Mitosis and Meiosis cell division – The course is designed for the basic understanding of anatomical structures and physiological functions of human body, musculoskeletal system, digestive system, respiratory system; cardiovascular system; urinary system, endocrine system, reproductive system, nervous system, hematologic system, sensory organs, integumentary system, and immune system. The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills regarding anatomy and physiology.
Mitosis and Meiosis cell division
| Mitosis | Meiosis | |
| Definition: | A process of reproduction in which the cell divides in two producing a replica, with an equal number of chromosomes in each resulting diploid cell | A type of cellular reproduction in which the number of chromosomes are reduced by half through the separation of homologous chromosomes, producing two haploid cells. |
| Function: | Cellular Reproduction & general growth and repair of the body | Sexual reproduction |
| Occurs in: | Occurs when somatic (body) cells divide. Example of somatic cells are skin, liver, stomach, etc | Occurs only in germ cells that produce sex cells (egg & sperm). Sex cells are called gametes. |
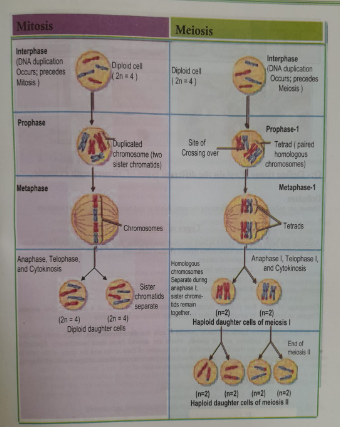
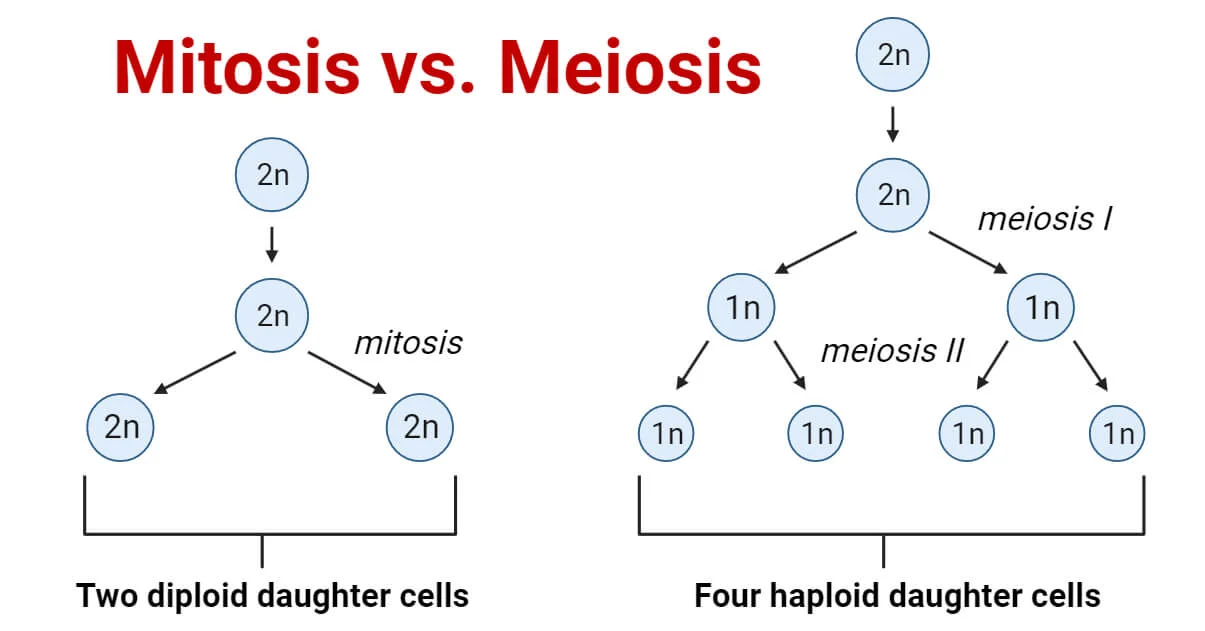
| Number of Divisions: | 1 cell division | 2 cell division |
| Number of Daughter Cells produced: | 2 diploid cells | 4 haploid cells |
| Chromosome Number: | Remains the same | Reduced by half |
| Steps: | The steps of mitosis are Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase and Cytokinesis | The steps of meiosis are Interphase, Prophase 1, Metaphase I, Anaphase I, Telophase 1, Prophase II, Metaphase II. Anaphase II and Telophase II. |
| Discovered by: | Walther Flemming | Oscar Hertwig |
As body cells become damaged, diseased, or worn out, they are replaced by cell division, the process whereby cells reproduce themselves.
There are two distinct type of cell division as-
- Meiosis or Reproductive cell division: Reproductive cell division or meiosis is the process that produces gametes (sex cell), sperm and oocytes the cells needed to form the next generation of sexually reproducing organisms. Sex cells are called gametes. Female gamete egg which produce in the ovary and Male gamete = sperm which produce in the testes.
- Mitosis: All body cells, except the gametes, are called somatic cells. In somatic cell division, a cell divides into two identical cells. After somatic cell division, each newly formed cell has the same number of chromosomes as the original cell. Somatic cell division replaces dead or injured cells and adds new ones for tissue growth. For example, skin cells are continually replaced by somatic cell divisions.
(Ref:- J. TORTORA, 8th edition, P-63, 64+ Stuart Ira Fox, Human physiology. 12th ed, P-76, 77, 78).
Mitosis 1: replication, 1 division = 2 genetically identical cells.
Interphase → Mitosis (Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase)→Cytokinesis
Meiosis:- I replication, 2 divisions (Meiosis-I & Meiosis-II) = 4 but not genetically identical cells.
1″ Division
Interphase-1 Meiosis-I (Prophase-I, Metaphase-I, Anaphase-I, Telophase-I) partial
2nd Division
NO Interphase-II (because no replication)-Meiosis-II (Prophase-II, Metaphase-II, Anaphase- II, Telophase-II Full Cytokinesis and differentiation into sperm or egg/polar bodies.