Government Responsibility for Health Care – Behavioral sciences explore the cognitive processes within organisms and the behavioral interactions between organisms in the natural world. It involves the systematic analysis and investigation of human and animal behavior through the study of the past, controlled and naturalistic observation of the present and disciplined scientific experimentation and modeling.
It attempts to accomplish legitimate, objective conclusions through rigorous formulations and observation. Generally, behavior science deals primarily with human action and often seeks to generalize about human behavior as it relates to society.
Government Responsibility for Health Care
Concept Of Government
A government is the system by which a state or community is controlled. Governments are generally responsible for making and enforcing laws, managing currency, and protecting the populace from external threats, and may have other duties or privileges. Governments also typically set tax rates, and may regulate investment practices as well. Government normally consists of legislators, administrators, and arbitrators.

Government normally consists of legislators, administrators, and arbitrators. Government is the means by which state policy is enforced, as well as the mechanism for determining the policy of the state. Forms of government, or forms of state governance, refers to the set of political systems and institutions that make up the organization of a specific government.
Definition of Government
According to Abraham Lincoln
“Government of the people, by the people, for the people, shall not perish from the Earth”
Or
According to Black’s Law Dictionary
“The institutions of the government ‘regulate the relationships among members of a society and between the society and outsiders’ and that they have the authority to make decisions for the society’ to meet goals and maintain order”.
or
Government is the governing body of a nation, state, or community. The system by which a nation, state, or community is governed.
or
Government is a group of people that governs a community or unit. It sets and administers public policy and exercises executive, political and sovereign power through customs, institutions, and laws within a state.
Types of Government
There are mainly three types of government:
Autocracy –
- Monarchy
- Republicanism
- Totalitarianism
- Fascism
- Dictatorship
- Communism
Democracy –
- Parliamentary
- Presidential
Oligarchy –
- Aristocracy
- Theocracy
Forms of Government in the World with Example
Most of the world’s governments fall into one of four categories: monarchy, democracy, authoritarianism, or totalitarianism.
Monarchy
Monarchy is a political system in which a representative from one family controls the government and power is passed on through that family from generation to generation. Most of the world’s monarchies are constitutional monarchies, in which the reigning member of the royal family is the symbolic head of state but elected officials actually do the governing. Many European countries have constitutional monarchies.
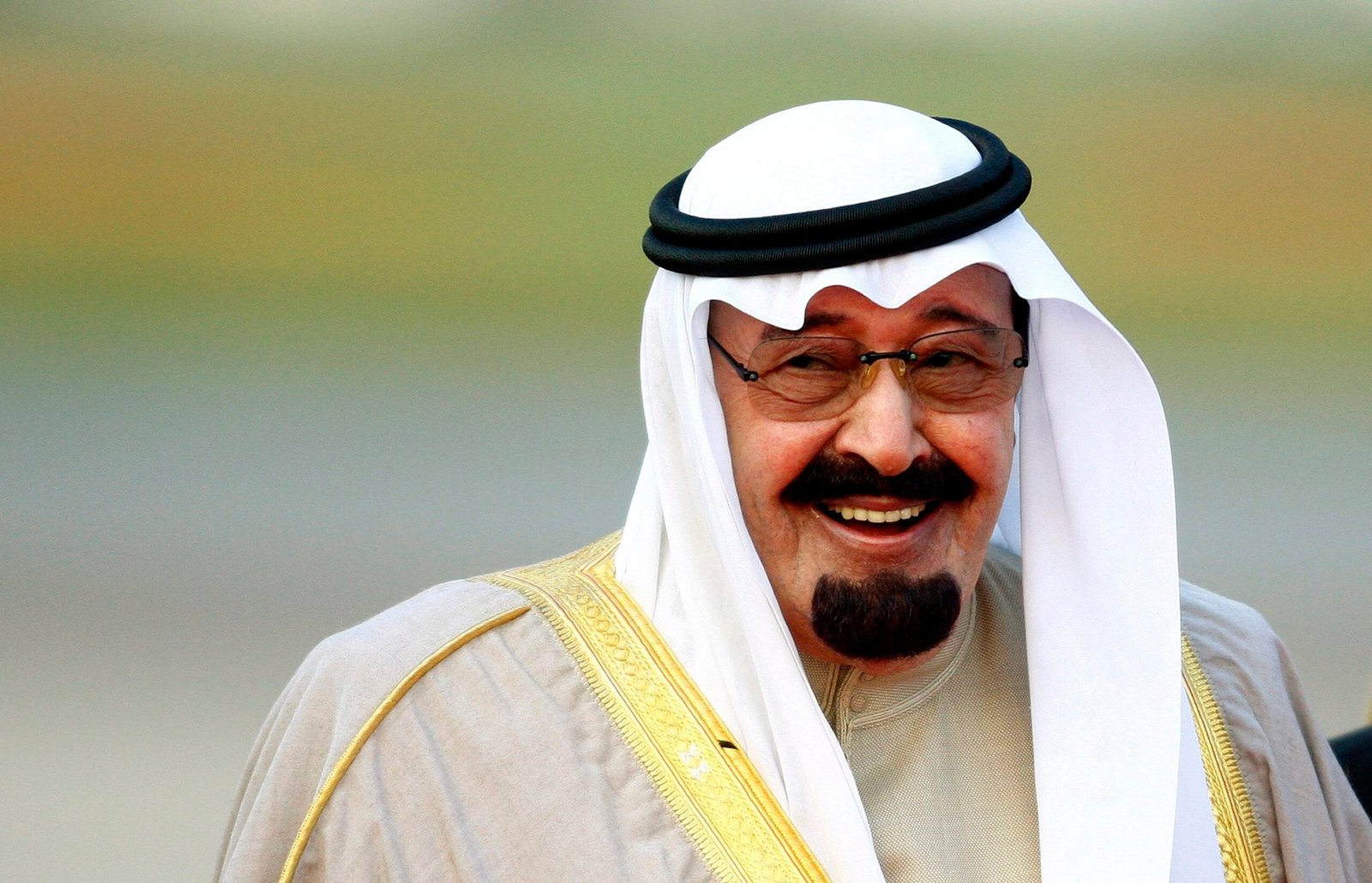

Example: Saudi Arabia is a monarchy. Until recently it was an absolute monarchy, meaning that the king had complete control of the country. The Saud royal family introduced a constitution in 1992.
Democracy
Democracy is a political system in which citizens periodically choose officials to run their government.
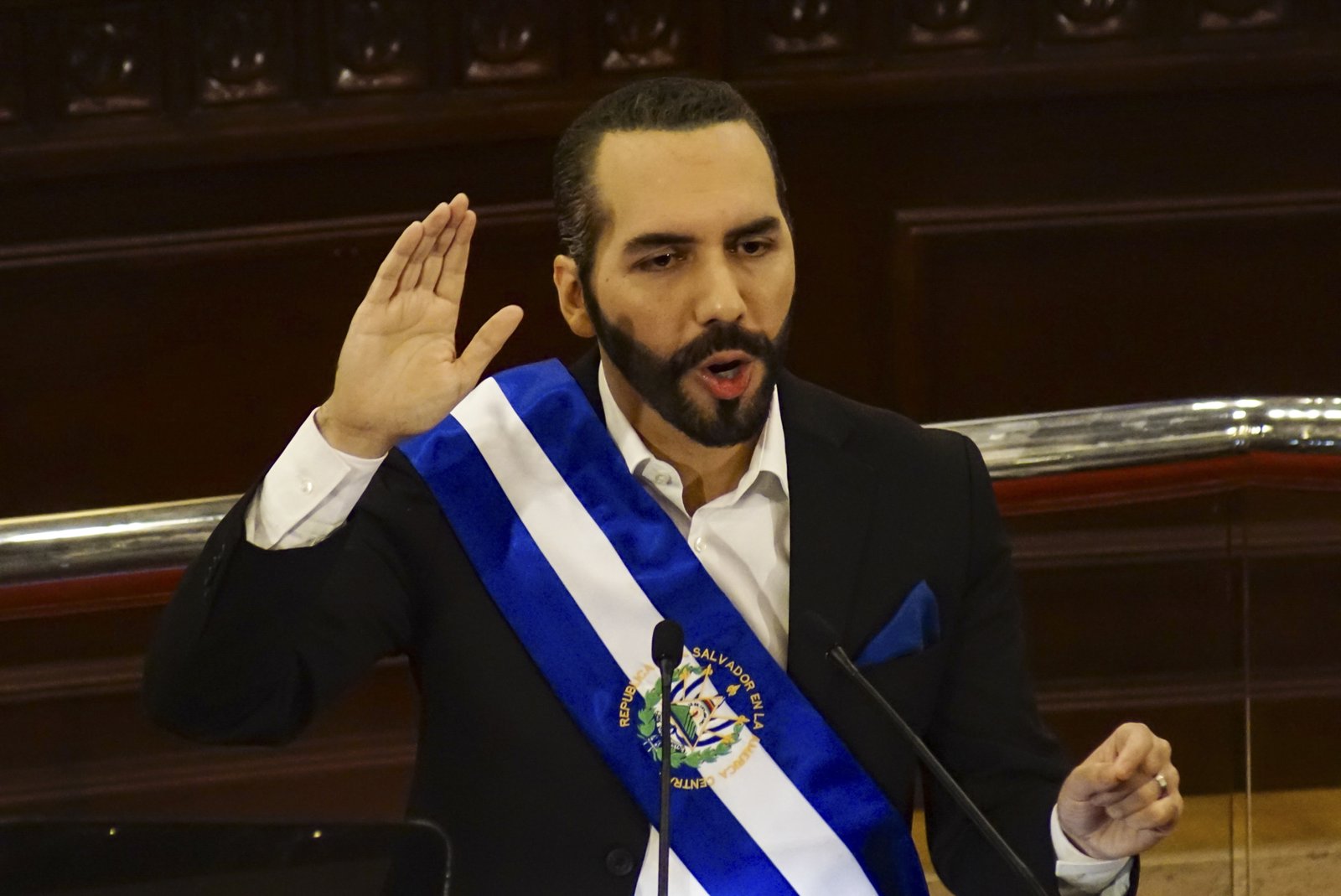

