Congestive Heart Failure – Health of the children has been considered as the vital importance to all societies because children are the basic resource for the future of humankind. Nursing care of children is concerned for both the health of the children and for the illnesses that affect their growth and development. The increasing complexity of medical and nursing science has created a need for special area of child care, i.e. pediatric nursing.
Pediatric nursing is the specialized area of nursing practice concerning the care of children during wellness and illness. It includes preventive, promotive, curative and rehabilitative care of children. It emphasizes on all round development of body, mind and spirit of the growing individual. Thus, pediatric nursing involves in giving assistance, care and support to the growing and developing children to achieve their individual potential for functioning with fullest capacity.
Congestive Heart Failure
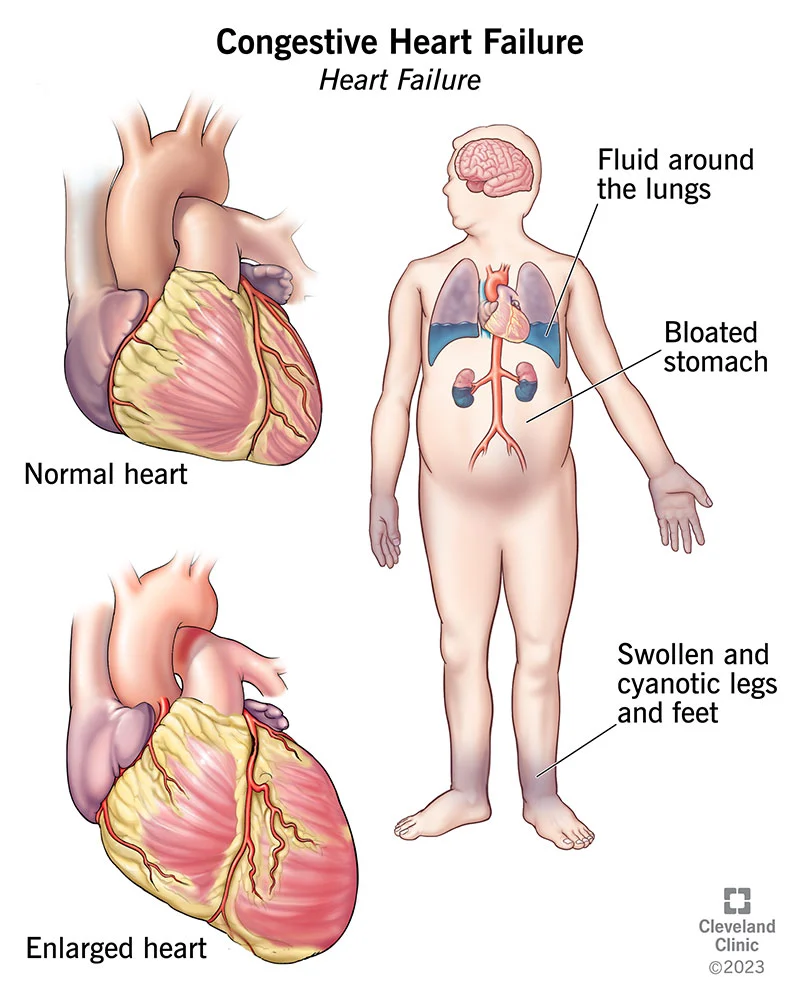
Definition of Heart Failure;
Heart failure is defined as a state in which heart cannot deliver on adequate cardiac output to meet the metabolic needs of the body.
Congestive Cardiac Failure/Congestive Heart Failure:
Congestive cardiac failure can be defined as “inability of the heart to maintain an output at rest or during stress necessary for the metabolic needs of the body (systolic failure) and inability to receive blood into the ventricular cavities at low pressure during diastole (diastolic failure).
(Ref: Paediatric Nursing, Parul Datta/3rd/310)
Causes/etiology of CCF:
A. Congenital heart disease
B. Acquired heart disease
a) Cardiac cause:
- Acute rheumatic fever
- Rheumatic heart disease
- Myocarditis
- Hypertension
- Cardiomyopathy
- Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia.
b) Non-cardiac cause:
- Chronic pulmonary disease
- Respiratory infections
- Anemia
- Nephrotic syndrome
- latrogenic fluid over load
Clinical features of CCF:
The clinical features of CCF are related to
A. Impaired myocardial functions
B. Pulmonary congestion and
C. Systemic venous congestion.
Features of impaired myocardial function:
- Tachycardia
- Poor peripheral perfusion
- Weak peripheral pulses
- Cool extremities
- Pallor
- Easy fatigability
- Excessive perspiration
- Restlessness
- Exercise or activity intolerance
Features of pulmonary congestion:
- Tachypnea
- Cyanosis
- Chest retractions
- Nasal flaring
- Grunting
- Nonproductive persistent cough
- Pulmonary edema
- Dyspnea at rest (orthopnea) or on exertion.
Features of systemic venous congestion:
- Hepatomegaly
- Peripheral edema
- Scrotal and orbital edema
- Oliguria
- Weight gain
- Nek vein distension Abdominal discomfort Anorexia
- Feeding difficulties.

Management of CCF (Congestive Cardiac Failure);
Management of the child with CCF to be done with –
- Bed rest in propped up position (45°) and restricting activities.
- Oxygen therapy is important to improve tissue oxygenation.
- Sedative should be administered to manage restlessness and to reduce anxiety.
- Digitalis is the most important drug for the management of CCF.
- It should be administered with calculated dose in stat and maintenance purpose.
- Diuretics (furosemide) is given orally or parenterally (0.5-1.5 mg/kg).
- Potassium-sparing mild diuretics (amiloride, spironolactone) is also used in a dose of 1 to 4mg/kg/day.
- Potassium supplement to be given during digitalis therapy
- Iron supplement may be needed for correction of anemia.
- Antibiotic should be given to treat co-existing infection.
- Vasodilator and ACE inhibitors can be given to reduce cardiac work.
- Diet should be planned with low salt for sodium restriction and to be given in small amount frequently.
- Correction of anemia may be done by improving iron containing food intake whenever needed.
Supportive nursing care;
- Skin care and other hygienic measures
- Prevention of infections and fluid-electrolyte imbalance
- Diet
- Administration of medications with necessary precautions
- Continuous monitoring of child’s condition
- Maintenance of intake-output and other records.
Emotional support and health teaching with necessary instructions should include –
- Dietary and activity restrictions
- Features of complications
- Drug intake
- Prevention of complications.
- Daily hygienic care
- Measures for prevention of infections and injury of edematous skin
- Need for emergency medical help
- Regular follow-up.
Common Causes of Joint Pain in Children:port the wall
- Acute Rheumatic fever
- Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
- Trauma
- Acute leukaemia
- Reactive arthritis
- Haemophilic arthritis.
Read more:
