Network Topology – This book covers the entire syllabus of “Computer & Information Technology” prescribed by the BNMC for B.Sc. in Nursing Science & Diploma in Nursing Science & Midwifery students. We tried to accommodate the latest information and topics.
This book is an examination setup according to the teachers’ lectures and examination questions. We hope in touch with the book students’ knowledge will be upgraded and flourished. The unique way of presentation may make your reading of the book a pleasurable experience.
Network Topology
Definition of Network Topology:
A network topology is the arrangement of a network, including its nodes and connecting lines. There are two ways of defining network geometry: the physical topology and the logical (or signal) topology.
or
Network Topology refers to layout of a network. How different nodes in a network are connected to each other and how they communicate is determined by the network’s topology.
or
Network topology refers to the physical or logical layout of a network. It defines the way different nodes are placed and interconnected with each other.
Types of Network Topology:
1. Bus-topology,
2. Star-topology,
3. Ring-topology,
4. Mesh-topology,
5. Tree-topology,
6. Hybrid-topology
A. Mesh Topology: In a mesh network, devices are connected with many redundant interconnections between network nodes. In a true mesh topology every node has a connection to every other node in the network.

There are two types of mesh topologies:
a) Full mesh topology: occurs when every node has a circuit connecting it to every other node in a network.
b) Partial mesh topology: Partial mesh topology is less expensive to implement and yields less redundancy than full mesh topology.
B. Star Topology: In a star network devices are connected to a central computer, called a hub. Nodes communicate across the network by passing data through the hub.

- Main Advantage: In a star network, one malfunctioning node doesn’t affect the rest of the network.
- Main Disadvantage: If the central computer fails, the entire network becomes unusable.
C. Bus Topology: In networking a bus is the central cable — the main wire — that connects all devices on a local-area network (LAN). It is also called the backbone. This is often used to describe the main network connections composing the Internet. Bus networks are relatively inexpensive and easy to install for small networks. Ethernet systems use a bus topology.
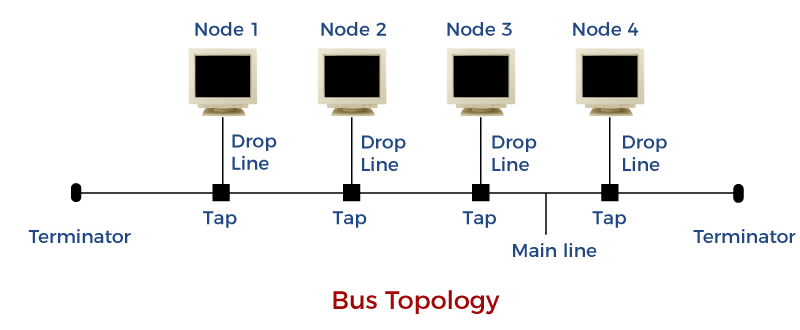
- Main Advantage: It’s easy to connect a computer or device and typically it requires le cable than a star topology.
- Main Disadvantage: The entire network shuts down if there is a break in the main wi and it can be difficult to identify the problem if the network shuts down
D. Ring Topology: A local-area network (LAN) whose topology is a ring. That is, all of 1 nodes are connected in a closed loop. Messages travel around the ring, with each nc reading those messages addressed to it.
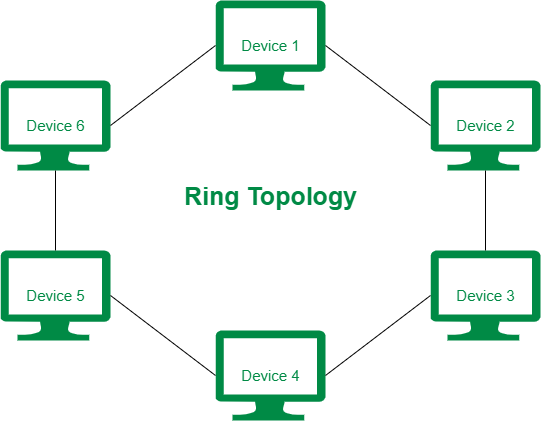
- Main Advantage: One main advantage to a ring network is that it can span larger distances than other types of networks, such as bus networks, because each node regenerates messages as they pass through it.
E. Tree Topology: This is a “hybrid” topology that combines characteristics of linear bus and star topologies. In a tree network, groups of star-configured networks are connected to a linear bus backbone cable.

- Main Advantage: A Tree topology is a good choice for large computer networks as the tree topology “divides” the whole network into parts that are more easily manageable.
- Main Disadvantage: The entire network depends on a central hub and a failure of the central hub can cripple the whole network.
Advantages of Bus Topology:
- It is easy to set up, handle, and implement.
- It is best-suited for small networks.
- It costs very less.
Disadvantages
- The cable length is limited. This limits the number of network nodes that can be connected.
- This network topology can perform well only for a limited number of nodes. When the number of devices connected to the bus increases, the efficiency decreases.
- It is suitable for networks with low traffic. High traffic increases load on the bus, and the network efficiency drops.
- It is heavily dependent on the central bus. A fault in the bus leads to network failure.
- It is not easy to isolate faults in the network nodes.
- Each device on the network “sees” all the data being transmitted, thus posing a security risk.
Advantages of Ring Topology:
- The data being transmitted between two nodes passes through all the intermediate nodes. A central server is not required for the management of this topology.
- The traffic is unidirectional and the data transmission is high-speed.
- In comparison to a bus, a ring is better at handling load.
- The adding or removing of network nodes is easy, as the process requires changing only two connections.
- The configuration makes it easy to identify faults in network nodes.
- In this topology, each node has the opportunity to transmit data. Thus, it is a very organized network topology.
- It is less costly than a star topology.
Disadvantages
- The failure of a single node in the network can cause the entire network to fail.
- The movement or changes made to network nodes affect the entire network’s performance.
- Data sent from one node to another has to pass through all the intermediate nodes. This makes the transmission slower in comparison to that in a star topology. The transmission speed drops with an increase in the number of nodes.
- There is heavy dependency on the wire connecting the network nodes in the ring.
Advantages Mesh Topology
- The arrangement of the network nodes is such that it is possible to transmit data from one node to many other nodes at the same time.
- The failure of a single node does not cause the entire network to fail as there are alternate paths for data transmission.
- It can handle heavy traffic, as there are dedicated paths between any two network nodes.
- Point-to-point contact between every pair of nodes, makes it easy to identify faults.
Disadvantages
- The arrangement wherein every network node is connected to every other node of the network, many connections serve no major purpose. This leads to redundancy of many network connections.
- A lot of cabling is required. Thus, the costs incurred in setup and maintenance are high.
- Owing to its complexity, the administration of a mesh network is difficult.
Advantages Star Topology:
- Due to its centralized nature, the topology offers simplicity of operation.
- It also achieves isolation of each device in the network
- Adding or removing network nodes is easy, and can be done without affecting the entire network.
- Due to the centralized nature, it is easy to detect faults in the network devices.
- As the analysis of traffic is easy, the topology poses lesser security risk.
- Data packets do not have to pass through many nodes, like in the case of a ring network.
- Thus, with the use of a high-capacity central hub, traffic load can be handled at fairly decent speeds.
Disadvantages
- Network operation depends on the functioning of the central hub. Hence, central hub failure leads to failure of the entire network.
- Also, the number of nodes that can be added, depends on the capacity of the central hub.
- The setup cost is quite high.
Advantages Tree Topology:
- The tree topology is useful in cases where a star or bus cannot be implemented individually. It is most-suited in networking multiple departments of a university or corporation, where each unit (star segment) functions separately, and is also connected with the main node (root node).
- The advantages of centralization that are achieved in a star topology are inherited by the individual star segments in a tree network.
- Each star segment gets a dedicated link from the central bus. Thus, failing of one segment does not affect the rest of the network.
- Fault identification is easy.
- The network can be expanded by the addition of secondary nodes. Thus, scalability is achieved.
Disadvantages
- As multiple segments are connected to a central bus, the network depends heavily on the bus. Its failure affects the entire network.
- Owing to its size and complexity, maintenance is not easy and costs are high. Also, configuration is difficult in comparison to that in other topologies.
- Though it is scalable, the number of nodes that can be added depends on the capacity of the central bus and on the cable type.