Gender equity and equality – This book covers the entire syllabus of “Community Health Nursing” prescribed by the Universities of Bangladesh- for Basic and diploma nursing students. We tried to accommodate latest information and topics.
This book is examination friendly setup according to the teachers’ lectures and examination’s questions. At the end of the book previous university questions are given. We hope in touch with the book students’ knowledge will be upgraded and flourished. The unique way of presentation may make your reading of the book a pleasurable experience.
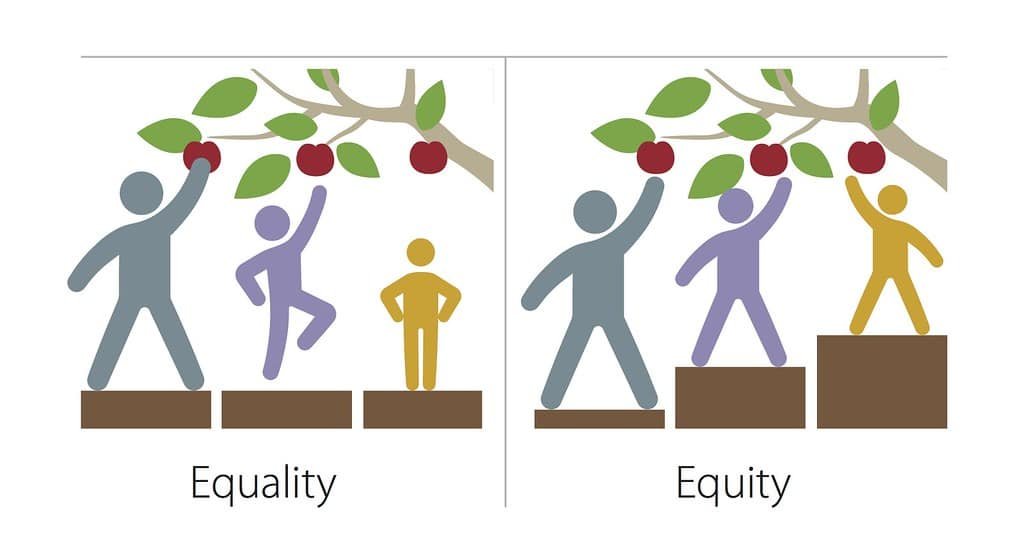
Gender equity and equality
Definition of Equity
The term equity refers to the system of justice and fairness, where there is an even-handed treatment of all the people. Under this system, the individual needs and requirements are taken into account and treated accordingly.
Equity demands fairness in every situation, i.e., whether it is the distribution of benefits or burdens. Therefore, people are treated fairly but differently as their circumstances are given weight. It seeks to provide all the individuals an equal opportunity, to let them attain their maximum potential. In this way, equity ensures that all the individuals are provided the resources they need to have access to the same opportunities, as the general population.
Or
Gender Equity
Gender Equity is the process of allocating resources, programs, and decision making fairly to both males and females without any discrimination on the basis of sex and addressing any imbalances in the benefits available to males and females.
Gender Equity is the process of allocating resources, programs and decision-making fairly to both males and females. This requires ensuring that everyone has access to a full range of opportunities to achieve the social, psychological and physical benefits that come from participating and leading in sport and physical activity.
It does not necessarily mean making the same programs and facilities available to both males and females. Gender equity requires that girls and women be provided with a full range of activity and program choices that meet their needs, interests and experiences.
Therefore, some activities may be the same as those offered to boys and men, some may be altered, and some may be altogether different. Human rights legislation, including the 1982 Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms, has affirmed the principles of equity while making provisions for affirmative action programs to eliminate disadvantages.
Gender Equity also requires an examination of organizational practices and policies that may hinder the participation of girls and women. For example, this requires service providers to assess:
- Hiring and recruitment practices to ensure women have leadership roles, and involved in decision-making, and are available as role models for other girls and women;
- Resource allocation to determine how budgets are allocated across programs;
- Facility bookings – to ensure that both females and males have access to prime time slots and prime facilities;
- Participation rates to evaluate current programs and services to identify potential barriers, and to determine whether co-ed programs are truly co-ed;
- Activity programming to assess the types of activities offered for males and females; and
- Promotional materials to ensure girls and women are not being excluded or stereotyped in pictures or language.
Positive initiatives that target specific groups are important because they take into account years of socialization and historical traditions that have created imbalances, subsequentlymarginalizing sectors of the population because these conditions are accepted as the norm.
