Midwifery For Diploma In Nursing – This course is designed to understand the care of pregnant women and newborn: antenatal, intra-natal and postnatal; breast feeding, family planning, newborn care and ethical issues, The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and develop competencies regarding midwifery, complicated labour and newborn care including family planning.
Midwifery For Diploma In Nursing
Chapter 01: Introduction to Midwifery
- Introduction to midwifery
- Epidemiology of maternal and newborn health in Bangladesh
- High risk pregnancy
- Infant mortality rate (IMR)
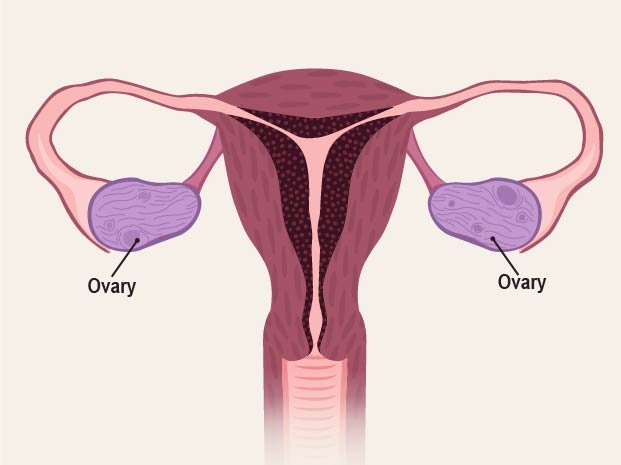
Chapter 02: Anatomy and physiology of reproductive system
- Male and female Reproductive organs
- Uterus
- Menstruation
- Fertilization and implantation.
- Embryo and fetus
- Amniotic fluid
- Umbilical cord
- Placenta
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Female pelvis
- Fetal skull
Chapter 03: Physiological, Psychosocial, spiritual changes and adaptations during pregnancy
- Changes in pregnancy
- Adaptation during pregnancy
Chapter 04: Nutrition during Pregnancy
- Nutrition during pregnancy
Chapter 05: Health Promotion and Health Education in Midwifery
- Health promotion
- Childbirth preparation
- Breast Feeding
Chapter 06: Antenatal Assessment of Women’s Physical Conditions
- Initial Antenatal Visit
- Nutritional status of woman
- Antenatal History Format
- Routine antenatal tests
- Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
- Ultrasound in pregnancy
- Antenatal vital sign assessment
Chapter 07: Care and management during the antenatal period
- Antenatal Care (ANC)
- Antenatal visits
- Intranatal Care
- Postnatal Care
- Maternal & child health
- Decision points
- Preparation for Parenthood
- Safe Motherhood
Chapter 08: Introduction to Abnormal Obstetrics
- Abnormal obstetrics
- Risk assessment of pregnant women
- EOC (Emergency obstetric care)
Chapter 09: Care of pregnant women with abnormal obstetric complications
- Teenage Pregnancy
- Grand Multiparity
- Elderly Primigravida
- Multiple Pregnancy
- Polyhydramnios
- Oligohydramnios
- Hyperemesis Gravidarum
- Anaemiain Pregnancy
- Iron-Deficiency Anemia
- Ectopic Pregnancy
- Tubal Pregnancy
- Placenta Praevia
- Thalassemia

Chapter 10: Care of pregnant women with medical complications
- Heart disease in pregnancy
- Pregnancy induced hypertension
- Pre-eclampsia
- Eclampsia
- Impending eclampsia
- Pregnancy induced hypertension
Chapter 11: Bleeding in early and late pregnancy
- Abortion
- Ante-Partum Haemorrhage
- Abruptio Placenta
- Placenta Praevia
Chapter 12: Care of pregnant women with medical complications
- Hepatitis
- Rubella
- Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs)
- Syphilis
- Gonorrhea
- HIV-AIDS
- Hyperthyroidism
- Hypothyroidism
- Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
- Respiratory Disease
- Asthma In Pregnancy
- Tuberculosis
- Cardiovascular Disease In Pregnancy
- Weight Gain In Pregnancy
- Jaundice In Pregnancy
- Abdominal Pain In Pregnancy

Chapter 13: Labour
- Concept Of Labour
- First Stage Of Labor
- Second Stage Of Labor
- Third Stage Of Labor
- Partograph
- Obstructed Labour
Chapter 14: Emergency Obstetric and Neonatal Care (EmNOC) and life-threatening situations
&
Referral system of Bangladesh health care facilities
- Emergency Obstretic Care (EOC)
- Emergency Neonatal Care (ENC)
- Warm Chain
- Health Care Delivery System in Bangladesh
Chapter 15: Induction of Labour
- Induction of Labour
- Surgical Induction of Labour
- Oxytocin
- Ergometrine
- Prostaglandin
Chapter 16: Operative obstetrics
- Obstetric operations
- Episiotomy
- Instrumental deliveries
- Vacuum extraction/ventouse delivery
- Caesarean section
- Destructive operations
- Version
Chapter 17: Nursing care for high risk pregnancy
- Preterm Labour
- Premature Rupture Of Membrane (PROM)
- Post Term Labor
- Cord Prolapse
- Precipitate Labor
- Prolong labour
- Obstructed Labour
- Rupture Uterus
- Genital Prolapse
- Hydatidiform Mole
- Uterine Inversion
- Cervical Incompetence
- Shoulder dystocia
Chapter 18: Postpartum care
- Post-Partum Hemorrhage (PPH)
- Retained Placenta
- Puerperal Sepsis
- Involution Of Uterus
- Birth Injuries
- Rupture Of The Uterus
- Cervical And Perineal Tear
- Postpartum Infection
- Mastitis
- Obstetric Shocker
- Postpartum Depression
- Postpartum Psychosis
- Postpartum Baby Blues
- Abruptio placenta
- V.V.F
Chapter 19: Postpartum physiological and psychologicalchanges
- Postpartum physiological and psychological changes
Chapter 20: Care of mother and newborn during postpartum period
- Postnatal care (PNC)
- Postpartum Assessments of a women
- Attachment and positioning
Chapter 21: Health assessment of newborn
- Assessment
- Newborn health assessment
- APGAR score
- Physical examination of newborn
- Behavioral assessment
Chapter 22: Management of high risk conditions at birth
- High risk newborn
- Low birth weight (LBW)
- Preterm / premature newborn
- Birth asphyxia/ Neonatal asphyxia
- Respiratory support
- Hydration
- Nutrition
Chapter 23: Nursing care of newborn with congenital anomalies
- Medical genetics
- Congenital anomalies
- Cleft lip and cleft palate
- Esophageal atresia/tracheoesophageal fistula
- Gastroschisis
- Anorectal malformation/Imperforated anus mean
- Spina bifida
- Meningocelt/myelomeningocele
- Omphalocele
- Hydrocephalus
Chapter 24: Nursing care of newborn with abnormal condition at birth
- Common health problems of newborn
- Hyperbilirubinemia/jaundice
- Physiological jaundice
- Pathological jaundice
- Phototherapy
- Exchange transfusion
- Hemolytic disease of the newborn
- Respiratory distress syndrome (RDS)
- Neonatal convulsion/seizure
- Common infections of neonate
- Neonatal sepsis
- Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC)
Chapter 25: Birth Injury
- Birth injury
- Caput succedaneum & Cephalohematoma
- Subconjunctival hemorrhage
- Brachial plexus palsy or Erb’s palsy
Chapter 26: Family planning
- Family planning
- Contraception
- OCP (Oral contraceptive pill)
- Condom
- Intrauterine contraceptive device
- Norplant
- Emergency contraception.
- Safe period
- Female sterilization
- MR (menstrual regulation)
- Vasectomy
- Tubectomy
Chapter 27: Post Abortion Care (PAC)
- Abortion
- Incomplete abortion
- Complete abortion
- Septic abortion
- Missed abortion
- Spontaneous abortion
- Habitual abortion
- Inevitable abortion
- Threatened abortion