Example: El Salvador has a democratic form of government. Throughout most of the nineteenth century, El Salvador was beset by revolution and war, and from 1931 to 1979 it was ruled by military dictators. From 1980 to 1992, the country was torn apart by civil war. The country currently has a stable government and elected president.
Authoritarianism
Authoritarianism is a political system that does not allow citizens to participate in government.

Example: Zimbabwe is controlled by an authoritarian leader whose human rights violations and disastrous economic policies have brought on international condemnation. However, not all authoritarian governments are outcasts. China has an authoritarian government, but it is a member of the World Trade Organization and a major player in international politics.
Totalitarianism
Totalitarianism is a political system under which the government maintains tight control over nearly all aspects of citizens’ lives
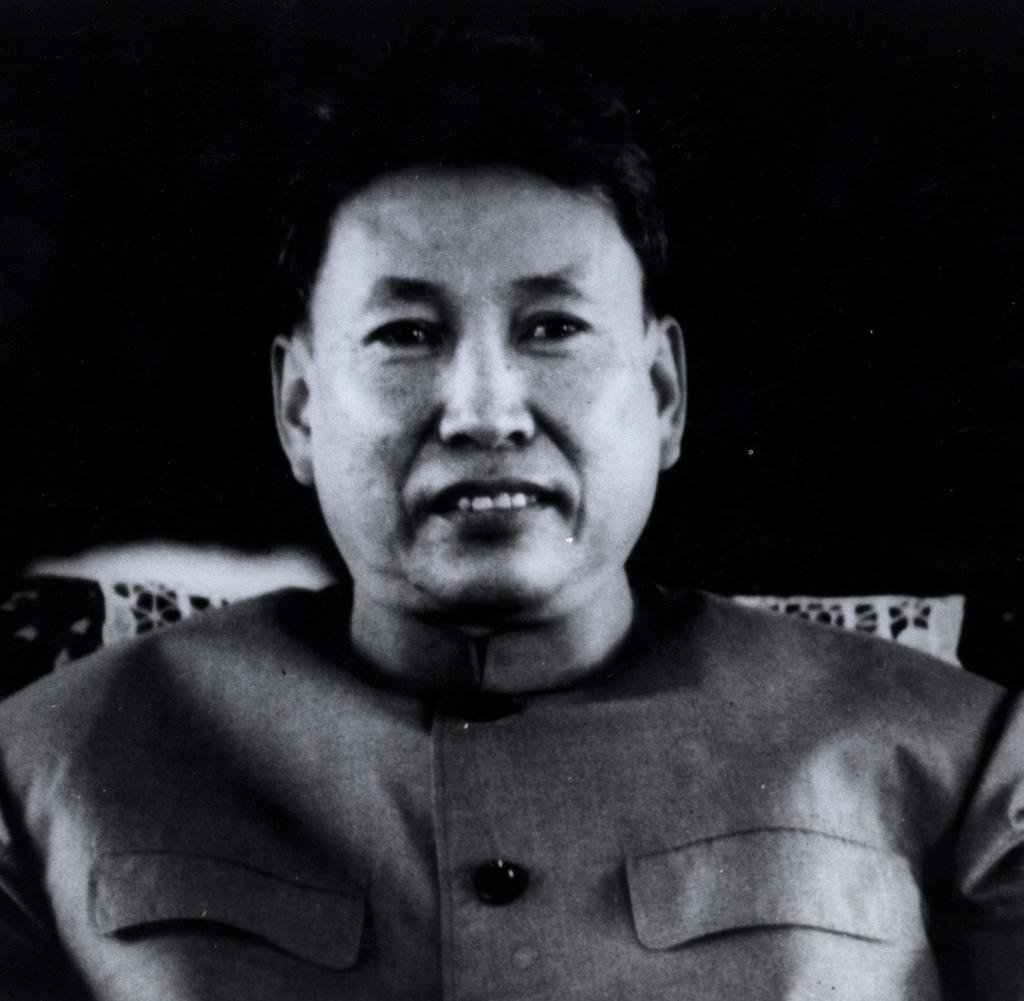

Pol Pot
Example: Cambodia under the regime of Pol Pot and the Khmer Rouge from 1976 to 1978 was totalitarian. Under the banner of socialism, Pol Pot attempted a radical reformation of Cambodia. He forced the evacuation of the country’s cities and relocated citizens to communal farms in the countryside, where they were to be “reeducated” to become part of an idealized communist agrarian society. Pol Pot’s secret police tortured and murdered over a million “dissenters,” especially those he viewed as urban intellectuals.
Functions of Government
- To form a more perfect Union – The national government will be fair across different state boundaries, helping keep the union together.
- To establish justice – The government’s responsibility is to protect those who do obey the law and punish those who do not.
- To insure domestic tranquility – In order that all may lead a tranquil and quiet life, according to their own conscience, in a godlike and dignified manner.
- To provide for the common defense – All life is held as sacred, with the protection of innocent life at the base of capital punishment. The government is to provide an army for protection from external threats.
- To promote the general welfare – Civil rulers are servants for the general good. All classes of citizens are to be represented equally by any laws the government may pass. The government may not provide or aid special interest groups above others. It is to promote, not provide, for the people.
- To secure the blessings of liberty – As stated in the Declaration of Independence, blessings are endowed upon men by their creator, not a privilege granted by government. These blessings include life, liberty, and property. Government cannot provide these, only secure them.
- Foreign Relations – Diplomacy and Defense
- Develop business strength – Incubate small business, special research and development, such as space research, job training, unemployment insurance and more.
- Protect and regulate the sustainable use of natural resources.
- Enforce and regulate fair and responsible business practices. Included in this is monitoring monetary policy, giving consumer protection and regulating banking practices.
- Determine and enforce civil laws of property and conduct. This includes the freedoms of the press, religion and rights of property.
- Provide public goods and services for the well-being of the community as a whole, such as infrastructure, vaccination programs, disaster relief, fireworks show, public parks, basic healthcare, subsidized housing, public education and public utilities.
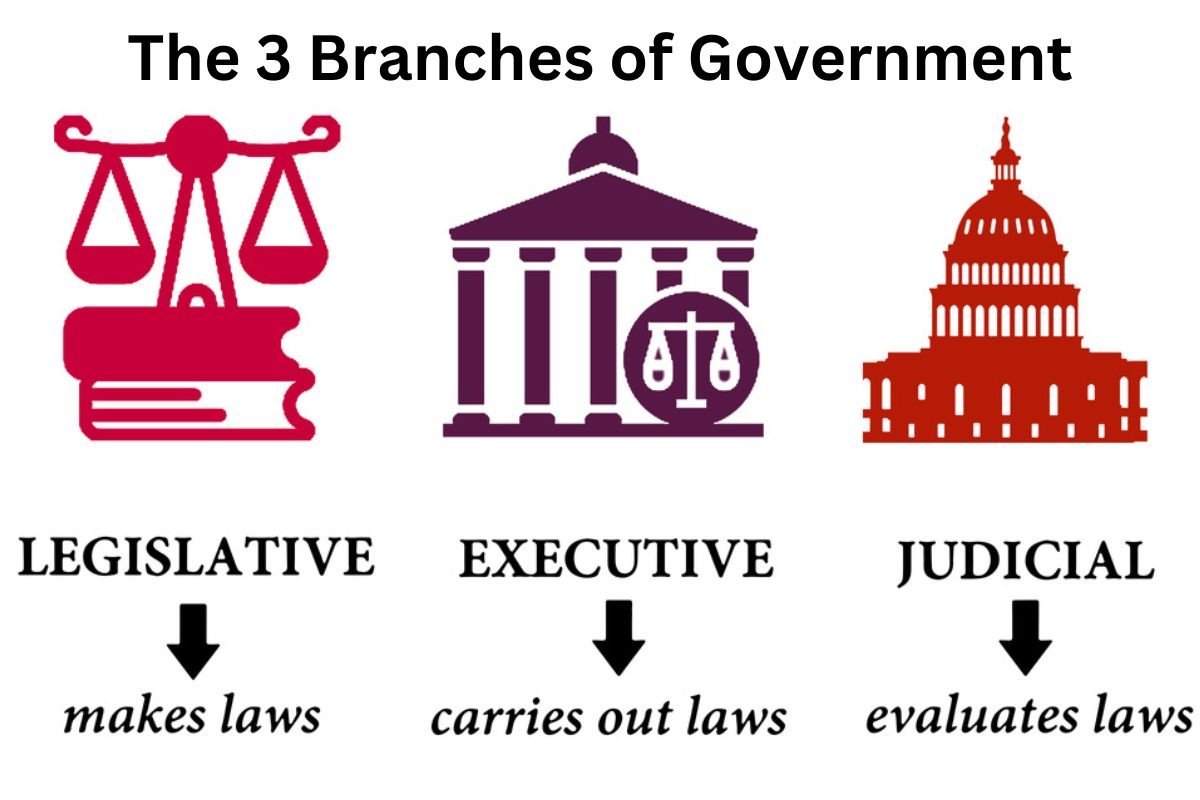
Branches/Main power of a Government
There are mainly three Branches/Main power of government
1. Legislative – Makes laws (Congress)
2. Executive – Carries out laws (President, Vice President, Cabinet)
3. Judicial-Evaluates laws (Supreme Court and Other Courts)
Legislative Branch
The legislative branch enacts legislation, confirms or rejects presidential appointments, and has the authority to declare war. This branch includes Congress (the Senate and House of Representatives) and several agencies that provide support services to Congress. The country citizens have the right to vote for senators and representatives through free, confidential ballots.
Executive Branch
The executive branch carries out and enforces laws. It includes the president, vice president, the Cabinet, executive departments, independent agencies, and other boards, commissions, and committees. The country citizens have the right to vote for the president and vice president through free, confidential ballots.
Key roles of the executive branch include:
- President The president leads the country. He/she is the head of state, leader of the federal government, and commander-in-chief of the Armed Forces. The president serves a mentioned term.
- Vice President – The vice president supports the president. If the president is unable to serve, the vice president becomes president.
- The Cabinet Cabinet members serve as advisors to the president. They include the vice president and the heads of executive departments.
Judicial Branch
The judicial branch interprets the meaning of laws, applies laws to individual cases, and decides if laws violate the Constitution. The judicial branch is comprised of the Supreme Court and other federal courts.
- Supreme Court – The Supreme Court is the highest court of a country. The justices of the Supreme Court are nominated by the president and must be approved by the
- Other Federal Courts – The Constitution grants Congress the authority to establish other federal courts.
