Drug Parasite – This book covers the entire syllabus of “Pharmacology” prescribed by BNMC- for a diploma in nursing science & midwifery students. We tried to accommodate the latest information and topics. This book is an examination set up according to the teachers’ lectures and examination questions.
At the end of the book, previous questions are given. We hope in touch with the book students’ knowledge will be upgraded and flourish. The unique way of presentation may make your reading of the book a pleasurable experience.

Drug Parasite
Definition of Parasite:
The term “parasite” came from the Greek “parasilos” (para, alongside of + silos, food) meaning “eating at the side of, or at the same table.” got all aditaab yaad O Parasite can be defined as “A living organism which-depends on living organism for food and accommodation.” A parasite cannot live independently.
Or,
Parasite can be defined as living organism which receives nourishment and shelter from another organism where it lives.
[Ref by- Prof. Akram/24/1]
Common Parasitic Infection in Bangladesh
| Parasite | Vector | Parasitic disease. |
Giardia intestinalis | House fly | Giardiasis |
Entamoeba histolytica | House fly | Amoebiasis |
Plasmodium species | Female anopheles mosquito | Malaria |
Leishmania donovani | Sand fly | Kala-azar |
Wuchereria bancrofti Brugia malayi | Female culex mosquito | Filariasis |
Onchocerca volvulus | Female black fly | Onchocerciasis |
| Loa loa | Deer fly | Loiasis. |

Criteria of Parasitism
Following are some of the important criteria for parasitism
- Ecological relationship between two different organisms, one designated the parasite, the other the host.
- The parasite is physiologically or metabolically dependent upon its host.
- Heavily infected hosts may be killed by their parasites.
Classification of Parasites
Types of Parasite:
A. According to Structure:
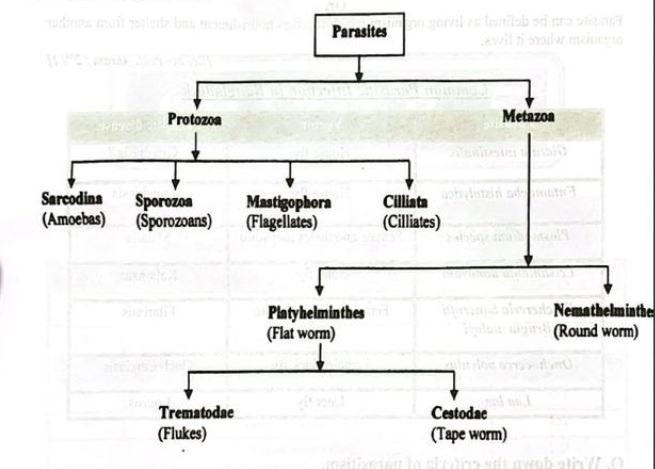
B. On the basis of site of infection:
a) Ectoparasite: e.g. lice (surface of host)
b) Endoparasite: e.g. malarial parasite (inside of body)
C. On the basis of period of infection:
a) Permanent: A lunbricoides in mm
b) Temporary: Larva of Cordylobia antropophaga
D. On the basis of pathogenicity:
a) Pathogenic: e.g. L. donovani (Harmful to man)
b) Commensal: e.g. Entamoeba coli (Normal flora)
Read more:
