The levels of structural organization of Human body – The course is designed for the basic understanding of anatomical structures and physiological functions of human body, musculoskeletal system, digestive system, respiratory system; cardiovascular system; urinary system, endocrine system, reproductive system, nervous system, hematologic system, sensory organs, integumentary system, and immune system. The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills regarding anatomy and physiology.
The levels of structural organization of Human body
ORGANIZATIONAL LEVELS
One approach to the structural and functional study of the body is to organize the body into the following six hierarchical levels:
(1) CHEMICAL LEVEL OF ORGANIZATION
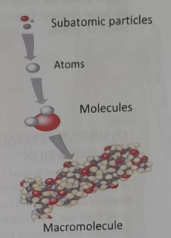
The chemical level is the lowest level of organization.
- Atoms (such as ions of sodium, potassium, calcium, etc.).
- Molecules (such as carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids, etc.), and their chemical interactions play an essential role in the structural and functional aspects of the cell.
- Macromolecule protein molecule, DNA molecule, etc
(2) CELLULAR LEVEL OF ORGANIZATION
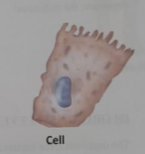
Cells are dependent upon the structural and functional aspects of their chemistry and are the building blocks of tissues. According to the cell theory, all living things are made of cells, cells are the basic units of life, and cells come only from preexisting cells.
(3) TISSUE LEVEL OF ORGANIZATION
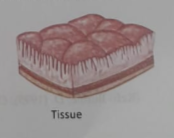
Tissues are groups of similar cells united to perform a particular function and are the building blocks of organs.
There are four fundamental groups of tissues
- Epithelial tissue,
- Connective tissue.
- Muscular tissue, and
- Nervous tissue.
(4) ORGAN LEVEL OF ORGANIZATION
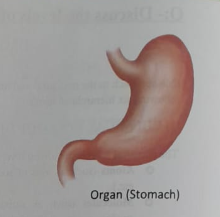
Organs are formed from the organization of several tissues that enable it to perform a particular function. Organs are the building blocks of systems
(5) ORGAN SYSTEM LEVEL OF ORGANIZATION
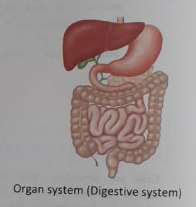
Organ systems are formed from the interaction of associated organs. Systems are the building blocks of the organism. There are eleven systems of the body that work together to form the structural and functional components of the organism, the individual
(6) ORGANISM LEVEL
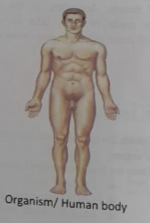
The organism is the highest level of organism and is organized from the eleven organ systems and working together to promote life (eg-The human)
(Ref:- Burnie, D(1995).ConciseEncyclopedia Human Body . London:Dorling Kindersley.)
The structural and functional study of the body is to organize the body into the following hierarchical levels:
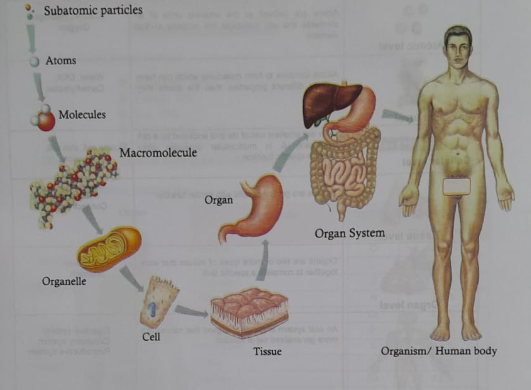
Atomic level:
Explanation: Atoms are defined as the smallest unite of an elements that still maintains the property of that element.
Example: Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen.
Molecular level:
Explanation:Atoms combine to form molecules which can have entirely different properties than the atoms they contain.
Example: Water, DNA. Carbohydrates
Cellular level:
Explanation:Cells are smallest unit of life and enclosed by a cell membrane & in multicellular organism often perform specific function.
Example: Muscle cell, skin cell, Neuron
Tissue level:
Explanation: Tissues are groups of cells with similar function.
Example: Muscle, Epithelial, Connective
Organ level:
Explanation: Organs are two or more types of tissues that work together to complete a specific task.
Example: Heart, Liver Stomach
Organ system level:
Explanation:An oral system is group of organs that carries out more generalized set of function.
Example: Digestive system, Circulatory system, Reproductive system.
Organismal level:
Explanation:An organism has several organ systems that function together.
Example: Human
