Elements of computer system – This book covers the entire syllabus of “Computer & Information Technology” prescribed by the BNMC for B.Sc. in Nursing Science & Diploma in Nursing Science & Midwifery students. We tried to accommodate the latest information and topics.
This book is an examination setup according to the teachers’ lectures and examination questions. We hope in touch with the book students’ knowledge will be upgraded and flourished. The unique way of presentation may make your reading of the book a pleasurable experience.
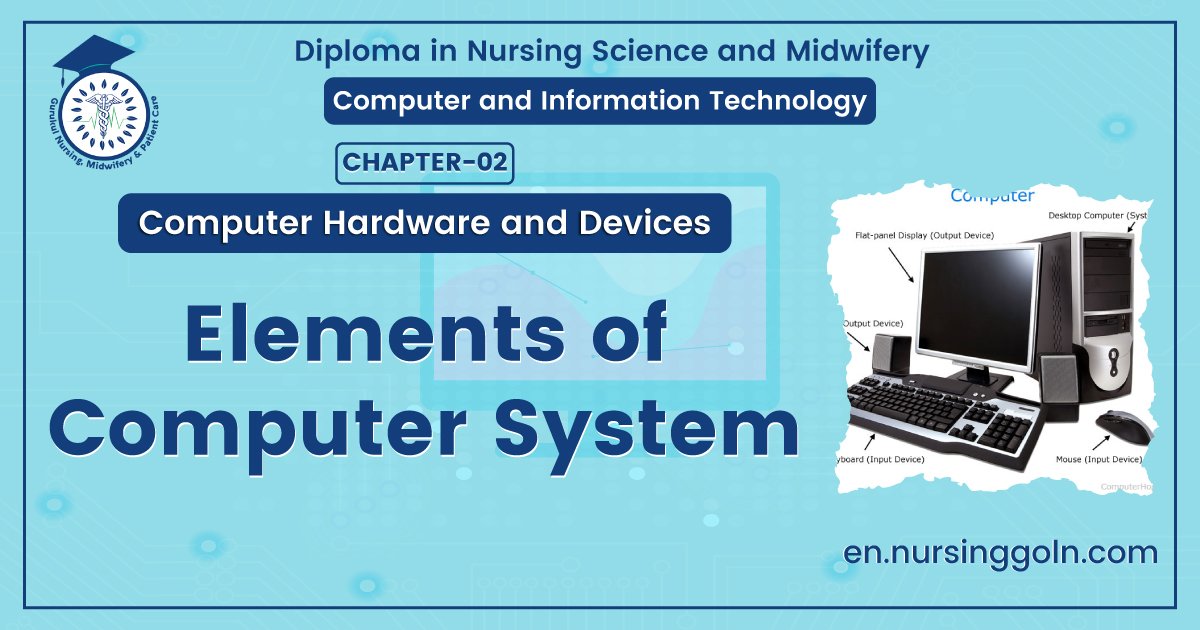
Elements of computer system

Elements of Computer:
A computer system is a set of six elements viz.:
1. Hardware,
2. Software,
3. People,
4. Procedures,
5. Data and
6. Connectivity.
A. Hardware: The physical components of a computer constitute its Hardware. These include keyboard, mouse, monitor and processor. Hardware consists of input devices and output devices that make a complete computer system.
B. Software: A set of programs that form an interface between the hardware and the user of a computer system are referred to as Software.
C. Procedures: Procedure is a step by step series of instructions to perform a specific function and achieve desired output.
D. Data: The facts and figures that are fed into a computer for further processing are called data. Data is raw until the computer system interprets it using machine language, stores it in memory, classifies it for processing and produces results in conformance with the instructions given to it. Processed and useful data is called information which is used for decision making.
E. Connectivity: When two or more computers are connected to each other, they can share information and resources such as sharing of files (data/music etc.), sharing of printer, sharing of facilities like the internet etc. This sharing is possible using wires, cables, satellite, infra-red, Bluetooth, microwave transmission etc.
Definition of Software
The Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (IEEE) defines software as a – “Collection of computer programs, procedures, rules and associated documentation and data.”
Or,
Software, in its most general sense, is a set of instructions or programs instructing a computer to do specific tasks.
Or
Software is a collection of instructions that enable the user to interact with a computer, its hardware, or perform tasks. Sometimes software is abbreviated as SW and S/W.
Characteristics of Software
Software characteristics are classified into six major components.
| 1. Functionality: | Refers to the degree of performance of the software against its intended purpose. |
| 2. Reliability: | Refers to the ability of the software to provide desired functionality under the given conditions. |
| 3. Usability: | Refers to the extent to which the software can be used with ease. |
| 4. Efficiency: | Refers to the ability of the software to use system resources in the most effective and efficient manner. |
| 5. Maintainability: | Refers to the ease with which the modifications can be made in a software system to extend its functionality, improve its performance, or correct errors. |
| 6. Portability: | Refers to the ease with which software developers can transfer software from one platform to another, without (or with minimum) changes. In simple terms, it refers to the ability of software to function properly on different hardware and software platforms without making any changes in it. |

Classification/Types of Software
There are mainly two types of software-
1. System software
2. Application software.
A. System software: System software consists of programs that control the operations of a computer and its devices. System software serves as the interface between a user, the application software, and the computer’s hardware.
The System Software are divided into 3 types, they are:
a) Operating System Software
b) Programming Language Translator
c) Utility Software
a) Operating System Software (O.S): An Operating System is a program designed to run other programs on a computer.
There various types of operating system are –
- General Purpose O.S
- Special Purpose O.S
- Batch Processing O.S
- Single Use O.S
- Multi-User O.S
b) Programming Language Translator: It is another system software which convert the high level language to machine level language for the purpose of machine understanding.
There are 3 types of language translator, they are as follows:-
- Compiler.
- Interpreter.
- Assembler.
c) Utility Software: Utility Software is a kind of system software designed to help, analyze, configure, optimize and maintain the computer.
For example –
- Antivirus: Utility scan for computer virus
- Memory tester checks for memory failure etc.
B. Application software: Application software consists of programs designed to perform specific tasks for users.
Now a days there are mainly millions of application software are available in different sectors. Some of them are given below:
| Application Software Type | Examples |
| 1. Word processing software |
|
| 2. Database software |
|
| 3. Spreadsheet software |
|
| 4. Multimedia software |
|
| 5. Presentation Software |
|
| 6. Enterprise Software |
|
| 7. Information Worker |
|
| 8. Educational Software |
|
Difference between System Software and Application Software
| SL .No. | System Software | Application Software |
| 1. | System software is used for operating computer hardware. | Application software is used by user to perform specific task. |
| 2. | System software’s are installed on the computer when operating system is installed. | Application software’s are installed according to user’s requirements. |
| 3. | In general, the user interacts with system software because it works in the background. | In general, the user interacts with application software’s. |
| 4. | System software can run independently. It provides platform for running application software’s. | |
| 5. | Some examples of system software’s are compiler, assembler, debugger, driver, etc. | Some examples of application software’s are word processor, web browser, media player, etc. |
Read more