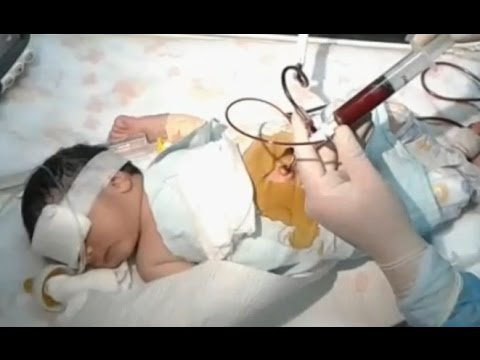
Exchange transfusion – Health of the children has been considered as the vital importance to all societies because children are the basic resource for the future of humankind. Nursing care of children is concerned for both the health of the children and for the illnesses that affect their growth and development. The increasing complexity of medical and nursing science has created a need for special area of child care, i.e. pediatric nursing.
Pediatric nursing is the specialized area of nursing practice concerning the care of children during wellness and illness. It includes preventive, promotive, curative and rehabilitative care of children. It emphasizes on all round development of body, mind and spirit of the growing individual. Thus, pediatric nursing involves in giving assistance, care and support to the growing and developing children to achieve their individual potential for functioning with fullest capacity.
Exchange transfusion
Exchange transfusion is a potentially life-saving procedure that is done to counteract the effects of serious jaundice or changes in the blood due to diseases such as sickle cell anemia. The procedure involves slowly removing the person’sblood and replacing it with fresh donor blood or plasma.
Or,
An exchange transfusion is a blood transfusion in which the patient’s blood or components of it are exchanged with (replaced by) other blood or blood products.
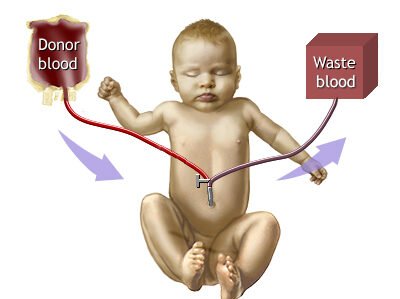
Aims and objectives of exchange blood transfusion:
- To correct anaemia.
- To remove damaged & Ab coated RBC.
- To remove unfixed Abs.
- To reduce unconjugated (toxic) bilirubin.
[Ref-Dr.Tanvir/Newborn Nursing/4]
Indications of exchange blood transfusion:
1. Birth wt. <2.5 Kg in a case with hyperbilirubinaemia or unconjugated bilirubin
- 20 mg/dl in term &
- 15-18 mg/dl in pre-term
2. H/O previous severely affected infants or stillbirth.
3. Cord Hb level < 10 gm/dl.
4. Cord bilirubin level > 5 mg/dl
5. Development of more than mild jaundice within first 24 hours (rise of bilirubin at a rate of faster than 0.5 mg/dl/hour.)
6. Clinical severe signs e,g. icterus, pallor, hepatosplenomegaly, petechiae, oedema.
7. Early signs of bilirubin encephalopathy.
8. Reticulocyte count > 15 mg/dl.
9. Maternal Ab titre is above 1 in 64
[Ref-Dr.Tanvir/Newborn Nursing/4]
Risks of an Exchange Transfusion:
As with any blood transfusion, there are some risks and side effects related to this procedure. These risks include:
1. mild allergic reactions
2. fever due to infection
3. trouble breathing
4. anxiety
5. electrolyte abnormalities
6. nausea
7. chest pains