Disorders and terminology of Respiratory system-The course is designed for the basic understanding of anatomical structures and physiological functions of human body, musculoskeletal system, digestive system, respiratory system; cardiovascular system; urinary system, endocrine system, reproductive system, nervous system, hematologic system, sensory organs, integumentary system, and immune system.The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills regarding anatomy and physiology.
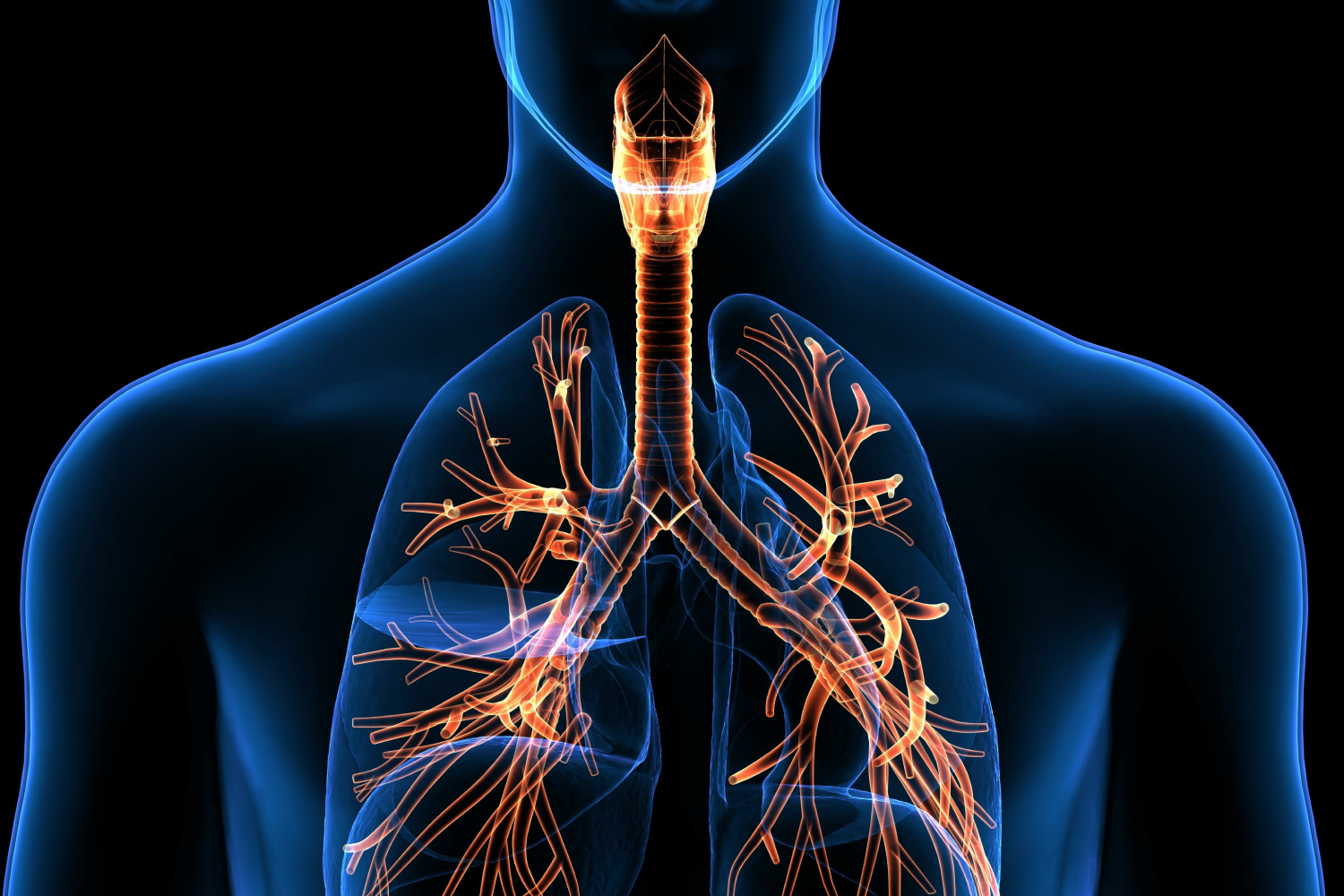
Disorders and terminology of Respiratory system
Abdominal thrust maneuver.
First-aid procedure to clear the airways of obstructing objects. It is performed by applying a quick upward thrust between the navel and lower ribs that causes
sudden elevation of the diaphragm and forceful, rapid expulsion of air from the lungs, forcing air out of the trachea to eject the obstructing object Also used to expel water from the lungs of near drowning victims before resuscitation is begun. Also known as the Heimlich maneuver
Asphyxia Oxygen starvation due to low atmospher oxygen or interference with ventilation. external respiration, or internal respiration
Asthma: The dyspnea, wheezing, and other symptoms of asthma are produced by an obstruction of air flow through the bronchioles that occurs in episodes, or “attacks.” This obstruction is caused by mflammation, mucous secretion, and bronchoconstriction
Aspiration: Inhalation into the bronchial tree of a substance other than air, for instance, water, food, or a foreign body
Atelectasis: collapse of lung tissue (alveoli)
Auscultation: to listen, a physical examination method of listening to the sounds within the body with the aid of a stethoscope, such as auscultation of the chest for heart and lung sounds
Bronchoscopy: The visual examunation of the bronchi through a bronchoscope, an illuminated. tubular instrument that is passed through the mouth (or nose) larvns and traches into the bronchi obstructive putnunars disease (COPD): a respiratory disorder characterized by Chronic obstruction of airtlow The principal types of COPD are emphysema and chronic bronchitis
Cyanosis: bluish coloration of the skin caused by a deficient amount of oxygen in the blood Cystic fibrosis (CF) An inhented disease of secretory epithelia that affects the airways, liver. pancreas, small intestine, and sweat grands Clogging and infection of the airways leads to difficulty in breathing and eventual destruction of lung tissue
Dyspnea: (dys painful, difficult) Painful or labored breathing
Emphysema: obstructive pulmonary disease characterized by overexpansion of the alveoli with air and destructive changes in their walls. resulting in loss of lung elasticity and gas exchange.

Empyema: accumulation of pus in the pleural cavity.
Epistaxis: Loss of blood from the nose due to trauma, infection, allergy, malignant growths, or bleeding disorders. It can be arrested by cautery with silver nitrate, electrocautery, or firm packing. Also called nosebleed.
Hemothorax: blood in the pleural cavity
Hypopnea: shallow breathing.
Hyperpnea: deep breathing
Hypoxia: A deficiency of O2 at the tissue level that may be caused by a low PO2 in arterial blood, as from high altitudes, too little functioning hemoglobin in the blood, as in anemia, inability of the blood to carry 02 to tissues fast enough to sustain their needs, as in heart failure, or inability of tissues to use 02 properly, as in cyanide poisoning
Lobectomy: removal of a lobe of a lung.
Mechanical ventilation: The se of an respitator in est bowathing A plasth tube e inserted into the nose or mouth and the tube attached to a device that forces air into the lungs Exhalation occurs pasuvely due to the elastic recoil of the lungs.
Orthopnca: Difficult to take breath in laying position but ability to breathe only in an upright position
Pleurisy: Inflammation of the pleural membranes which causes friction during breathing that can be quite painful when the swollen membranes rub against each other Also known as pleuritis
Pleural effusion: accumulation of fluid in the pleural cavity.
Pneumonia: inflammation in the lung resulting from infection by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites or from aspiration of chemicals.
Pneumothorax: The elastic nature of lung tissue is revealed when air enters the intrapleural space This condition, called a pneumothorax.
Rales: Sounds sometimes heard in the lungs that resemble bubbling or rattling. Different types are due to the presence of an abnormal type or amount of fluid or mucus within the bronchi or alveoli, or to bronchoconstriction that causes turbulent airflow.
Respiratory distress syndrome (RDS): A breathing disorder of premature newborns in which the alveoli do not remain open due to a lack of surfactant. Surfactant reduces surface tension and is necessary to prevent the collapse of alveoli during exhalation
Respiratory failure: A condition in which the respiratory system either cannot supply enough O2 to maintain metabolism or cannot eliminate enough CO2 to prevent respiratory acidosis (a higher-than-normal H_level in interstitial fluid).
Rhinitis Chronic or acute inflammation of the mucous membrane of the nose.
