Nursing Process – Nursing is a profession within the healthcare sector focused on the care of individuals, families, and communities so they may attain, maintain, or recover optimal health and quality of life. Nurses may be differentiated from other healthcare providers by their approach to patient care, training, and scope of practice. Nurses practice in many specialisms with differing levels of prescriber authority.
Many nurses provide care within the ordering scope of physicians, and this traditional role has shaped the public image of nurses as care providers. However, nurses are permitted by most jurisdictions to practice independently in a variety of settings depending on training level. In the postwar period, nurse education has undergone a process of diversification towards advanced and specialized credentials, and many of the traditional regulations and provider roles are changing.
Nurses develop a plan of care, working collaboratively with physicians, therapists, the patient, the patient’s family, and other team members, that focus on treating illness to improve quality of life. Nurses may help coordinate the patient care performed by other members of an interdisciplinary healthcare team such as therapists, medical practitioners, and dietitians. Nurses provide care both interdependently, for example, with physicians, and independently as nursing professionals.
Nursing Process
Definition of Assessment:
Assessment is the gather, verify, differentiate and impart data about the patient to establish a data base. It is done by collection of data through-
- History taking.
- Physical examination.
- Review of investigations reports and
- Record analysis.
Or,
Assessment is the systematic gathering of information related to the physical, mental, spiritual, socio-economic and cultural states of an individual or group.
Or
Assessment is the first step of the nursing process, refers to systematic appraisal of all factors relevant to a client’s health.
Or
Assessment is defined as a systematic and continuous collection of data on the health status of the patient to determine the patient’s health status and to identify any actual or potential health problems.

Definition of Nursing Assessment:
Nursing assessment is the continuous, systematic, critical, orderly and precise method of collecting, validating, analyzing and interpreting information about physical, psychological and social needs of an individual nature of self-care deficits and other factors influencing conditions.
Purposes/Significance/Benefits/Importance of Health Assessment:
10. To gather data/ information that:
- Surveying the client’s health status and risk factors for particular health problem.
- Identifying latent or occult (undetected) disease.
- Screening for a specific disease such as diabetes or hypertension (ie, case finding).
- Identifying risks for particular health problems.
- Determining functional impact of disease (ie, human response to actual or potential health problems.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of the health care plan.
11. To perform physical examination.
12. Early detection of the disease.
13. Identification of the patients’ individual actual problem.
14. To review the records.
15. To establish a nursing diagnosis.
16. To identify the nursing needs of the patient.
17. To prepare a nursing care plan.
18. To provide complete nursing care.
Components/Elements Assessment Process:
8. Good communication.
9. A systematic approach to data collection
10. Interpretation based on nursing knowledge.
11. Empirics’ measurement of knowledge with scientific fact.
12. Aesthetics gained through empathy and is how a nurse becomes sensitive to a patient’s pain, worry or joy.
13. Ethics concerned with motivation, morality, human rights and law.
14. Personal knowledge awareness that the nurse has an impact on patient care.
Assessment Strategies:
4. Observation/Inspection.
5. Asking question to the clients.
6. Physical examination by-
- Inspection
- Palpation.
- Auscultation.
- Percussion.

Phases/Steps of Assessment in the nursing process
5. Subjective data collection.
6. Objective data collection.
7. Validation of data. Bon
8. Documentation of data.
E. Subjective data collection:
d) Subjective data are sensation or symptoms (e.g. pain, hunger), feelings (e.g. Happiness, sadness), perceptions desires, preferences, beliefs, ideas, values, and personal information that can be elicited and verified only by the client.
e) To elicit accurate subjective data, the nurse must learn to see effective interviewing skills with a variety of clients in different settings.
f) The major areas of subjective data include.-
- Biographical information, (e.g. name, age, religion, occupation).
- Physical symptoms related to each body part or system (e.g. eyes and ears, abdomen).
- Past and family history
- Holistic information regarding the client’s health (eg. Health practices that put the client at risk, nutrition, activity, relationships).
F. Objective data collection:
d) Objective data are directly observed or indirectly observed through measurements. This data can be
- Physical characteristic (skin color, posture).
- Body functions (heart rate, respiratory rate).
