Norplant and Injectable contraceptive – This book covers the entire syllabus of “Community Health Nursing” prescribed by the Universities of Bangladesh- for Basic and diploma nursing students. We tried to accommodate latest information and topics.
This book is examination friendly setup according to the teachers’ lectures and examination’s questions. At the end of the book previous university questions are given. We hope in touch with the book students’ knowledge will be upgraded and flourished. The unique way of presentation may make your reading of the book a pleasurable experience.
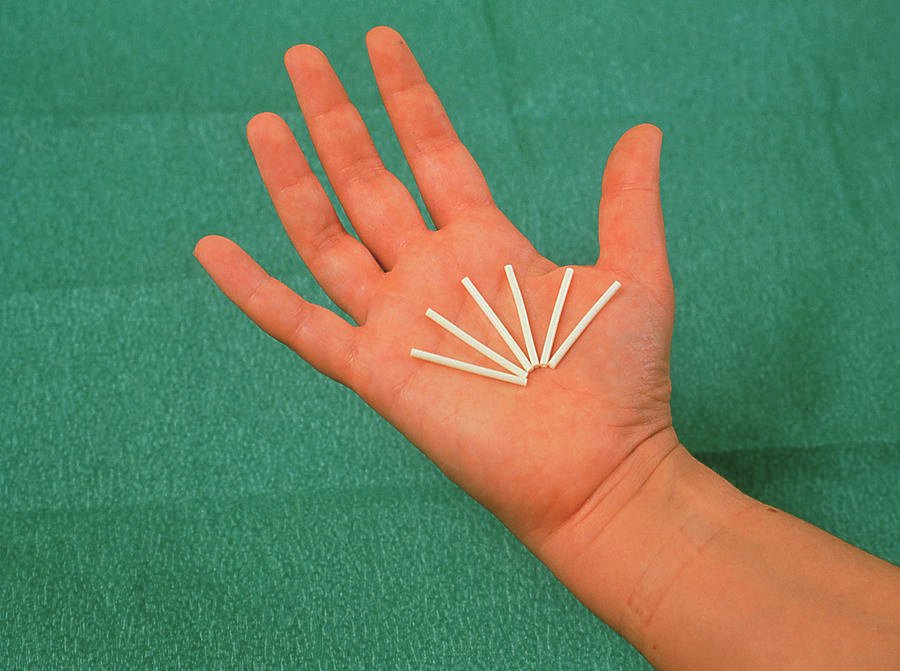
Norplant and Injectable contraceptive
Norplant
Norplant consists of 6 sciolistic rods inseted subdermally in the upper arm, which release the progesterone levonogestrel and last for 5 yejrs. Insertion & removal of Norplant must be done by a trained healthcare professional.
| A. Advantages of Norplant: |
|
| B. Disadvantages: |
|
Injectable contraceptive
A. Injectable contraceptive:
These are-
1. Depot medroxy progesterone acetate 150 mg (DMPA or Depo provera) Im injection lasts around 3 months.
2. Norethisteroneenanthate 200 mg IM only last for 2 months. Most women choose Depo provera
B. Mode of action:
1. Atrophic change in the endometrium, thus prevents implantation
2. Making cervical mucus thick, so sperm cannot enter into the cervix
3. Inhibition of ovulation by suppressing the mid cycle LH Peak.
C. Indication of Depo provera:
1. A short term basis following a pregnancy or abortion (when irregular bleeding is of little account)
2. Long term basis in women for whom other contraceptive are unsuitable or contra indicated
3. Difficulty in remembering to take a pill
4. Painful periods
5. PMS
D. Side effects:
1. Weight gain of around 6 Ib in the 1 year
2. Delay in return of fertility-it may take about 6 months longer to conceive than after stopping COC
3. Persistent menstrual irregularity
4. Very long term use may slightly increase the risk of osteoporosis (because of low estrogen levels).
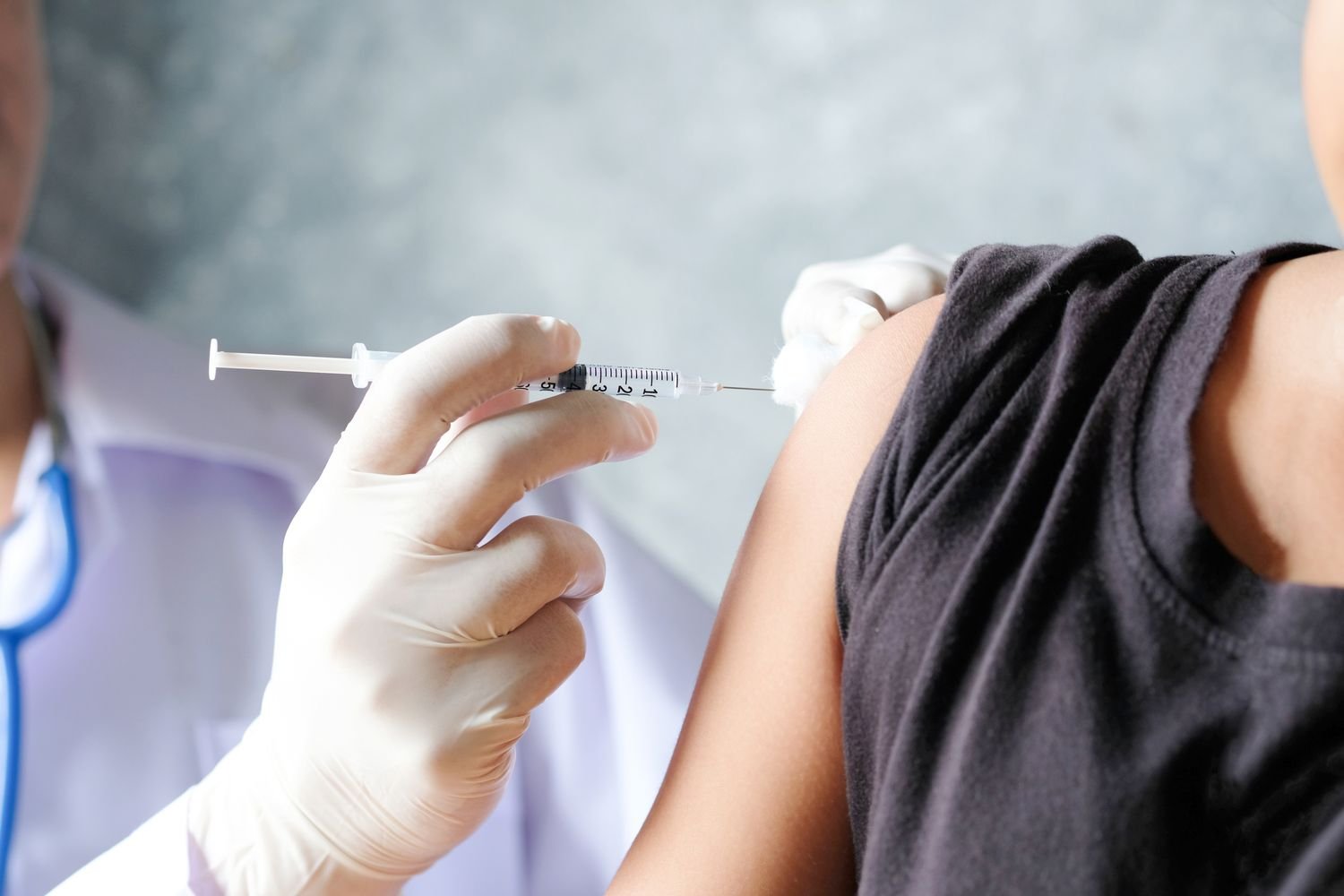
Complication of Injectable Contraceptive
1. Irregular bleeding
2. Weight gain
3. Delayed return of fertility
4. Galactorrhoea
5. Enuresis
6. Amenorrhoea
7. Persistent menstrual.
