Male and female gonads-The course is designed for the basic understanding of anatomical structures and physiological functions of human body, musculoskeletal system, digestive system, respiratory system; cardiovascular system; urinary system, endocrine system, reproductive system, nervous system, hematologic system, sensory organs, integumentary system, and immune system.The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills regarding anatomy and physiology.
Male and female gonads
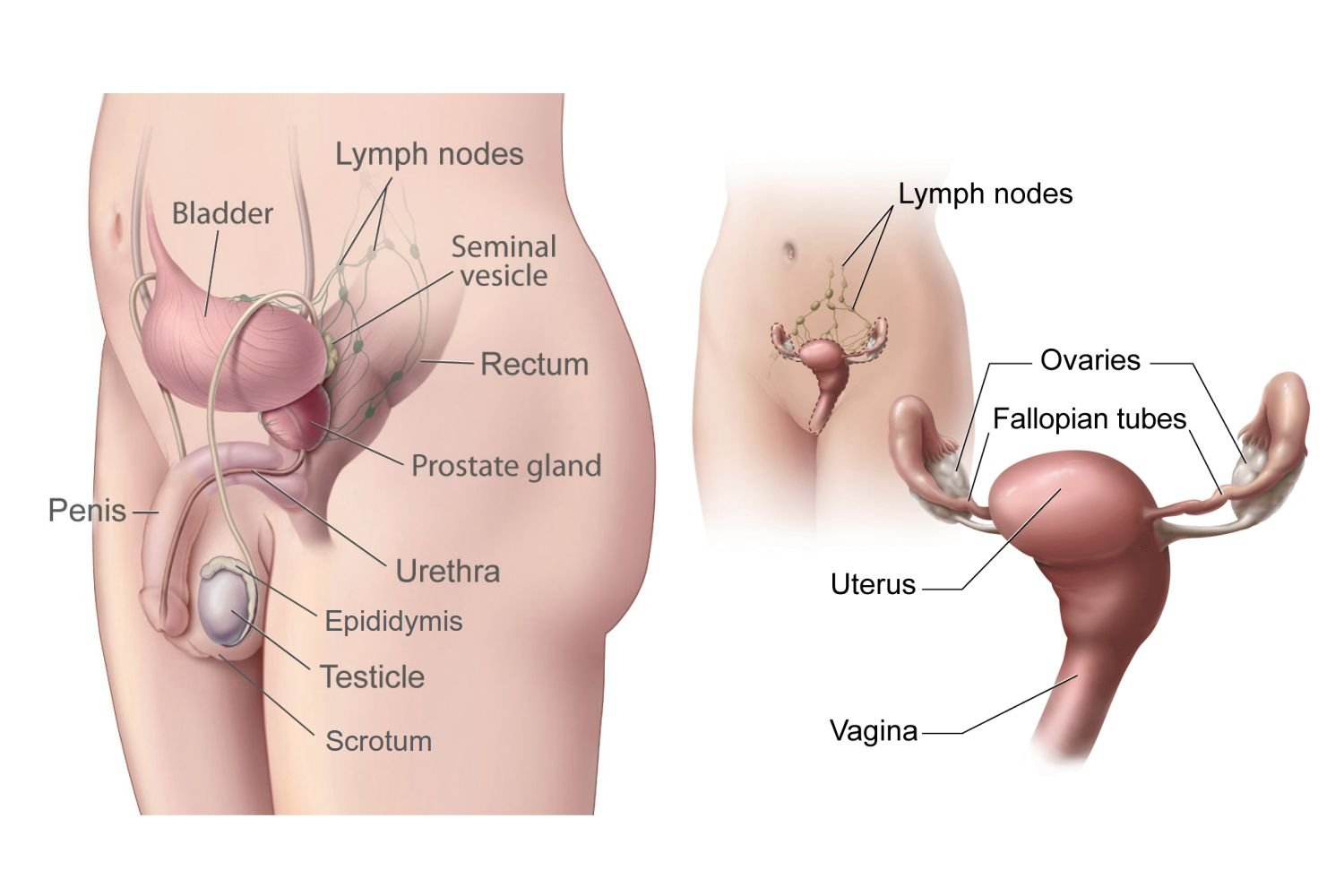
- The male gonads are two testes which produces sex hormones and the sperm
- The female gonads are two ovaries which produces sex hormones and the ova.
Hormones of male gonad (testes)
Testes secrete the following male sex hormones (androgens) as-
- Testosterone
- Dihydrotestosterone
- Androstenedione
Hormones of female gonad (ovarics)
Ovaries secrete the following female sex hormones as –
- Oestrogen
- Progesterone
Placenta
Definition :
The placenta can be defined as a discoid organ in pregnant uterus having both maternal and fetal origin which is attached to the uterine wall and establishes connection between the mother and the fetus through the umbilical cord.”
(Ref:- DC Dutta’s Obst, 7th ed, P-28)
Anatomical features:-
- Shape: Circular, dise shape.
