Today our topic of discussion is Nursing Implementation.
Nursing Implementation
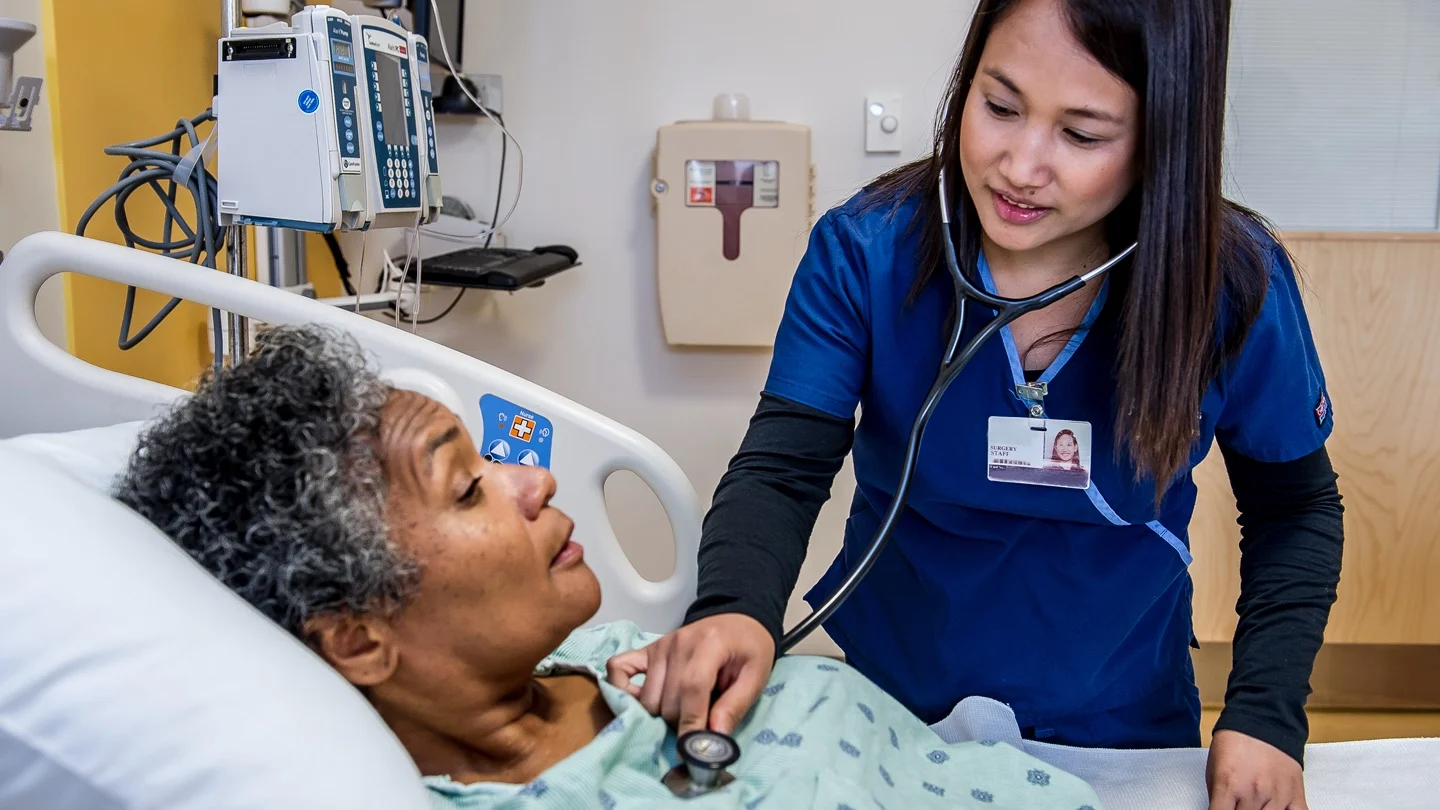

Nursing interventions are the actual implementation of the care plan. Nursing interventions are designed to promote, maintain or restore the client’s health.
Nursing interventions have following seven characteristics:
- Be congruent with the overall plan of care.
- Be based on scientific principles.
- Be individualized to the client.
- Be designed to provide a safe and therapeutic environment.
- Consider the need for teaching and learning.
- Use resources appropriately.
- Be clearly communicated.
Providing self-care:
The nurse should identify what skills are required for providing the intervention. It is important to remember that when a skill is delegated to another health care team member, the registered nurse remains legally responsible for the client’s outcome.
Another aspect of providing self-care is continuous monitoring for complication. There are many complications that can allow surgery, medication administration and disease states.
While the care is being given, the nurse continues to assess the client and evaluate his or her response to the care. The nurse also needs to consider which of the interventions could be modified, if the client shows no progress toward the desired outcome.

Nursing roles:
Providing care teller into seven categories, according to Benner: Helper role, teaching coaching, diagnostic and patient monitoring, management of rapidly changing conditions, administering and monitoring therapeutic regimens, monitoring and ensuring quality of health care practices and organizational and work role competencies.
Rationale:
At times, the scientific rationale for an within a standardized plan of care. It is important that the care given has its basis in scientific study, not in habit or old wives tales. The use of rationale assists in identifying the professional nurse from other providers of health care.