Introduction of respiratory system-The course is designed for the basic understanding of anatomical structures and physiological functions of human body, musculoskeletal system, digestive system, respiratory system; cardiovascular system; urinary system, endocrine system, reproductive system, nervous system, hematologic system, sensory organs, integumentary system, and immune system.The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills regarding anatomy and physiology.
Introduction of respiratory system
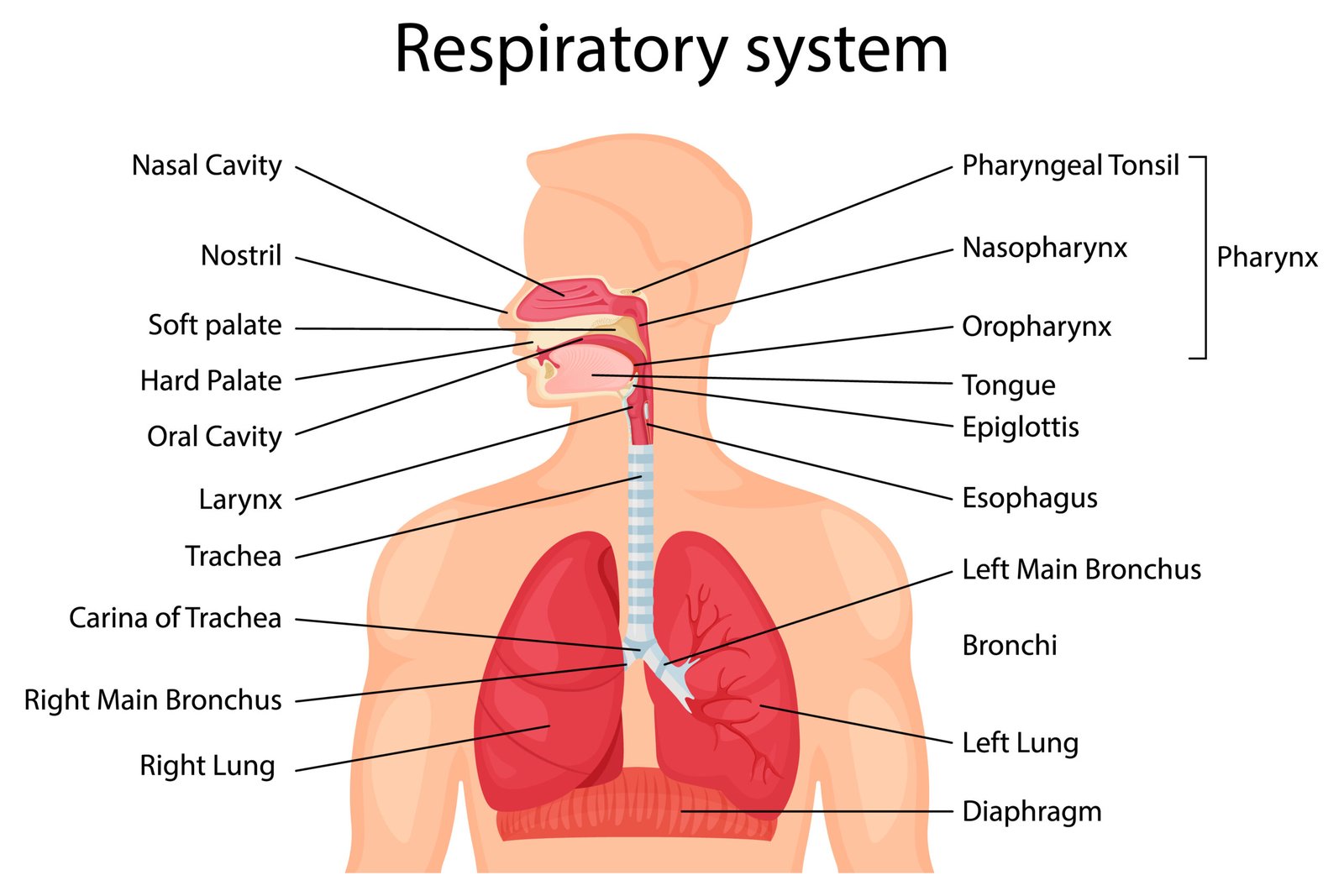
The respiratory system, which includes the nose, pharynx (throat), larynx (voice box), trachea (windpipe), bronchi, and lungs that provide for gas exchange, the intake of 02, and the removal of CO2. Structurally, the respiratory system consists of two parts.
The upper respiratory system includes the nose, pharynx, the larynx and associated structures, the lower respiratory system consists of trachea, bronchi, and lungs. The respiratory system is divided into a respiratory zone, which is the site of gas exchange between air and blood, and a conducting zone. The exchange of gases between air and blood occurs across the walls of respiratory alveoli, which permit rapid rates of gas diffusion.
Functions of the Respiratory System
- Provides for gas exchange intake of O2 for delivery to body cells and removal of CO2 produced by body cells.
- Helps to regulate blood pH.
- Contains receptors for the sense of smell,
- Filters inspired air,
- Produces sounds, and
- Excretes small amounts of water and heat.
(Ref-J. TORTORA, The essentials of anatomy and physiology, 8th edition, P-459, 460)

Three basis steps in respiration
The entire process of gas exchange in the body, called respiration, which occurs in three basic steps:
- Pulmonary ventilation, or breathing, is the flow of air into and out of the lungs.
- External respiration is the exchange of gases between the air spaces (alveoli) of the lungs and the blood in pulmonary capillaries. In this process, pulmonary capillary blood gains O2 and loses CO2
- Internal respiration is the exchange of gases between blood in systemic capillaries and tissue cells. The blood loses O2 and gains CO2. Within cells, the metabolic reactions that consume 02 and give off CO2 during the production ATP are termed cellular respiration
There are two systems are cooperating to supply O2 and eliminate CO2- the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. The first two steps are the responsibility of the respiratory-system, while the third step is a function of the cardiovascular system.
(Ref:- J. Tortora, The essentials of anatomy and physiology, 8th edition, P-460)
Organs of respiratory system

The respiratory tract divided into upper and lower respiratory tract
A. The organs of иррет годигatory tract are
- Nose
- Nasal cavity
- Pharynx
- Larynx (voice box)
B. The organs of lower respiratory tract are…
- Trachea (windpipe)
- The lungs and it’s covering, the pleura
- Bronchus (Primary, secondary, Tertiary, bronchioles, terminal bronchioles, respiratory bronchioles)
- Alveoli
- The intercostal muscles and
- Diaphragm
Read more:
