Helicobacter Pylori – Basic microbiology, parasitology, and immunology; nature, reproduction, growth, and transmission of common microorganisms and parasites in Bangladesh; prevention including universal precaution and immunization, control, sterilization, and disinfection; and specimen collections and examination. Students will have an understanding of common organisms and parasites caused human diseases and acquire knowledge about the prevention and control of those organisms.
Helicobacter Pylori
Helicobacter pylori is the bacteria which is strongly associated with peptic ulcer disease.
Disease Caused by Helicobacter Pylori:
- Gastritis.
- Peptic ulcer disease: Duodenal ulcer & Gastric ulcer.
- Infection with H. pylori is a risk factor for gastric carcinoma.
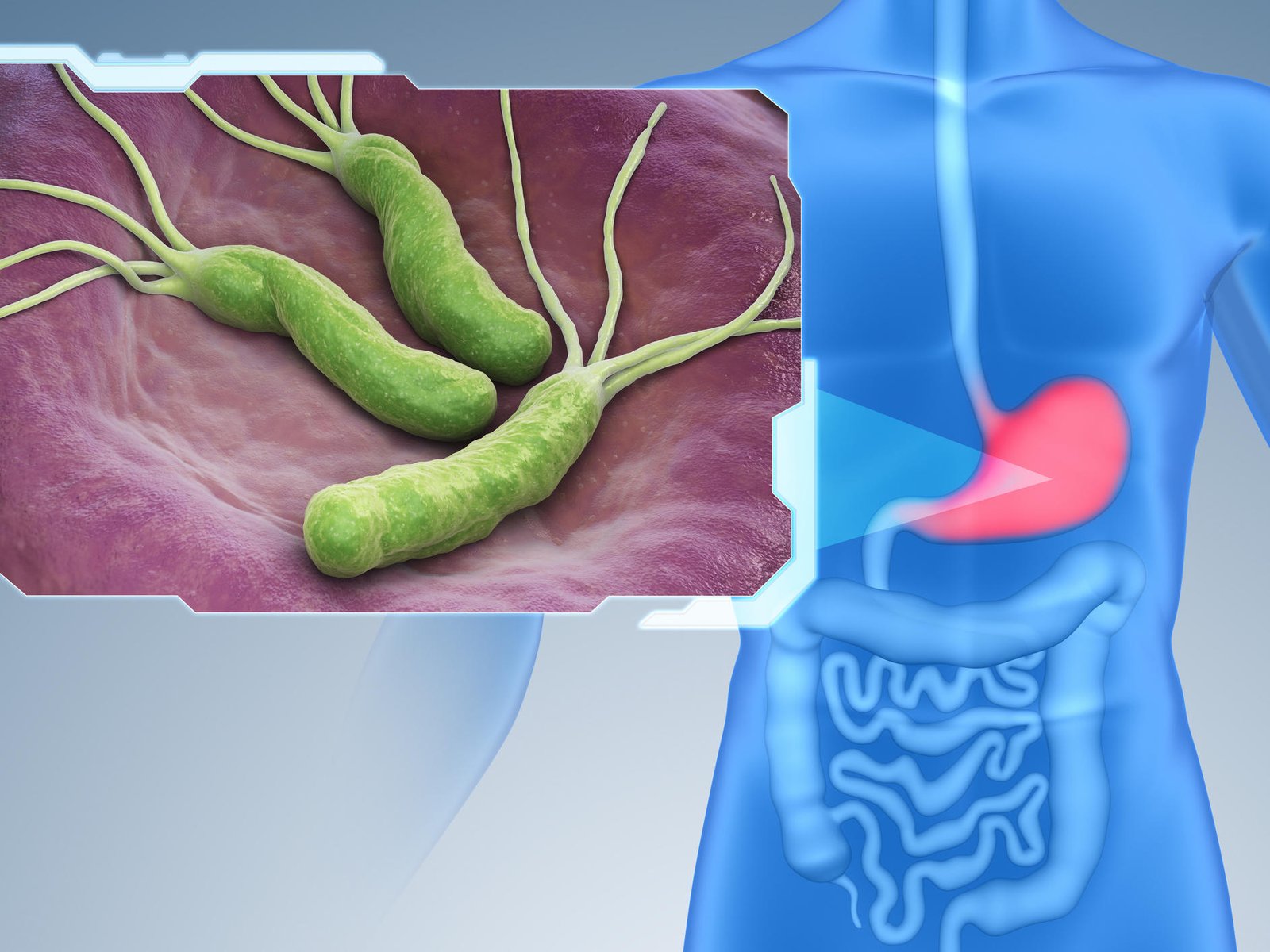
Lab. Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori:
Principle:
Diagnosis is based on demonstration of causative organism by microscopic examination and isolation & identification by bacteriological techniques. Serological tests are also helpful.
Steps:
➤ Specimen collection:
- Biopsy specimen of gastric mucosa
- Blood for serum antibodies
➤ Non-invasive tests:
- Urea breath test.
- Serological test: Ab detection
- 13C bicarbonate assay.
- Antigen detection in stool & urine.
- PCR in stool, dental plaque and water supplies
➤ Invasive tests:
- Endoscopy & biopsy.
- Rapid urease test (RUT).
- Histopathology & microscopy: Gram staining & Giemsa staining
- Culture (Skirrow’s media at 42°C).
- PCR in gastric juice
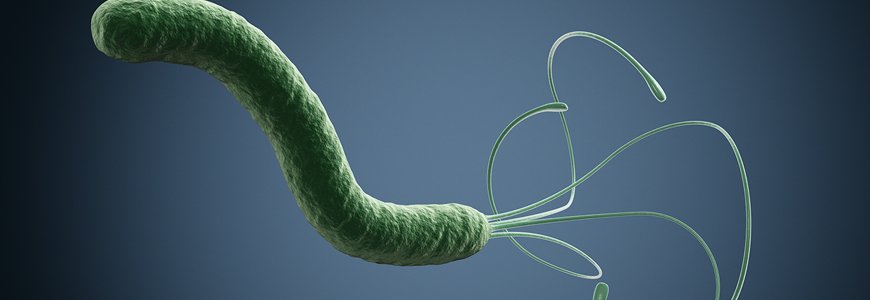
Important properties of H. pylori:
- Gram-negative
- Curved rods.
- Urease positive.
- It has multiple flagella at one pole and is actively motile
- Microaerophilic (i.e.- requires less O2 concentration for survival)
- Oxidase positive, catalase positive.
Pathogenesis of H. pylori:
Large number of H. pylori enters into the stomach
↓
Produce the enzyme urease
↓
Breakdown of urea to ammonia
↓
An alkaline media is created and therefore the bacteria escapes from the action of gastric HCI.
↓
H. pylori multiply under the mucous & produce tissue degrading enzymes
↓
Peptic ulcer disease

