Health of the children has been considered as the vital importance to all societies because children are the basic resource for the future of humankind. Nursing care of children is concerned for both the health of the children and for the illnesses that affect their growth and development. The increasing complexity of medical and nursing science has created a need for special area of child care, i.e. pediatric- nursing.
Pediatric nursing is the specialized area of nursing practice concerning the care of children during wellness and illness. It includes preventive, promotive, curative and rehabilitative care of children. It emphasizes on all round development of body, mind and spirit of the growing individual. Thus, pediatric nursing involves in giving assistance, care and support to the growing and developing children to achieve their individual potential for functioning with fullest capacity.
Hirschsprungs disease
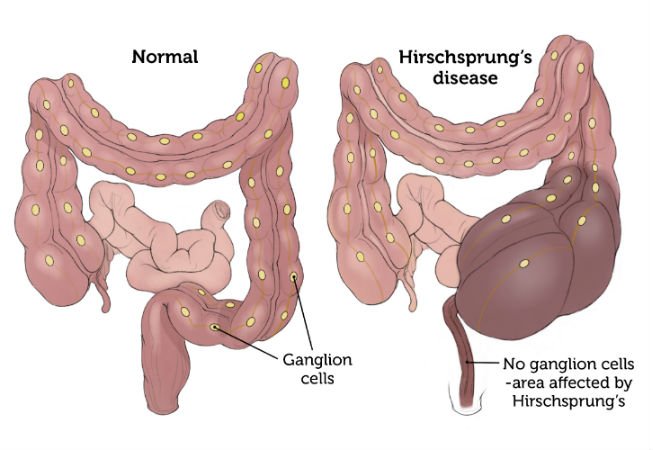
Definition of Hirschsprung’s Disease
Hirschsprung’s disease is a condition that affects the large intestine (colon) and causes problems with passing stool. The condition is present at birth (congenital) as a result of missing nerve cells in the muscles of the baby’s colon.
Or
A congenital abnormality (birth defect) of the bowel in which there is absence of the ganglia (nerves) in the wall of the bowel. Nerves are missing starting at the anus and extending a variable distance up the bowel.
Or
Hirschsprung’s disease occurs due to congenital absence of the parasympathetic ganglionic nerve cells, both in muscle layer or submucosal layer of distal colon and rectum, which result in extreme dilatation of the colon.
(Ref: Paediatric Nursing, Parul Datta/3rd/289)
Clinical Features of Hirschsprung’s Disease:
| Features in neonate; |
|
| Features in older children: |
Other features are-
|
(Ref by: Paediatric Nursing, Parul Datta/3rd/289)
Types of Hirschsprung’s Disease:
1. Short segmented or classical – 70%: Involves anus, rectum and part of sigmoid colon.
2. Ultra short segment: Involves anus, part of rectum below the pelvic floor.
3. Long segment: Aganglionosis up to proximal part of sigmoid colon
4. Total colonic aganglionosis: Absent of ganglionic cells throughout the entire large gut
Features in older children:
- Enterocolitis – serious complication occurs due to proliferation of bacteria in the colonic lumen which presents with severe toxemia.
- Abdominal distension
- Profuse watery diarrhea mixed with blood
- Vomiting
- Lethargy
- Fever
- Shock.
Other complications:
- Bowel perforation
- Intestinal obstruction
- Hydroureter or hydronephrosis
- Failure to thrive
- Multiple nutritional deficiencies
Definition of Colostomy:
Colostomy is a surgically created opening between the colon and the abdominal wall to allow fecal elimination.

Nursing Management of Colostomy Patient Suffering from Hirschsprung’s Disease:
- Prepare the parents and child (if possible) preoperatively by explanation about the colostomy, stoma characteristics and ostomy management with a pouching system.
- Determine the site of colostomy before operation by the specialist ostomy nurse.
- Prepare the child as for general abdominal surgery.
- Support the family and the patient with psychological considerations of ostomy surgery.
- Monitor the stoma color and amount of stoma discharge postoperatively at every shift.
- Record and report any abnormalities.
- Assess hydration status and prevent dehydration.
- Change the pouching system over the ostomy to avoid leakage and protect the peristomal skin. Pouching system should be properly fitted over the stoma.
- Assess the peristomal skin during change of pouching system for skin breakdown, allergy, infections, etc. and all findings to be recorded.
- Teach the parents or caregiver about routine pouch emptying (when it is 1/4 to 1/3 full), cleansing skin and stoma and change of pouching system.
- Care of the reusable bag, prevention and treatment of skin excoriation around the stoma are of primary concern.
- Demonstrate these techniques to the parents.
- Instruct the parent about the control of gas and odor of colostomy. Care during bathing and travel with attention to clothing should be informed.
- Inform the parents about increased fluid intake, diet, possible complications, necessary medical help, follow up, good hygiene, safety measures and promotion of normal growth and development of the child.
- Prepare and explain about the next definitive surgical procedures or colostomy closure as indicated. Encourage to verbalize feelings. Explain that colostomy irrigation is not a part of management in small children. It should be done only in preparation for diagnostic tests or surgery and occasionally for the treatment of constipation,
- Refer the child to ostomy support group or ostomy association, if available.
(Ref: Paediatric Nursing, Parul Datta/3/291)
