Nurses role and intervention in the community – This book covers the entire syllabus of “Community Health Nursing” prescribed by the Universities of Bangladesh- for Basic and diploma nursing students. We tried to accommodate latest information and topics.
This book is examination friendly setup according to the teachers’ lectures and examination’s questions. At the end of the book previous university questions are given. We hope in touch with the book students’ knowledge will be upgraded and flourished. The unique way of presentation may make your reading of the book a pleasurable experience.
Nurses role and intervention in the community
Nurses role and intervention in the community
Eight Characteristics of Community Health Nursing:
1. Field of nursing shift from individual to aggregate, into
2. Combines public health with nursing community-based & population focused public health sciences & nursing theory
3. Population focused
4. Emphasizes prevention
5. Promotes client responsibility & self-care
6. Use aggregate assessment measurement & analysis
7. Uses principles of organizational theory
8. Involves inter-professional collaboration.

7 roles of community health nurses that influence on community health
1. Clinician: focus on holism, health promotion & prevention while using expanded skills.
2. Educator: plan for community wide impact.
3. Advocate: Support client self-determination and responsive systems.
4. Manager: Participative approach with community.
5. Collaborator: multidisciplinary collegiality and leadership.
6. Leadership: Change agent
7. Researcher: Systematic investigation, collection, and analysis of data for solving problems and bring evidence-based findings to community settings
Six Components of community Health Practice
1. Promotion of health
2. Prevention of health problems.
3. Treatment of disorders
4. Rehabilitation
5. Evaluation
6. Research
Continuity of caге
Continuity of care is provision of health service without disruption, regardless of movement between settings. Continuity of care is a concern across the health care continuum. It ensures that the client is a part of the decision-making team and that appropriate information and plans are clearly communicated to both formal and informal caregivers. In this, the nurse facilitates collaboration, coordination, and cooperation among caregivers.
Significance of continuity of care
Continuity of care is provision of uninterrupted service as a client take between settings. Now in a new century, health-care delivery will continue to change, bring new opportunities to nurse ready to accept the challenges. The following significance of continuity of care are;
1. Provide primary and preventive care for both healthy and ill consumer.
2. Services people of all ages and at all levels of health.
Principles and process of Continuity of Care
Principles and process to guide all caregivers in providing continuity of care include the following:
1. Client/Family Involvement in Decision-Making:
- A systematic process occurs that involves the client/family in care planning.
- Current, appropriate, evidence-based information is provided in a timely manner. including discussion of realistic goals and expected outcomes, to enable clients/family to
make informed choices.
2. Comprehensive Client Information:
- Initial assessment is a critical component of planning and includes assessment of the client/family needs strength and resources.
- Transfer information includes a plan of care with measurable outcomes that is understandable to the client and all caregivers.
- Confidential health information collected is current comprehensive, and appropriately disseminated to team members.
3. Communication:
- Communication must be open, honest, and facilitate equal sharing of information among health cate professionals.
- Communication between providers and the client/family occurs through regular discussions and written documentation following current legislation and employer policies.
- Client information and the plan of care are easily accessible to team members.
- Communication is timely to ensure that all team members are aware of their role in providing for continuity of care. This becomes more important to the quality of client care as patterns of service delivery move toward increased reliance on numerals community based providers.
4. Clear Systematic Process:
- A system-wide process is initiated that enables quality care across a variety of settings.
- Assessment, planning, implementation, and evaluation of continuity of care activities are client-focused and comprehensive
- Policies, role descriptions, protocols, methods of follow-up, and program evaluation provide consistency in continuity of care.
5. Coordination of Care Through Each Transition of the Client:
- Continuity of care requires a coordinated, interdisciplinary team approach. Each discipline brings a different perspective to planning.
- Knowledge about available resources and services is shared.
- Transitions are an uninterrupted succession of events.
