Neissería Gonorrhoeae – Basic microbiology, parasitology, and immunology; nature, reproduction, growth, and transmission of common microorganisms and parasites in Bangladesh; prevention including universal precaution and immunization, control, sterilization, and disinfection; and specimen collections and examination. Students will have an understanding of common organisms and parasites caused human diseases and acquire knowledge about the prevention and control of those organisms.
Neissería Gonorrhoeae
Gonorrhea is an infection caused by a sexually transmitted bacterium that can infect both males and females. Gonorrhea most often affects the urethra, rectum or throat. In females, gonorrhea can also infect the cervix.
Classification of Neisseria:

Comparison of N. menineitides with N. gonorrhoeae:
| Traits | N. meningitides (Meningococcus) | N. gonorrhoeae (Gonococcus) |
| Portal of entry | Respiratory tract | Genital tract |
| Polysaccharide capsule | Present | Absent |
| Maltose fermentation | Yes | No |
| B-lactamase production | None | Some |
| Preventable by vaccine | Yes | No |
| Endotoxin | Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) | Lipooligosaccharide (LOS) |
| Plasmids | Rare | Common |
Morphology of Gonococcus:
- Gram-negative cocci (arranged in pairs).
- They resemble paired kidney beans. (Each having a concave margin & a convex margin, concave sides are adjacent)
- Non-acid fast.
- Usually intracellular within neutrophils in lesions and exudates.
- Contain endotoxin in their outer membrane.
- [Endotoxin of N. gonorrhoeae is lipo-oligosaccharide (LOS)]
- Non-flagellated, non-motile.
- Non-spore forming.
- Possesses pili.
- Non-capsulated. (they have no polysaccharide capsule)
Virulence factors of N. gonorrhoeae:
➤ Pili.
➤ Endotoxin (Lipo-oligosaccharide).
➤ Outer membrane proteins (OMP 1,2 and 3):
- OMP2- plays a role in attachment of the organism to cells and varies antigenically.
➤ IgA 1 protease:
- Cleaves IgA 1 that defends mucosal surface.
➤ Iron binding protein (FBP)
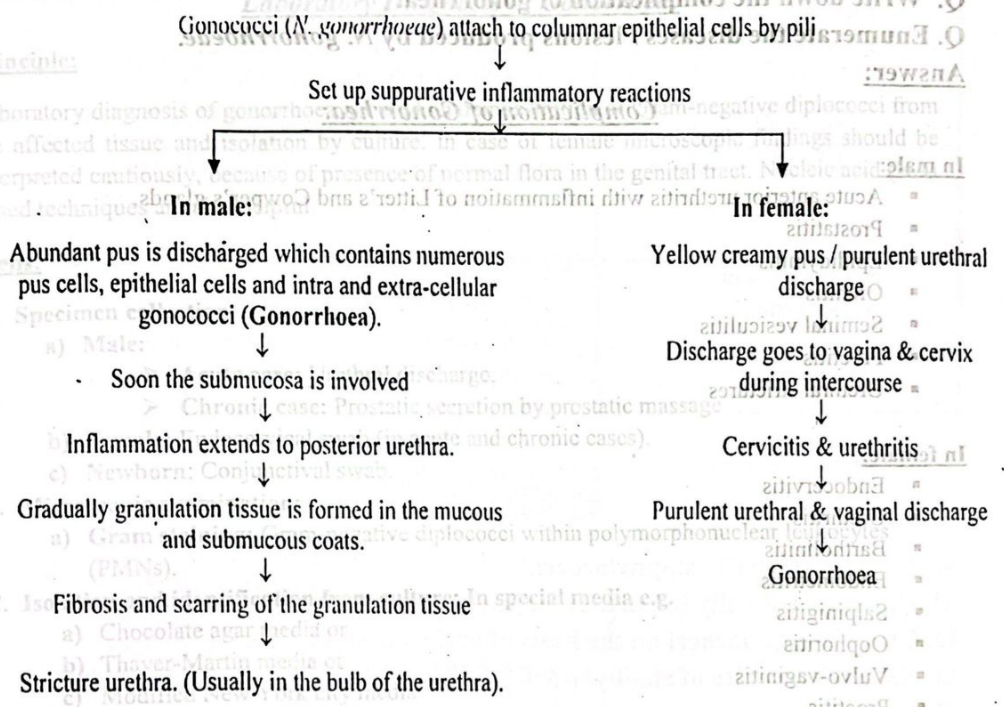
Pathogenesis of Gonorrhea:
Sign and Symptoms of Gonorrhea:
A. Signs and symptoms of gonorrhea infection in men include:
- Painful urination
- Pus-like discharge from the tip of the penis
- Pain or swelling in one testicle
B. Signs and symptoms of gonorrhea infection in women include:
- Increased vaginal discharge
- Painful urination
- Vaginal bleeding between periods, such as after vaginal intercourse
- Painful intercourse
- Abdominal or pelvic pain
Complication of Gonorrhea
In male:
- Acute anterior urethritis with inflammation of Litter’s and Cowper’s glands.
- Prostatitis
- Epididymitisms
- Orchitis
- Seminal vesiculitis
- Proctitis
- Urethral strictures
In female:
- Endocervitis
- Urethritis
- Bartholinitis
- Endometritis
- Salpinigitis
- Oophoritis
- Vulvo-vaginitis
- Proctitis
- Pelvic pritonitis
- Cystitis
New-born infants:
- Purulent conjunctivitis (ophthalmia neonatorum)
Other lesions in both sexes:
- Septicaemia (Disseminated gonococcal infection- DGI)
- Ulcerative endocarditis
- Arthritis-dermatitis-tenosynovitis syndrome
- Spondylitis deformans
- Gonococcal pharyngitis (In case of oral sex).
Laboratory Diagnosis of Gonorrhea:
Principle:
Laboratory diagnosis of gonorrhoea is based on demonstration of Gram-negative diplococci from the affected tissue and isolation by culture. In case of female microscopic findings should be interpreted cautiously, because of presence of normal flora in the genital tract. Nucleic acid (NA) based techniques are also helpful.
Steps:
A. Specimen collection:
a) Male:
➤ Acute case: Urethral discharge.
➤ Chronic case: Prostatic secretion by prostatic massage
b) Female: Endocervical swab (in acute and chronic cases).
c) Newborn: Conjunctival swab
B. Microscopic examination:
a) Gram staining: Gram-negative diplococci within polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs)
C . Isolation and identification from culture: In special media egri
a) Chocolate agar media or
b) Thayer-Martin media or
c) Modified New York city media
➤ Incubation temperature: 37°
➤ Incubation period: 18-24 hours
➤ Incubation environment: 5-10% C02 (in candle jar)
D. Biochemical test:
a) Oxidase positive
b) Ferments glucose (but not maltose).
E. Serological tests: To detect Ab against gonococci are not useful for diagnosis. Following quiz tests may be done
a) ELISA.
b) DNA probe assay.
F. Nucleic acid based technique:
a) Polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
Treatment of Gonorrhea:
A. Uncomplicated gonorrhea:
- Cefixime 400mg orally. Or
- Ciprofloxacin 500mg orally. Or
- Ofloxacin 400mg orally. Or
- Amoxicillin, 3gm + probenecid 1gm orally.
B. Quinolones resistance:
- Ceftriaxone 250 mg Intramuscular route. Or
- Spectinomycin 2gm intramuscular route.
C. Pregnancy and breastfeeding:
- Cefixime 400 mg. Or
- Ceftriaxone, 250 mg intramuscular. Or
- Spectinomycin 2gm intramuscular route.
- Amoxicillin, 3gm + probenecid 1gm orally.