- Size: 15-20 cm in diameter.
- Thickness:-2.5 cm at the centre but thins off towards the periphery.
- Weight: 500-600 gm (approximately).
- Covers: 30% of the uterine wall.
- Surface: Fetal surface and maternal surface.
Hormones of placenta are:
- Human chorionic gonadotropin. (HCG)
- Estrogen
- Progesterone.
- Human chorionic somatomammotropin (HCS)
- Relaxin.
- Inhibin.
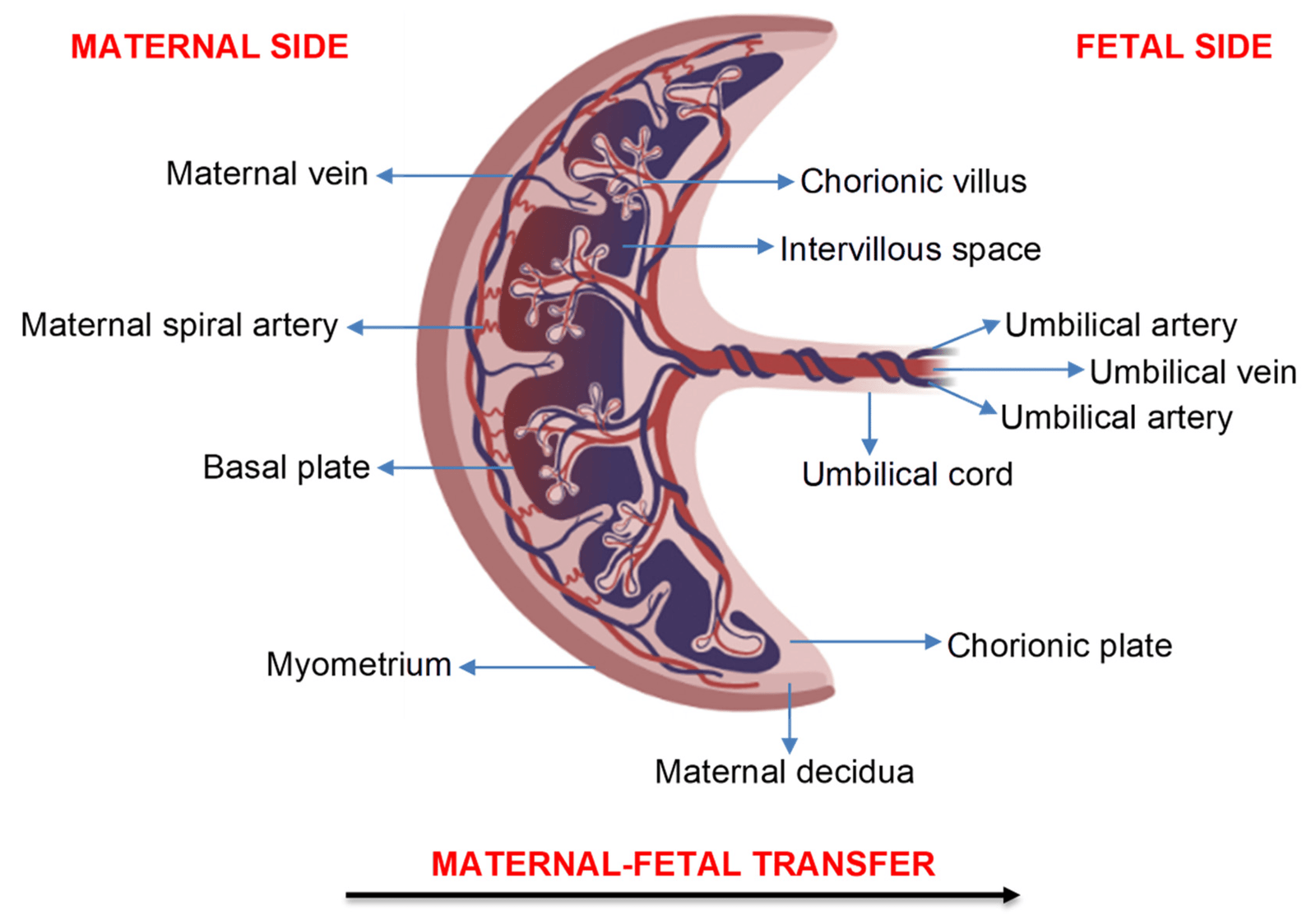
Functions of the placenta
- Provide foodstuff’s from the mother’s blood into the fetus’s blood by diffusion.
- Carry waste product from the fetus back into the mother’s blood by diffusion. Thus it acts like a kidney.
- Exchange of 02& CO2 between mother and fetus. Thus it acts like a lung
- Acts as a barner for certain harmful substance.
- Produce many hormones vital to the pregnancy, eg estrogen, HCG, HCS etc.
(Ref: DC Dutta’s Obst, 7th ed + Guyton & Hall, 12th ed. P-1005).