- Coordination over time and across a variety of settings is essential
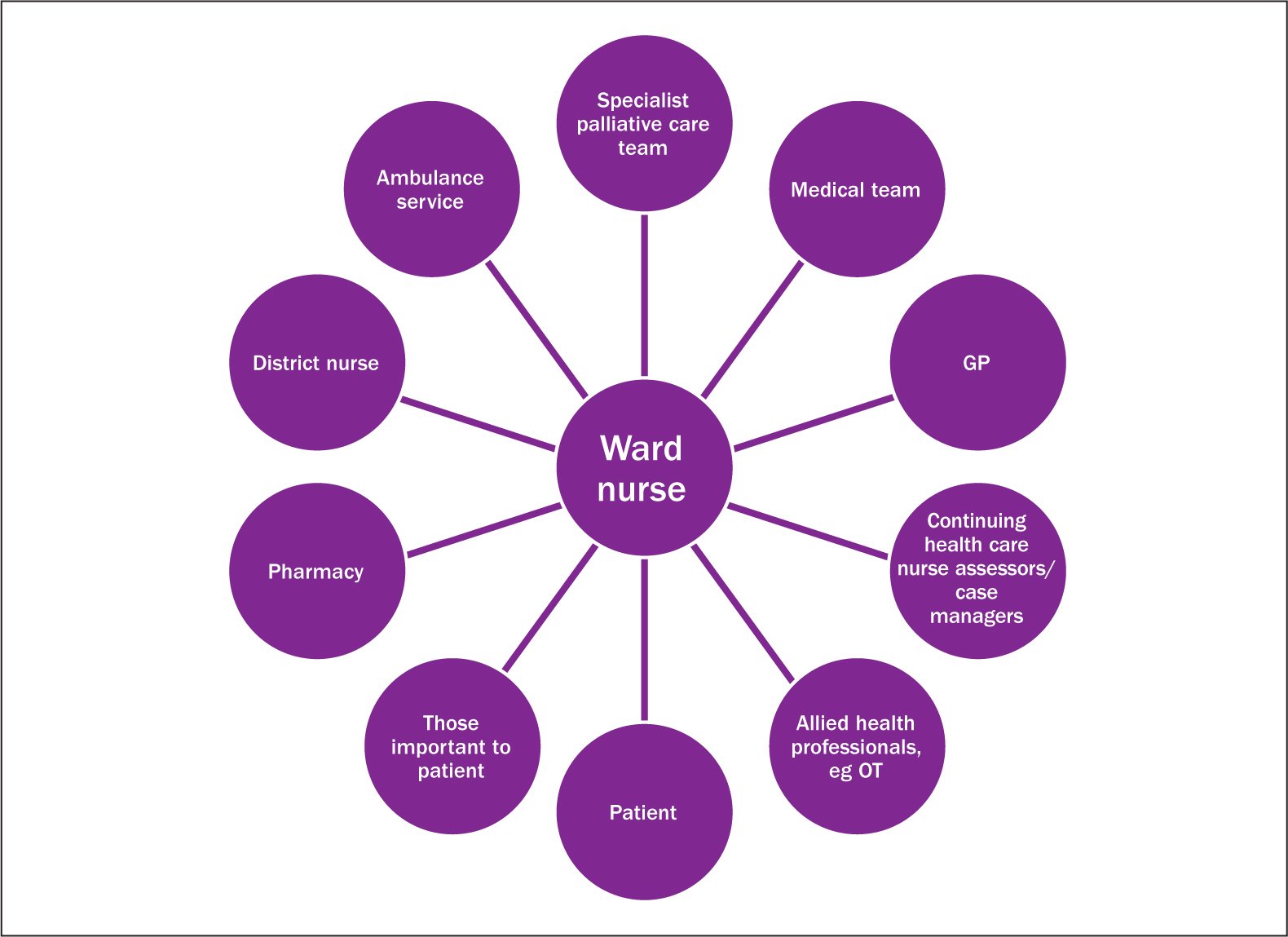
Roles of nurse in providing continuity of care
Registered nurses play a key role in the provision of health care services and patient care. Given their critical role in long-term care, community care, public health, home care, and acute care and the fact that the profession is based on evidence-based practice, registered nurses can contribute significantly to decisions regarding the types of health services which provide the best patient outcomes.
The nursing process in continuity of care is complex due to the number and variety of settings and people involved, as the client moves within the health system. Registered nurses are leaders in implementing collaborative practice. The RN, as a direct caregiver, has the most consistent presence in providing care to a client and has knowledge of a client’s continuing care needs. Therefore, a registered nurse can contribute significantly to the coordination and planning for continuity of care for a client.

Activities of the registered nurse in continuity of care include, but are not limited to
1. Conducting comprehensive assessments, including verification of the client’s health status, and consideration of formal and informal support systems, environment, lifestyle, culture, values, beliefs, and community resources.
2. Facilitating the coordination of care from all the providers or may oversee the designation of a coordinator of care.
3. Defining nursing’s responsibility and the contribution of nursing to the overall plan of care.
4. Providing direct client care.
5. Educating the client/family to enable informed and knowledgeable choices.
6. Understanding the respective roles and clearly defined responsibilities of other caregivers.
7. Advocating for workplace policies that support continuity of care.
8. Participating in evaluation of continuity of care.
9. Educating self and others regarding best practices in continuity of care.
Discharge planning
Discharge planning prepares a client to move from one level of care to another within or outside the current health care facility. Discharge planning occurs from all settings including ambulatory surgical centers, rehabilitation and childbirth centers it is a routine feature of health systems in many countries that aims to reduce hospital length of stay and unplanned readmission to hospital, and improve the CO ordination of services.
Following discharge from hospital thereby bridging the gap between hospital and place of discharge. Sometimes discharge planning is offered as part of an integrated package of care, which may cover both the hospital and community.
