopedic nursing, 1″ edition.page-265]
CRIF:
Closed Reduction Internal Fixation (CRIF) is reduction without any open surgery, followed by internal fixation. It appears to be an acceptable alternative in unstable displaced lateral condylar fractures of the humerus in children, but if fracture displacement after closed reduction exceeds 2 mm, open reduction and internal fixation is recommended. Various techniques of minimally invasive surgery for internal fixation of bones have been reported. The treatment of fractures of the distal third of the tibia has evolved with the development of improved imaging and surgical techniques.
