Effects of Radiations on Human Beings/ Radiation Sickness – Introduction to fundamental concepts of Biological Science including the organization and common characteristics of living matters, cell structures and functions, food production by photosynthesis, harvesting energy, mechanism of cells reproduction, genetics, evolutions, and Human Biology. Introduction to general chemistry including basic concepts about matter, atomic structure, chemical bonds, gases, liquid, and solids, solutions, chemical reactions, acid, bases, and salt;
organic and biochemistry including hydrocarbons and their derivatives, carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, enzymes, vitamins, and minerals, nucleic acids; principles of physics and applications to nursing including gravity and mechanics, pressure, heat and electricity; nuclear chemistry and nuclear physics, effects of radiation on human beings, and protection and disposal. The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills in general biological science, general chemistry and physics.
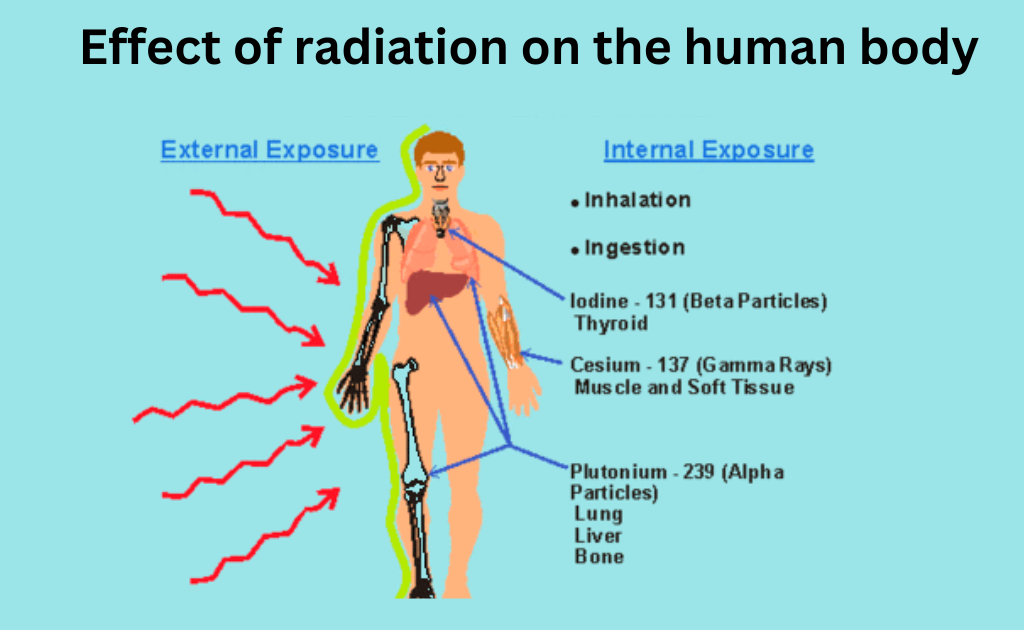
Effects of Radiations on Human Beings/ Radiation Sickness
Effects of Radiation on the Body
| 1. Hair | The losing of hair quickly and in clumps occurs with radiation exposure at 200 rems or higher. |
| 2. Brain | Since brain cells do not reproduce, they won’t be damaged directly unless the exposure is 5,000 rems or greater. Like the heart, radiation kills nerve cells and small blood vessels, and can cause seizures and immediate death. |
| 3. Thyroid | The certain body parts are more specifically affected by exposure to different types of radiation sources. The thyroid gland is susceptible to radioactive iodine. In sufficient amounts, radioactive iodine can destroy all or part of the thyroid. By taking potassium iodide, one can reduce the effects of exposure. |
| 4. Blood System | When a person is exposed to around 100 rems, the blood’s lymphocyte cell count will be reduced, leaving the victim more susceptible to infection. This is often refered to as mild radiation sickness. Early symptoms of radiation sickness mimic those of flu and may go unnoticed unless a blood count is done. |
| 5. Heart | Intense exposure to radioactive material at 1,000 to 5,000 rems would do immediate damage to small blood vessels and probably cause heart failure and death directly. |
| 6. Gastrointestinal Tract | Radiation damage to the intestinal tract lining will cause nausea, bloody vomiting and diarrhea. This is occurs when the victim’s exposure is 200 rems or more. The radiation will begin to destroy the cells in the body that divide rapidly. These including blood, GI tract, reproductive and hair cells, and harms their DNA and RNA of surviving cells |
| 7. Reproductive Tract | Because reproductive tract cells divide rapidly, these areas of the body can be damaged at rem levels as low as 200 rems. Long-term, some radiation sickness victims will become sterile. |
Symptoms of Radiation Sickness:
The signs and symptoms of acute radiation poisoning are:
- Vomiting, diarrhea, and nausea
- Loss of appetite
- Malaise, or feeling unwell
- Headache
- Rapid heartbeat
Symptoms depend on the dose, and whether it is a single dose or repeated,
- Loss of white blood cells
- Nausea and vomitingass
- Headaches
- Temporary hair loss
- Damage to nerve cells
- Damage to the cells that line the digestive tract

Stages of Radiation Sickness
Symptoms of severe radiation poisoning will normally go through four stages.
1. Prodomal stage: Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, lasting from a few minutes to several days
2. Latent stage: Symptoms seem to disappear, and the person appears to recover
3. Overt stage: Depending on the type of exposure, this can involve problems with the cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, hematopoietic, and central nervous system (CNS)
4. Recovery or death: There may be a slow recovery, or the poisoning will be fatal.
Protection against Radiation Exposure:
Damage by radiation is irreversible. Once the cells are damaged, they do not repair themse Until now, there is no way for medicine to do this, so it is important for someone who has been exposed to seek medical help as soon as possible.
Possible treatments include:
- Removing all clothing,
- Rinsing with water and soap.
- Use of potassium iodide (KI) to block thyroid uptake if a person inhales or swallows too much radioiodine
- Prussian blue, given in capsules, can trap cesium and thallium in the intestines and prevent them from being absorbed. This allows them to move through the digestive system and leave he body in bowel movements.
- Filgrastim, or Neupogen, stimulates the growth of white blood cells. This can help if radiation has affected the bone marrow.
Depending on exposure, radiation can affect the whole body. For cardiovascular. atestinal, and other problems, treatment will target the symptors.
Reducing exposure to radiation
Tips for reducing unnecessary exposure to radiation include:
- Keeping out of the sun around midday and using a sunscreen or wearing clothes that cover the skin
- Making sure any CT scans and x-rays are necessary, especially for children
- Letting the doctor know if you are or may be pregnant before having an x-ray, PET, or CT scan
It is not possible or necessary to avoid all exposure to radiation, and the risk posed to health by most sources is extremely small.