Inevitable abortion – This course is designed to understand the care of pregnant women and newborn: antenatal, intra-natal and postnatal; breast feeding, family planning, newborn care and ethical issues, The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and develop competencies regarding midwifery, complicated labour and newborn care including family planning.
Inevitable abortion
When the cervix dilates during a threatened abortion it is called inevitable abortion.
or
It is a clinical type of abortion when the changes have progressed to a state from which/ where continuation of pregnancy is not possible.
Inevitable abortion can be complete or incomplete depending on whether or not all fetal and placental tissues have been expelled from the uterus.
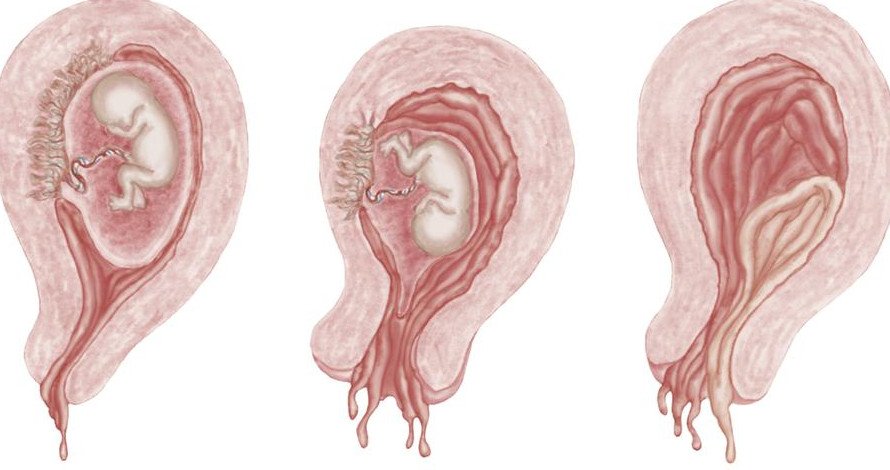
Management of Inevitable Abortion:
Symptom:
- H/O variable period of amenorrhoea.
- Heavy (sometimes intermittent) PV bleeding (with passage of clots & tissue) > threatened abortion
- Lower abdominal pain-usually severe.
- If these symptoms improve spontaneously, a complete abortion is more likely.
Signs:
- G/E: Anaemia, tachycardia. (& signs of shock may be present, if bleeding is more) Height of uterus corresponds to the period of amenorrhoea; contracted.
- P/V:
✓ Cervical os is open.
✓ Product is felt
✓ Bight blood
Investigation:
- Blood for Hb%
- Blood grouping and cross matching
- USG.
Treatment of inevitable abortion:
A. Conservative treatment:
1. Hospitalization
2. Bed rest until abortion is complete.
3. Vulva washed and prepared as for a surgical operation and kept covered with a sterile pad.
4. I/V fluid. BT-if features of shock.
5. Analgesic: Pethidine 100 mg I/M to relieve pain & anxiety.
6. Everything expelled from the uterus is examined, patient is examined vaginally after 2 weeks to see whether –
- Cervix is closed.
- Uterus is involuting normally and
- Bleeding has ceased.
B. Active treatment:
If the patient is in shock – immediate resuscitation by –
- I/V fluid.
- Analgesic & sedative: Pethidine
- Blood transfusion- If necessary (after blood grouping and cross matching)
C. Specific Rx:
1. Evaluatiion of the uterus:
a If uterus < 12 weekly size haemorrhage- D & C.
b If uterus 12 weeks size.
- Oxytocin drip to expel ouf the products completely. (IV SIU in 500 ml of 5% DA, 30- 60 drops/minute. If needed 10-15 U oxytocin can be used)
- For profuse bleeding, ergometrine/ syntometrine (each ampoule contains 5 units of oxytocin and .05 mg ergometrine) IM or IV – to control bleeding
If placenta retained: E & C (Evacuation & Curettage) under G.A
4. Broad spectrum antibiotic for prophylaxis of infection.or
5. TIG & TT should be given.
6. If the mother is Rh-ve – Inj. Anti D Ig.
Problem Based Question
Q. A 25 years old lady complaining of amenorrhoea for 4 months with lower abdominal pain and per vaginal bleeding. On examination uterus size corresponds with the period of gestation and os open. (CU-08ju)
a. What is your diagnosis?
b. What are the other clinical types of abortion?
Answer:
- Diagnosis: Inevitable abortion
- Other types of abortion: please write from above

