Mouth cavity- The course is designed for the basic understanding of anatomical structures and physiological functions of human body, musculoskeletal system, digestive system, respiratory system; cardiovascular system; urinary system, endocrine system, reproductive system, nervous system, hematologic system, sensory organs, integumentary system, and immune system.The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills regarding anatomy and physiology.
Mouth cavity
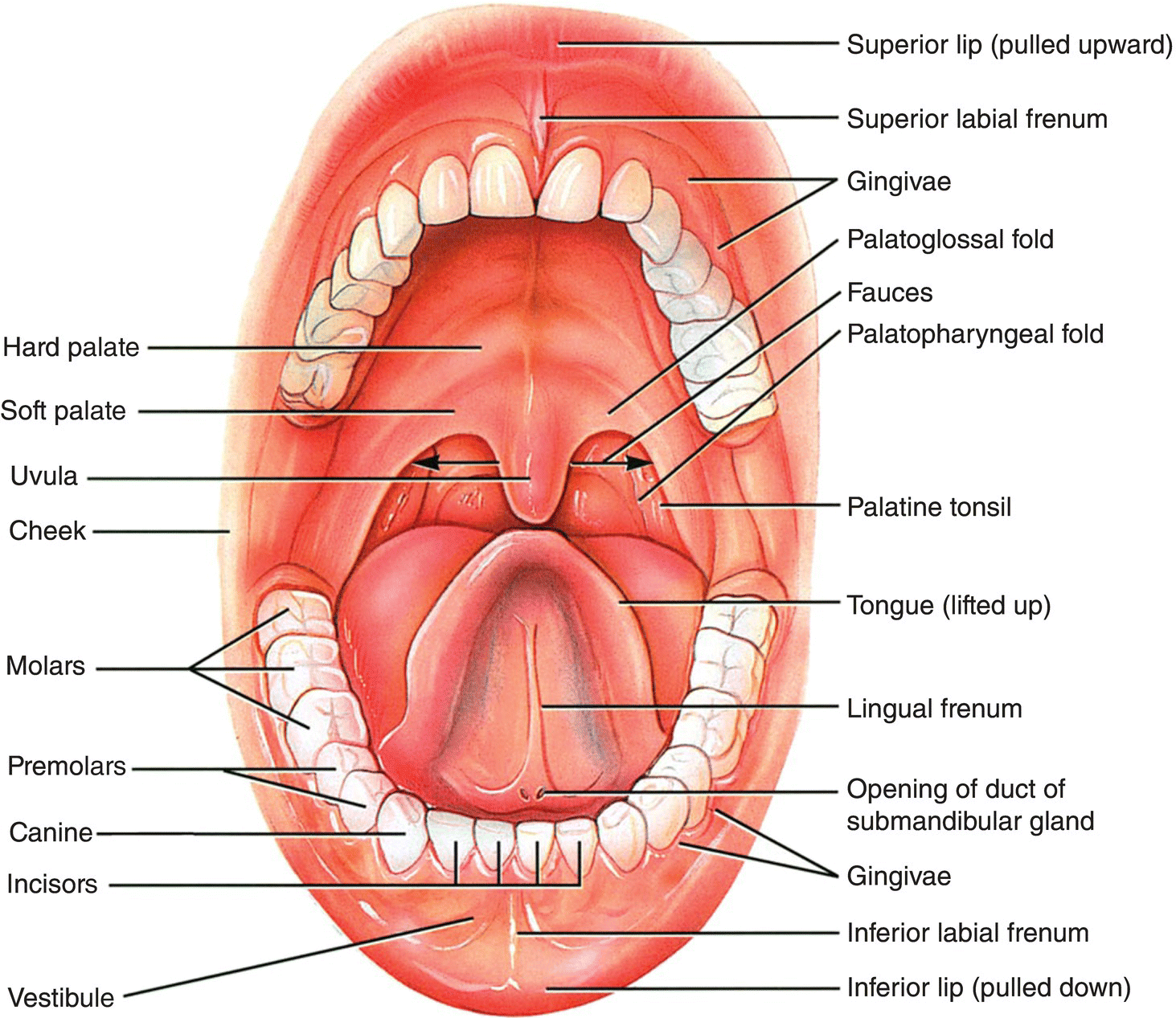
The mouth or oral cavity is formed by the cheeks, hard and soft palates, and tongue. The cheeks form the lateral walls of the oral cavity. The lips are fleshy folds around the opening of the mouth.
Both the cheeks and lips are covered on the outside by skin and on the inside by a mucous membrane. During chewing, the lips and cheeks help keep food between the upper and lower teeth. They also assist in speech.

The hard palate, consisting of the maxillae and palatine bones, forms most of the roof of the mouth. The rest is formed by the muscular soft palate. Hanging from the soft palate is a projection called the uvula.
During swallowing, the uvula moves upward with the soft palate, which prevents entry of swallowed foods and liquids into the nasal cavity. At the back of the soft palate, the mouth opens into the oropharynx. The palatine tonsils are just posterior to the opening.

(Ref:- J. TORTORA, The essentials of anatomy and physiology, 8th edition, P-490,491)
Read more:
