Major muscles of human body – The course is designed for the basic understanding of anatomical structures and physiological functions of human body, musculoskeletal system, digestive system, respiratory system; cardiovascular system; urinary system, endocrine system, reproductive system, nervous system, hematologic system, sensory organs, integumentary system, and immune system. The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills regarding anatomy and physiology.
Major muscles of human body
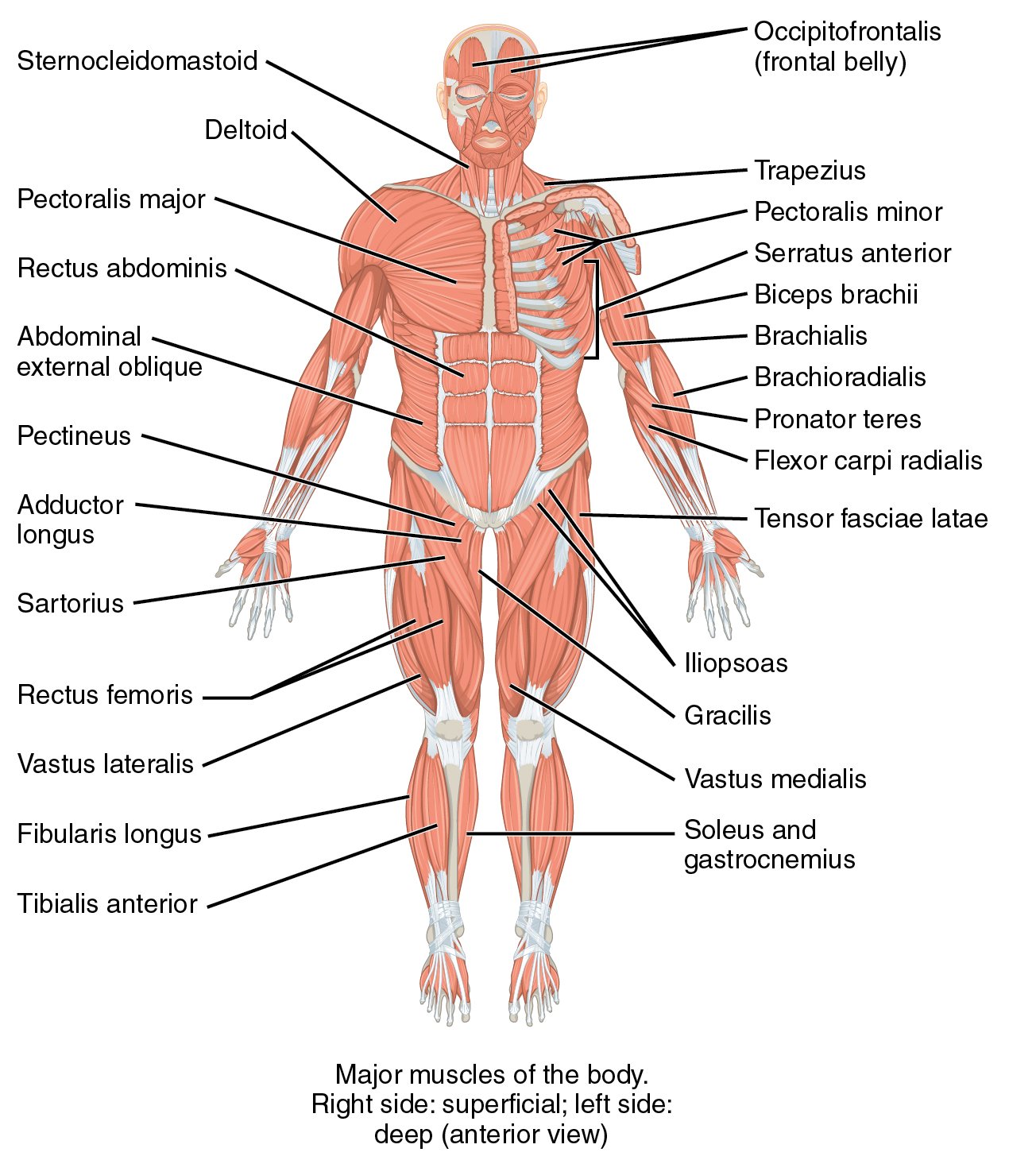
Location and function of some common and major muscles of human body:
Muscle – Location – Function
Biceps brachii – Anterior aspect of the Upper arm – Flexes the forearm
Triceps Brachii – Posterior aspect of the Upper arm – Extends the forearm
Sternocleidomastoid – Anterior aspect of the neck – Flexes the head and neck
Trapezius – Posterior aspect of the neck – Extends or hyperextendsthe head and neck
Deltoid – Covers the shoulder– Abducts the arm
Pectoralis Major – Chest – Adducts the arm
Latissimus Dorsi – Superficial muscle of the Thoracic and lumbar region Of the back – Extends a flexed arm or Hyperextend the arm from The anatomical position
Diaphragm – Internal muscle that Separates the thoracic and Abdominal cavities – Deflects the diaphragm Inferiorly increasing Volume of the thoracic Cavity
Gastrocnemius – Posterior aspect of the Lower leg – Plantar flexes the foot
Hamstring muscle Group – Posterior aspect of the Thigh – Flexes the lower leg
Quadriceps muscle Group – Anterior aspect of the thigh – Extends the lower leg
Gluteus Maximus – Buttocks region – Extends a flexed thigh or Hyperextends the thigh From the anatomical Position
Sphincter

Sphincter muscle, any of the ring like muscles surrounding and able to contract or close a bodily passage or opening. One of the most important human sphincter muscles is the sphincter pylori, a thickening of the middle layer of stomach muscle around the pylorus (opening into the small intestine) that holds food in the stomach until it is thoroughly mixed with gastric juices.
Sphincters:
Valve-like structures formed by muscles to control movement of substances in and out of passages
Example: A urethral sphincter prevents or allows urination
