Introduction to Microscope – Basic microbiology, parasitology, and immunology; nature, reproduction, growth, and transmission of common microorganisms and parasites in Bangladesh; prevention including universal precaution and immunization, control, sterilization, and disinfection; and specimen collections and examination. Students will have an understanding of common organisms and parasites caused human diseases and acquire knowledge about the prevention and control of those organisms.
Introduction to Microscope
A microscope is an instrument used to see objects that are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Microscopy is the science of investigating small objects and structures using such an instrument. Microscopic means invisible to the eye unless aided by a microscope.
Parts of Compound Microscope:
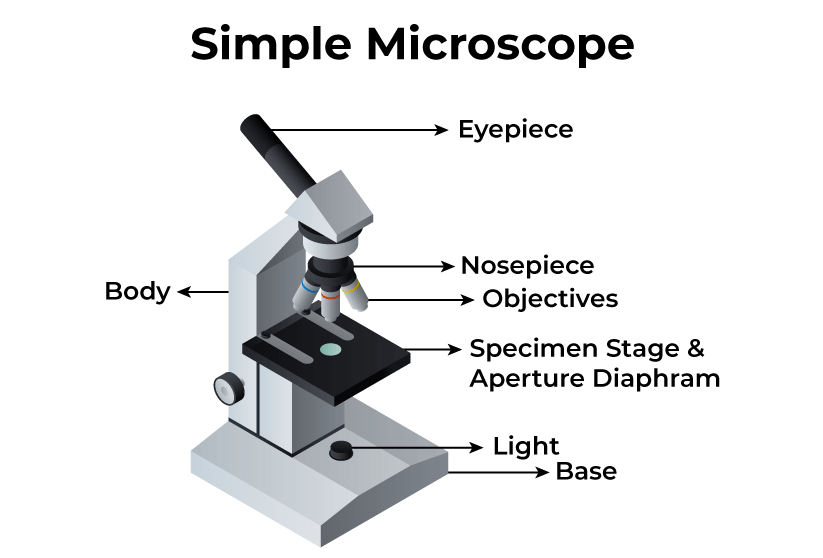
➤ Eyepiece: The lens the viewer looks through to see the specimen. The eyepiece usually contains a 10X or 15X power lens
➤ Diopter Adjustment: Useful as a means to change focus on one eyepiece so as to correct for any difference in vision between your two eyes.
➤ Body tube (Head): The body tube connects the eyepiece to the objective lenses.
➤ Arm: The arm connects the body tube to the base of the microscope.
➤ Coarse adjustment: Brings the specimen into general focus.
➤ Fine adjustment: Fine tunes the focus and increases the detail of the specimen.
➤ Nosepiece: A rotating turret that houses the objective lenses. The viewer spins the nosepiece to select different objective lenses.
➤ Stage: The flat platform where the slide is placed.
➤ Stage clips: Metal clips that hold the slide in place