Definition of integumentary system and it’s functions -The course is designed for the basic understanding of anatomical structures and physiological functions of human body, musculoskeletal system, digestive system, respiratory system; cardiovascular system; urinary system, endocrine system, reproductive system, nervous system, hematologic system, sensory organs, integumentary-system, and immune system.The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills regarding anatomy and physiology.
Definition of integumentary system and it’s functions
Integumentary System
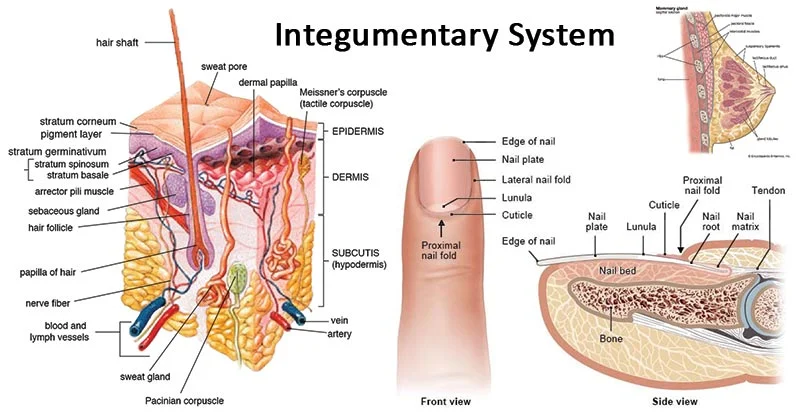
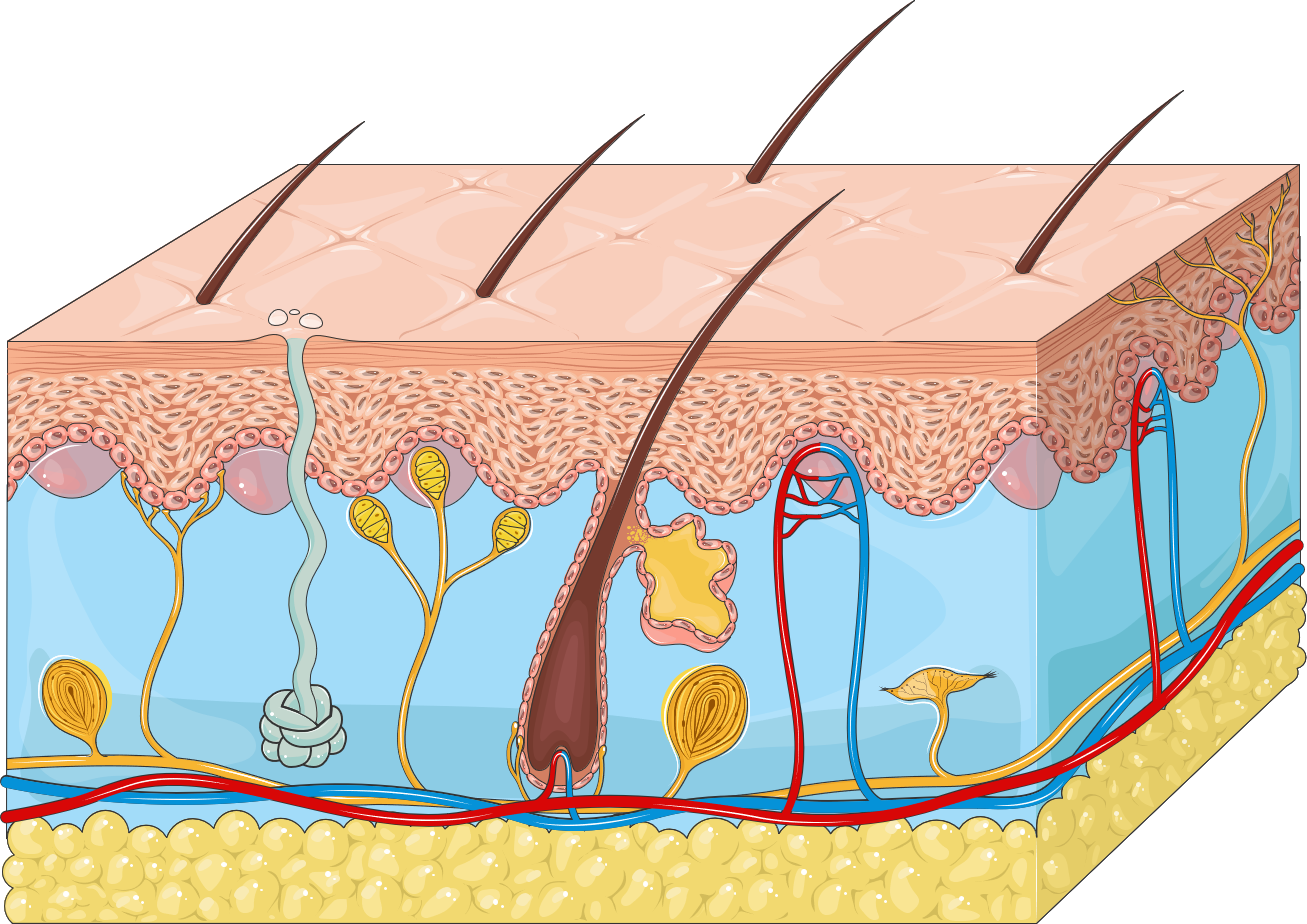
The integumentary system isthe largest organ of the body that forms a physical barrier between the external environment and the internal environment that it serves to protect and maintain. The integumentary system includes the epidermis, dermis, hypodermis, associated glands, hair, and nails.
The integumentary-system (in inward; tegere to cover) is composed of the skin, hair, oil and sweat glands, nails, and sensory receptors. The skin or cutaneous membrane covers the external surface of the body.
Components of the integumentary-system.
The integumentary-system includes the skin and its accessory structures hair, nails, and glands-along with associated muscles and nerves. The skin consists of a thin, superficial epidermis and a deep, thicker dermis. Deep to the skin is the subcutaneous layer, which attaches the dermis to underlying organs and tissues.
Functions of integumentary system
Major functions of integumentary-system are:-
- Protective function: It protects the underlying structures of body from any injury and acts as a barrier against microbial invasion.
- Sensory function: It plays an important role in the sensory perception.
- It is involved in the regulation of body temperature.
- Excretes and absorbs substances, etc.
(Ref: Ross & Wilson 9th ed. P-362+ K. Indu, 1″ edition, P-83-84)