Internal Fixations – An orthopedic nurse is a nurse who specializes in treating patients with bone, limb, or musculoskeletal disorders. Nonetheless, because orthopedics and trauma typically follow one another, head injuries and infected wounds are frequently treated by orthopedic nurses.
Ensuring that patients receive the proper pre-and post-operative care following surgery is the responsibility of an orthopedic nurse. They play a critical role in the effort to return patients to baseline before admission. Early detection of complications following surgery, including sepsis, compartment syndrome, and site infections, falls under the purview of orthopedic nurses.
Internal Fixations
Internal fixation is a method which can be used to compress two bony fragments (the technique is then called a leg screw) or a plate to the bone. When a fracture cab be -educed precisely a leg screw may be used to compress the fragments together to provide absolute stability.
[Ref-Bailey & Love’s, “Short Practice of Surgery”, 25th edition, P-363]
Or
Internal fixation is the method s of holding the bone fragment in correct position by using plate, screw and nail.
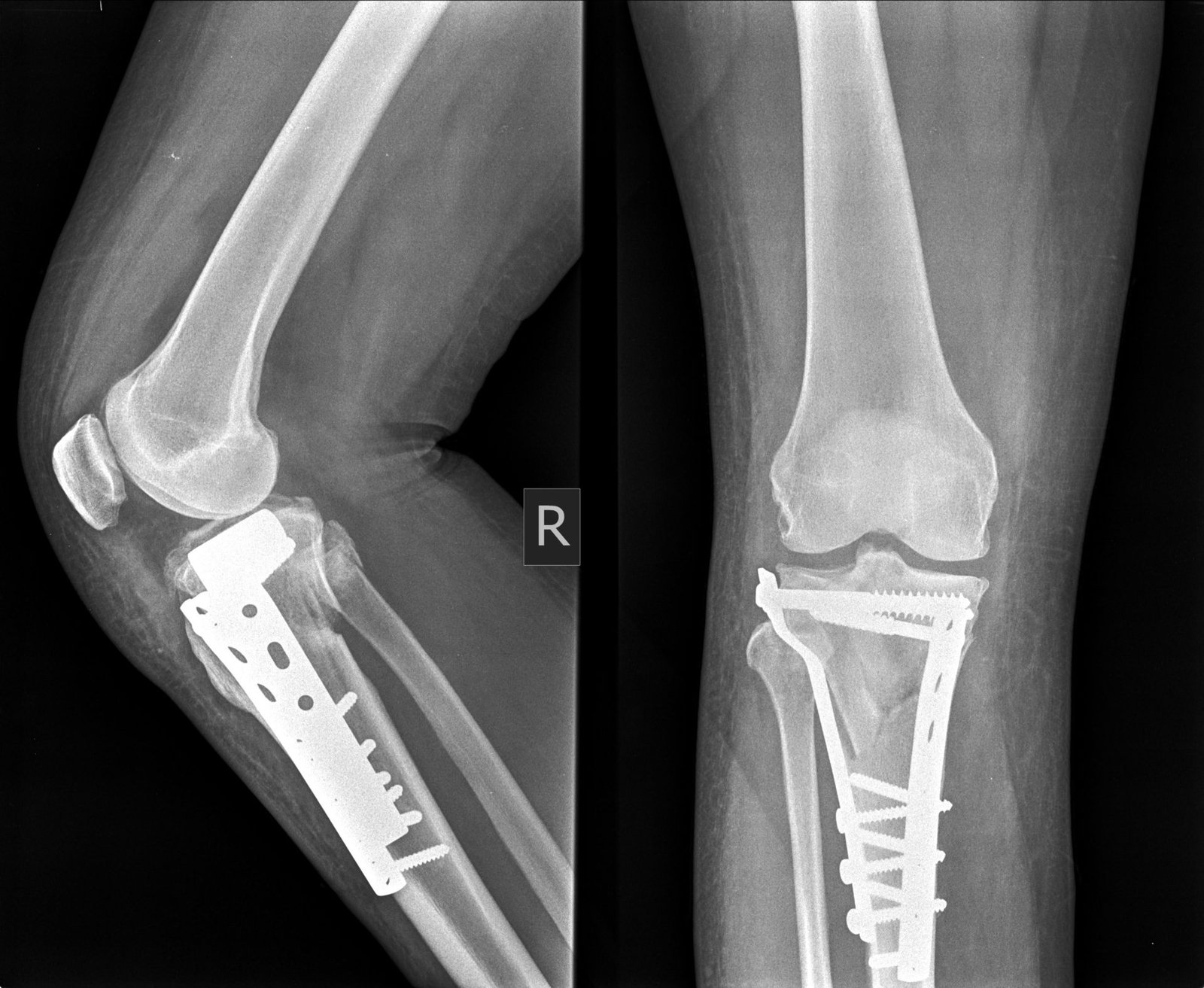
[Ref- Orthopaedic nursing and rehabilitation Marry powel, 9 edition]
Indications of internal fixation;
1) Open fractures.
2) Fractures which cannot be reduced or closed.
3) Displaced intra-articular fractures.
4) Grossly unstable, multiple fracture
5) Displaced children’s intra-articular fractures.
6) Tibial shaft fracture.
7) Head injuries.
[Ref-Bailey & Love’s, 25th edition, P-363+Adams, 11 edition,43]
Complications of internal fixation:
1. Infection: Osteomylitis.
2. Damage to the blood vessels and nerves.
3. Damage to the soft tissue.
4. Stiffness of proximal and distal joints.
5. Fat embolism.
6. Delayed union and nonunion.
[Ref-Bailey & Love’s, “Short Practice of Surgery”, 25 edition)
Methods of internal fixations:
1. Plate and screw.
2. Intramedullary nailing
3. Compression screw – plate.
4. Combined Nail and plate.
5. Transfixation screws.
6. Circumferential wires or bands.
7. Sutures through soft tissues.
Nursing care management of the person with internal fixation:
1) Pain reduction:
- Asses the level of pain with intensity, severity, and frequency.
- Keep the patients in comfortable positions
- Immobilize the limb by cast or splints.
- Avoid weight bearing activity in the operative limbs.
- Give analgesics according to doctor order
2) Improve physical mobility:
- Assist the patients in movement or getting up from bed.
- Assist the patients to turn transfer and ambulate with prescribed limits.
- Encourage the patients about active and passive movement of the joints.
- Determine in consultation with the physician, the limit of motion and weight bearing is permitted.
- Instruct the patients to use an appropriate ambulatory aid if the fracture is of a lower extremity.
3) Prevention of neurovascular problems:
- Performs neurovascular checks every hours for the first 24-48 hours.
- Notify the physician if any change from preoperative status because this may indicate pressure from swelling, constricting bandage, or damage to the nerves or vessels as surgery.
- Keep affected extremity elevated.
4) Maintain skin integrity:
- Regular observe skin on bony prominence area for pressure sores.
- Change the position 2 hourly when the patients is bed ridden.
- Give message on bony prominence to improve circulation.
5) Prevention of infections:
- Assess sign and symptoms of infection.
- Maintain area of fixation is clean and dry.
- High rich protein diet also fight against infections.