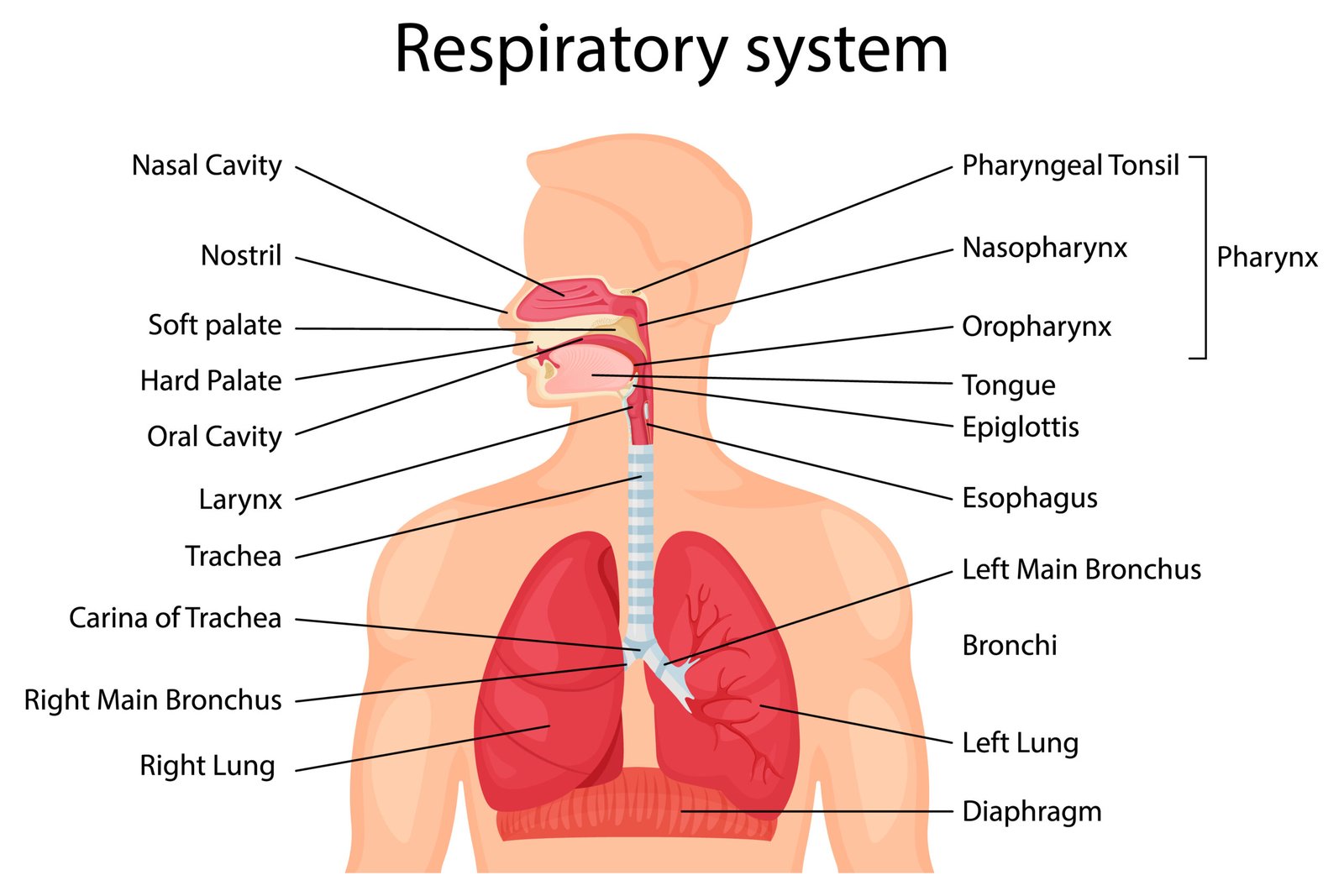
Sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS): Death of infants between the ages of 1 week and 12 months thought to be due to hypoxia that occurs while sleeping in a prone position (on the stomach) and rebreathing exhaled air trapped in a depression of the mattress. It is now recommended that normal newborns be placed on their backs for sleeping (remember: “back to sleep”).
Tachypnea: Rapid breathing rate more than 20b/min.
Tracheostomy: A tracheotomy is the procedure of surgically opening the trachea, and a tracheostomy involves the insertion of a tube into the trachea to permit breathing and to keep the passageway open
Wheeze: A whistling, squeaking, or musical high-pitched sound during breathing resulting from a partially obstructed airway.
(Ref: Ross and wilson- 9th ed)
Read more:
