Factors affecting vital capacity-The course is designed for the basic understanding of anatomical structures and physiological functions of human body, musculoskeletal system, digestive system, respiratory system; cardiovascular system; urinary system, endocrine system, reproductive system, nervous system, hematologic system, sensory organs, integumentary system, and immune system.The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills regarding anatomy and physiology.
Factors affecting vital capacity
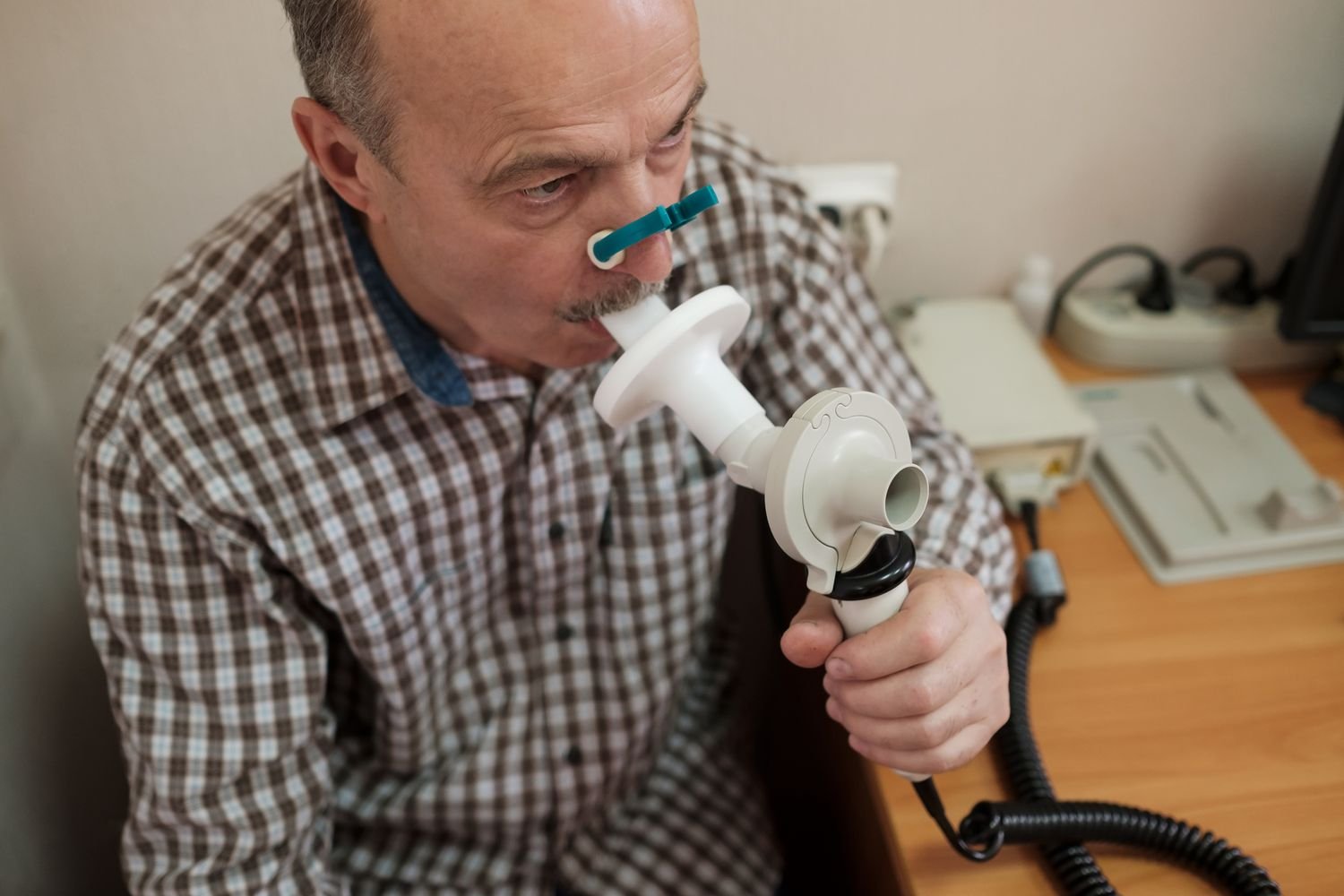
Measurement of vital capacity: Vital capacity is measured by spirometer.
Requirements:
1. Spirometer.
2. Beaker of 70% alcohol solution
Procedure:
- The mouthpiece of the spirometer is sterilized with alcohol or dettol solution. The subject should take sit comfortably and practiced exhaling through the spirometer mouthpiece (holding the nose shut with fingers); the inhalation would be through the nose. The scale of the spirometer must not be in view of the subject who engaged on reading a book
- The subject is asked to take the most forcible inspiration and then exhaled through the spirometer mouthpiece as maximum as possible. The forceful expiration must not be violent and in sudden spurts but it should be smooth. The scale is read. The procedure is repeated thrice. The average of the three readings is taken.

Factors affecting vital capacity:
Age: It is more in young and less in old age.
Sex: Vital capacity is lower in the female (20-25%) than male
Posture: In lying position it is low & is highest when seated in slightly reclined position in a chair
Physiological: In pregnancy (particularly in advanced stage) vital capacity is low
Pathological: Vital capacity is reduced in-
- Disease of the lungs e g. emphysema, fibrosis
- Disease of the pleura e g pleural effusion
- Disease of the heart e.g-congestive cardiac failure.
- Disease of the chest wall eg kyphosis,
- Disease of the abdominal wall. e.gascitis
(Ref: Concise Medical physiology, 2 ed, P-189.)
The O, carrying capacity of blood is influenced by-
- Quantity of dissolved O, in the blood.
- Blood flow to the tissue
- Cardiac output.
- Amount of Hb. in the blood.
Read more:
