Today our topic of discussion is ” Drugs that Affect the Autonomic System “. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is a marvel of human physiology, maintaining a balance of internal processes without our conscious input. Over time, scientists have developed drugs that can influence the ANS to treat various conditions. This article provides an in-depth exploration of these drugs, their mechanisms, and their implications for medicine.
Drugs that Affect the Autonomic System: The Autonomic Nervous System
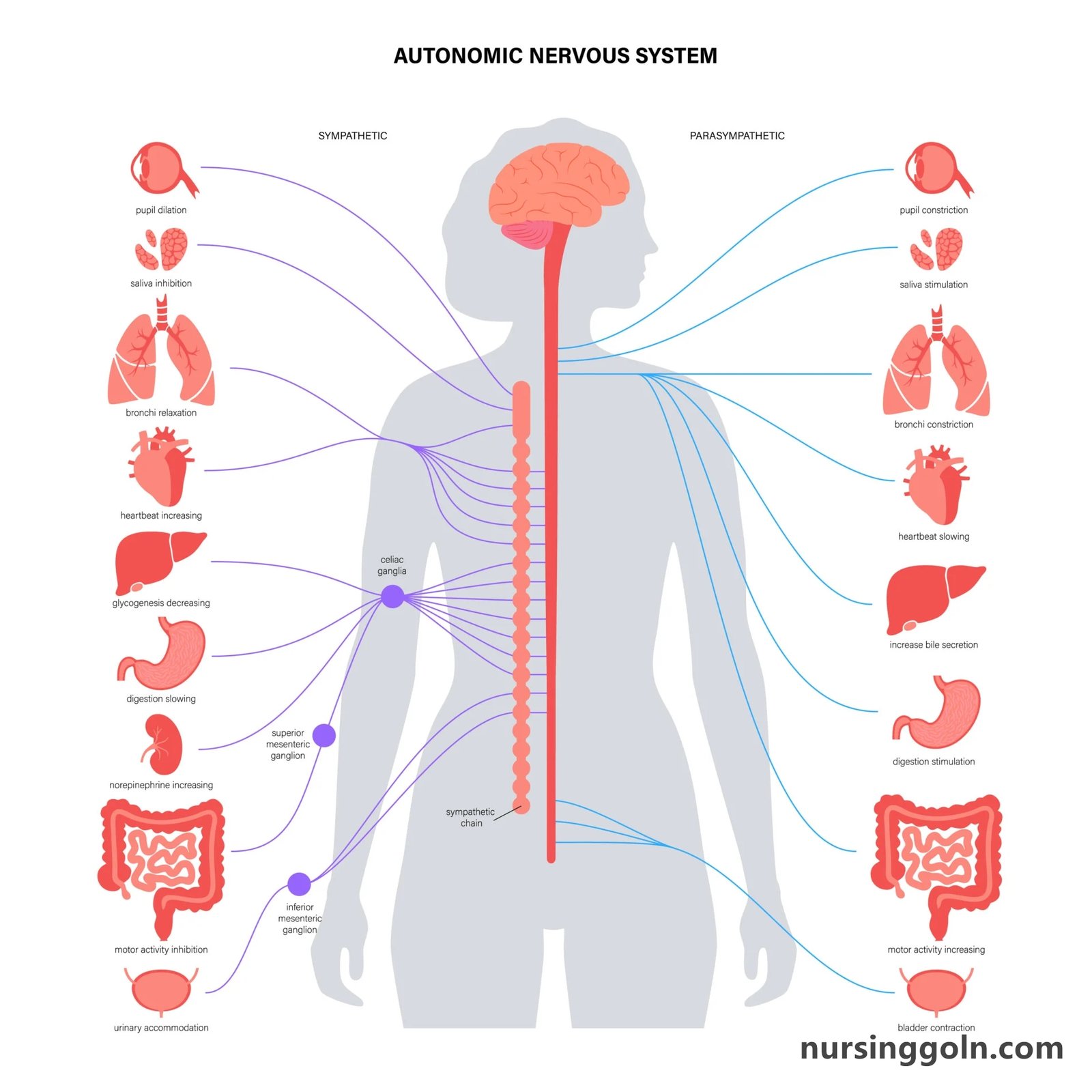
1. Introduction: The ANS Landscape
To comprehend the action of these drugs, one must first understand the ANS’s divisions:
- Sympathetic Nervous System (SNS): Often termed the “fight or flight” system, it prepares the body for stressful situations.
