Fracture of Humerus- An orthopedic nurse is a nurse who specializes in treating patients with bone, limb, or musculoskeletal disorders. Nonetheless, because orthopedics and trauma typically follow one another, head injuries and infected wounds are frequently treated by orthopedic nurses.
Ensuring that patients receive the proper pre-and post-operative care following surgery is the responsibility of an orthopedic nurse. They play a critical role in the effort to return patients to baseline before admission. Early detection of complications following surgery, including sepsis, compartment syndrome, and site infections, falls under the purview of orthopedic nurses.
Fracture of Humerus
Common sites of fracture of humerus :
1) Greater tuberosity.
2) Lesser tuberosity very rare.
3) Head.
4) Neck.
5) Shaft.
6) Supracondylar.
7) Intercondylar.
8) Epicondylar.
9) In children-there may be separation or fracture- separation of proximal or distal epiphysis.
[Ref-Dr. M.A.H.M. Jafar’s “Fracture and Dislocations” 2nd edition page-93]

Clinical features of proximal humerus fracture:
1. The patient will complain of pain and be reluctant to move the arm.
2. Again the patient may support the elbow with the contra-lateral hand.
3. Deformity may be present with associated bruising and/or fracture crepitus.
4. Impaired axillary nerve function. (Rare).
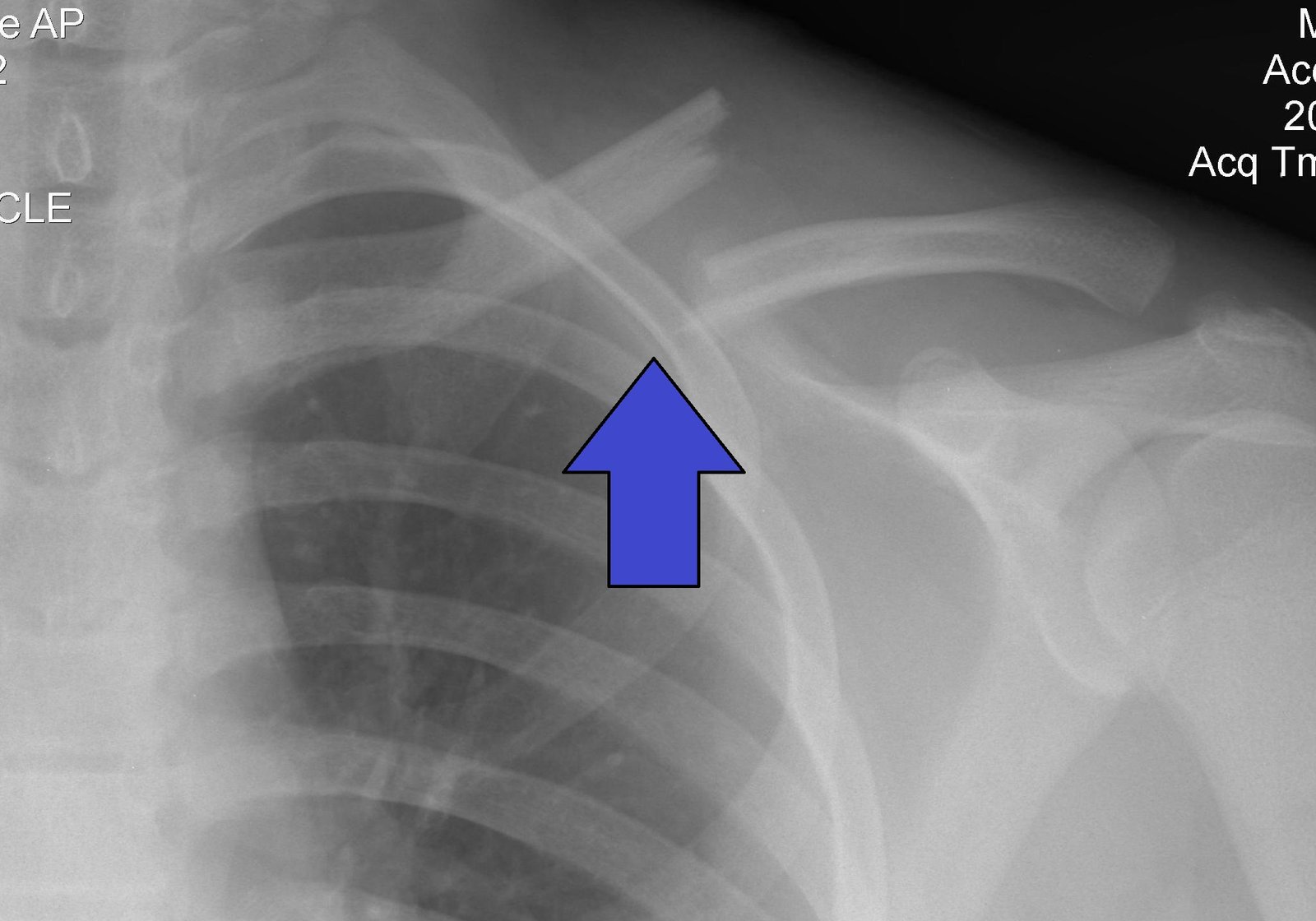
Radiological features of proximal humerus fracture:
1. AP combined with an apical oblique or a trans-lateral view is necessary to identify the fracture, but also to delineate the angulation.
2. Fracture line should be assessed according to the Neer classification.
3. A lipohaemarthrosis may be visible as a fat/fluid level inferior to the acromion process.
4. A significant haemarthrosis may displace the humeral head downwards resulting in a pseudo- subluxation.
5. Look for an associated dislocation (anterior or posterior).
Management of proximal humerus fracture:
1) ABCs.
2) With minimally displaced fractures, initial treatment consists of good analgesia and immobilization in a broad arm sling or collar and cuff. Where disimpaction is undesirable a broad arm sling is ecommended. A collar and cuff will allow gravitational correction of an angulated deformity.
3) The patient should be encouraged to mobilise with passive movements followed by more active exercises once clinical union has occurred.
4) Two, three and four part fractures with displacement should be referred to the orthopaedic team as surgical repair may be indicated.
5) Fracture dislocations (except simple dislocations with a greater tuberosity fracture) should also be discussed with the orthopaedic team. The principle of relocation followed by fracture treatment applies. Beware as forceful reduction can separate previously undisplaced fractures and thus closed reduction with X-ray screening is advised.