Government of Bangladesh
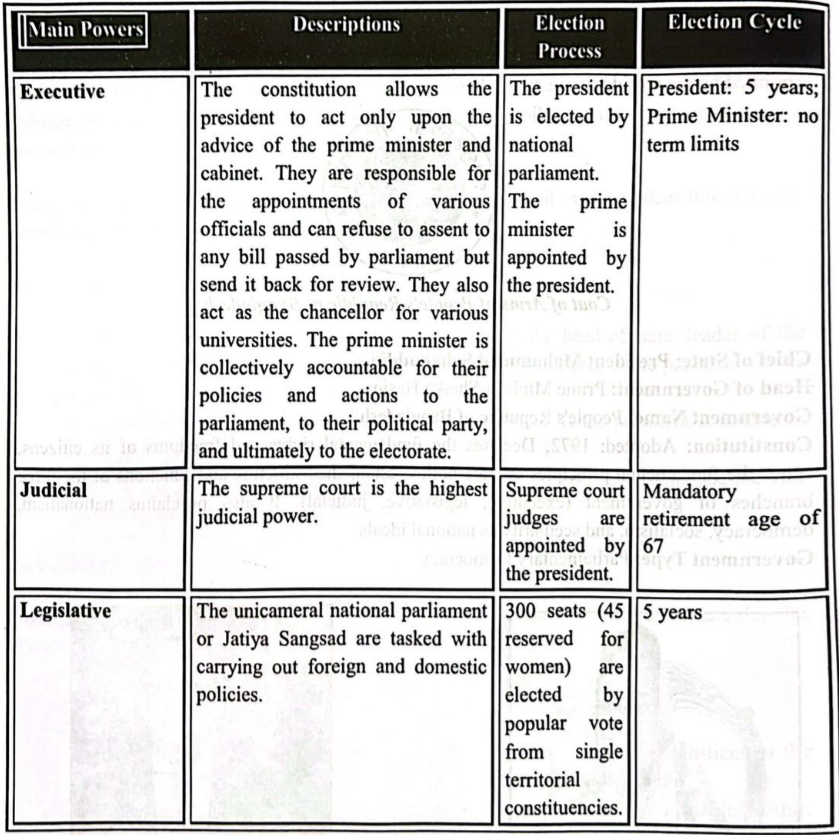
The Government of Bangladesh (Bengali: বাংলাদেশ সরকার Bangladesh Sôrkar) is led by the Prime Minister, who selects all the remaining Ministers. The Prime Minister and the other most senior Ministers belong to the supreme decision-making committee, known as the Cabinet. The President is the head of state, a largely ceremonial post. The real power is held by the Prime Minister, who is the head of government. The president is elected by the legislature every five years.
The prime minister is ceremonially appointed by the president, commanding the confidence of the majority of the MPs. The cabinet is composed of ministers selected by the prime minister and appointed by the president.

Coat of Arms of People’s Republic of Bangladesh
Chief of State: President Mohammad Sahabuddin
Head of Government: Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina
Government Name: People’s Republic of Bangladesh
Constitution: Adopted: 1972; Declares the fundamental rights and freedoms of its citizens, states the fundamental principles of state policy, establishes structure and functions of the three branches of government (executive, legislative, judicial). It also proclaims nationalism, democracy, socialism, and secularity as national ideals
Government Type: Parliamentary Democracy

President Mohammad Sahabuddin

Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina
Main power/ Branches of Bangladesh Government
There are mainly three main power of Bangladesh government
1. Executive
2. Judicial
3. Legislative
Government Responsibility for Health Care
- Leading improvement in public health
- Improving health care quality through regulations and accreditation
- Safeguarding and improving the health of underserved and at-risk populations
- Managing the delivery of health care at primary, secondary and tertiary levels
- Provide good-quality health services that are accessible and affordable to all who need them.
- Ensure policies, frameworks and standards for health and well-being are in place and acted on
- Ensure health services are well funded and run by professionals who are well trained
- Ensure roads and infrastructure are in place and in good condition so people can travel to use health and social services
- Make sure the cost of using services do not put people at risk of financial harm
- Give benefits to people who need them as this can help to protect against financial harm
- Enforce laws to protect people from violence and other unfair treatment
- Make sure people have the opportunity to be part of making decisions, such as about health services