- Parasympathetic Nervous System (PNS): The “rest and digest” system, it promotes relaxation and recovery.
2. Neurotransmitters of the ANS
The ANS primarily uses two neurotransmitters: acetylcholine (ACh) and norepinephrine (NE). While ACh is the main neurotransmitter for the PNS, the SNS chiefly uses NE.
3. Cholinergic Drugs: Influencing Acetylcholine Activity
Cholinergic drugs affect cholinergic receptors that bind ACh. They can be categorized as:
- Cholinergic Agonists (Parasympathomimetics): These drugs stimulate cholinergic receptors. Example: Pilocarpine, used to treat glaucoma.
- Anticholinergics (Parasympatholytics): These inhibit cholinergic receptor activity. Example: Atropine, which can increase heart rate and is used in some eye exams to dilate pupils.
4. Adrenergic Drugs: Modulating Norepinephrine Activity
Adrenergic drugs act on adrenergic receptors that bind NE. They include:
- Adrenergic Agonists (Sympathomimetics): These stimulate adrenergic receptors. Example: Albuterol, a bronchodilator used in asthma.
- Adrenergic Antagonists (Sympatholytics): These inhibit adrenergic receptor activity. Example: Propranolol, a beta-blocker used for hypertension.
5. Drugs that Affect Neurotransmitter Release or Availability
- Neuromuscular Blockers: Such as succinylcholine, interfere with ACh release at neuromuscular junctions, leading to muscle paralysis.
- Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs): These prevent the breakdown of NE, increasing its availability. They’re used as antidepressants.
6. Clinical Uses of Autonomic Drugs
- Cardiovascular Disorders: Beta-blockers can treat hypertension, while cholinergic drugs can manage heart rate abnormalities.
- Respiratory Conditions: Adrenergic agonists like salbutamol can dilate bronchi, helping asthma patients.
- Digestive Disorders: Anticholinergic drugs can reduce intestinal motility, aiding irritable bowel syndrome treatment.
7. Side Effects and Considerations
All drugs come with potential side effects. For instance:
- Adrenergic Agonists: Can cause tachycardia or hypertension.
- Anticholinergics: This may lead to dry mouth, blurred vision, and urinary retention.
It’s crucial to weigh the therapeutic benefits against potential side effects.

8. Recent Developments and Future Horizons
Emerging research has paved the way for more targeted drug therapies:
- Selective Receptor Agonists & Antagonists: Drugs that act specifically on subtypes of adrenergic or cholinergic receptors, ensuring more precise effects.
- Gene Therapy: Potential treatments that modify the expression of certain receptors or neurotransmitter-producing genes in the ANS.
9. Herbal and Natural Compounds
Many natural compounds influence the ANS:
- Ephedra: Contains ephedrine, a sympathomimetic agent.
- Deadly Nightshade (Belladonna): Contains atropine, an anticholinergic compound.
While natural doesn’t always mean safe, understanding these compounds’ actions is crucial for both traditional and modern medicine.

10. Navigating the Therapeutic Landscape
The ANS, with its delicate balance of sympathetic and parasympathetic activities, provides a rich therapeutic target. The drugs influencing this system exemplify the power of pharmacology to harness our body’s internal mechanisms. As science advances, it’s likely we’ll see even more refined and effective treatments, broadening the horizons of autonomic pharmacotherapy.