Definition of Equalit
Equality is when everyone is treated in the same way, without giving any effect to their need and requirements. In finer terms, it is a state of getting the same quantity or value or status. It is a situation where each and every individual is granted same rights and responsibilities, irrespective of their individual differences.
Equality is the lifeline of the democratic society, that aims to prevent discrimination and provides an equal opportunity to all. It can be racial equality, equality between rich and poor, men and women, etc. The central idea of equality is that all the individuals gets equal treatment in the society and are not discriminated on the basis of race, sex, caste, creed, nationality, disability, age, religion and so forth.
Or
Gender equality, also known as sexual equality, is the state of equal ease of access to resources and opportunities regardless of gender, including economic participation and decision-making, and the state of valuing different behaviors, aspirations and needs equally, regardless of gender.
Gender equality, equality between men and women, entails the concept that all human beings, both men and women, are free to develop their personal abilities and make choices without the limitations set by stereotypes, rigid gender roles and prejudices. Gender equality means that the different behaviour, aspirations and needs of women and men are considered, valued and favoured equally.
It does not mean that women and men have to become the same, but that their rights, responsibilities and opportunities will not depend on whether they are born male or female. Gender equity means fairness of treatment for women and men, according to their respective needs. This may include equal treatment or treatment that is different but which is considered equivalent in terms of rights, benefits, obligations and opportunities.
Differences between Equity and Equality
Key Differences between Equity and Equality:
| Equity | Equality |
| Equity refers to fairness, justice and impartiality | Equality refers to equal sharing and division, keeping everyone at the same level |
| Equity Fairness and justice | Equality- Sameness |
| Equity is need based approach | Equality is not affected by the need of the people or society |
| It justifies things on the basis of quality | It justifies things on the basis of quantity |
| It focuses on need and requirement of an individual. Thus, known as need based approach | It gives same thing to all the people, irrespective of their need |
| Equity makes sure what is needed and in which quantity to an individual | Equality does not look at what is needed for an individual |
| Equity is the means/process | Equality is the outcome/end result of the process |
| Equity is subjective. It differs from situation to situation and from person to person | Equality is measurable. It does not vary and neither matter whoever looks at it |
| It identifies the differences and tries to reduce the gap between the groups | It is not concerned with the differences or gap between two or more groups |
| Equity is positive discrimination | Equality might give rise to negative discrimination |
| People are treated fairly but differently | People are treated equally but may be unfairly |
| Here, people can get what they need | Here, people will only get what everyone else gets |
| Equity cannot be achieved through equality | Equality can be achieved through equity |
| It looks everyone differently | Does not look everyone differently |
| Proper analysis of the existing situation is needed to practice equity | No such as analysis is needed is needed to practice equality |
| Equity can work even if people do not start from the same point | Equality can only work if everyone starts from the same place |
| Equity is taking a rationale and logical decision | Equality is mostly treating equally irrespective of being rationale or not |
| Example: In a family, giving different quantity of food to all the family member as per their age, level of physical activity and dietary requirement of each of them is equity | Example: In a family, giving equal quantity of food to all the family members irrespective of their requirement and need is equality |
| Example: Providing extra classes to the weak students | Example: Same classes for all the students OR extra classes for all the students irrespective of their grades |
| Example: When distributing a pair of shoes to the football players, giving a right pair of shoes as per their feet size | Example: When distributing a pair of shoes to the football players, giving a pair of shoes to all the players without any concern to their feet size |
Benefits of Gender Equity
The Benefits of Gender Equity:
Organizations have much to gain by committing themselves to achieving gender equity:
1. Attracting more girls and women to sport and physical activity enhances the revenue base and increases the market segment to which the sport appeals.
2. Fully representing the population base and tapping the resources of every member results in a larger, stronger and more effective organization.
3. Skilled women provide the organization with an important talent pool of administrators,
coaches and officials.
4. Changing the image of women in sport attracts public interest and private investment. In turn, more members are attracted to the organization.
5. Taking the lead in promoting girls and women brings prestige and support to the organization.
6. Working together, women and men can learn to build equal partnerships.
7. Providing opportunities for mothers and daughters toget involved can enhance both the chosen sport or activity, and family relationships.

8. Sport and physical activity can provide opportunities for girls to understand and respect their bodies which in turn helps them to deal with health issues such as eating disorders and smoking.
9. By fulfilling their legal responsibility to treat fairly everyone involved in the organization and making a commitment to gender equity, organizations avoid a negative public image as well as the time and expense of dealing with unnecessary lawsuits.