- Measurement (Blood pressure, temperature, height, weight).
- The results of laboratory testing (platelet count, X-ray findings).
e) This type of data is obtained by general observation and by using the four physical examination techniques:
- Inspection.
- Palpation.
- Percussion.
- Auscultation.
f) Objective data may also be observations noted by the family or significant others about the client
G. Validation of data:
d) Validation of assessment data is a crucial part of assessment that often occurs along. with collection of subjective and objective data
e) It serves to ensure that the assessment process is not ended before all relevant data WeltA have been collected.
f) It helps prevent documentation of inaccurate data.
H. Documentation of data;
b) Documentation of assessment data is an important steps of assessment because it forms the database for the entire nursing process and provides data for all other members of the heath care team.
Nursing Diagnosis
Nursing diagnosis is defined as a statement supported by valid data of an actual or potential health problem whose etiology or significantly related condition or situation requires nursing intervention for effective and predictable management.
or
Nursing diagnosis is the term used to classify health problem within the scope of nursing. Clinical judgment about client responding to actual or potential health problems or life process provides basis for selection of nursing therapies.
or
A nursing diagnosis may be part of the nursing process and is a clinical judgment about individual, family, or community experiences/responses to actual or potential health problems/life processes.
Types of Nursing Diagnosis:
A. Wellness nursing diagnosis: Wellness nursing diagnosis represents those situations in which the client does not have a problem, but it is a point where he / she can attain a higher level of health.
- Example: Opportunity to enhance effective breast feeding related to confident mother.
B. Risk nursing diagnosis: A risk diagnosis indicates that the client does not currently have the problem but is at high risk for development it.
- Example: Risk for impaired skin integrity related to immobility, poor nutrition and incontinence.
C. Actual nursing diagnosis: When the client experiences that stated problem or has a dysfunctional pattern is considered as the actual nursing diagnosis. The clinical criteria or assessment findings that support an actual nursing diagnosis.
- Example: Impaired urinary elimination related to unconscious state. Neurological deficit due to stroke.
Characteristics of Nursing Diagnosis:
- They state a clean and concise health problem.
- They are derived from existing evidence about the patient and from sound nursing therapy.
- They are on the basis for planning and carrying out nursing care.
- They are patients centered.
Aims of Nursing Diagnosis:
- Identify actual or potential problem of the patient.
- Organize, analyze, synthesize and summarize the assessment data.
- Improves communication between nurses and other members of health care team.
- Nursing diagnosis helps the patient to reach the highest level of health.
Guide Line for Writing Nursing Diagnosis:
1. Write down a problem: do not write down a need.
2. Write without judgment.
3. Make sure that both parts of the diagnosis do not say the same things.
4. Write first the problem, then the related factors.
5. Use legally advisable terms, use facts instead of writing about negligence or blame.
6. Write the related factors in terms that can be changed,
7. Do not include medical diagnosis in the nursing diagnosis.
8. Write the diagnosis clearly and concisely.
9. Do not write a nursing action in the nursing diagnosis.
10. The ‘format’ of a correctly written nursing diagnosis.
Advantages of Nursing Diagnosis:
1. Nursing diagnosis provides efficiency, clarification and standardization.
2. Nursing diagnosis provides purpose and direction. 3. Nursing diagnosis facilitates research and education.
4. Nursing diagnosis would delineate independent nursing functions.
5. Nursing diagnosis increases the accountability.
Components of Nursing Diagnosis:
A guide that may be used to help prepare a nursing diagnosis is the “PES” format which consists of three components.
A. P-Stands for Problem: This component state the patient’s health’s an reflects his health status,
- •Example: The patient is suffering from anticipatory anxiety.
B. E-Stands for Etiology: the cause of the patient’s problem.
Example: The patient is worried about surgery, she is about to have.
C. S-Stands for Sign & symptoms of the problems he presents.
Example: The patient is suffering from sleeplessness, she is restless and cries from time to time.
Nursing Care Plan
A nursing care plan provides direction on the type of nursing care the individual/family/community may need.The main focus of a nursing care plan is to facilitate standardized, evidence-based and holistic care.
Importance/Purpose of Nursing Care Plan:
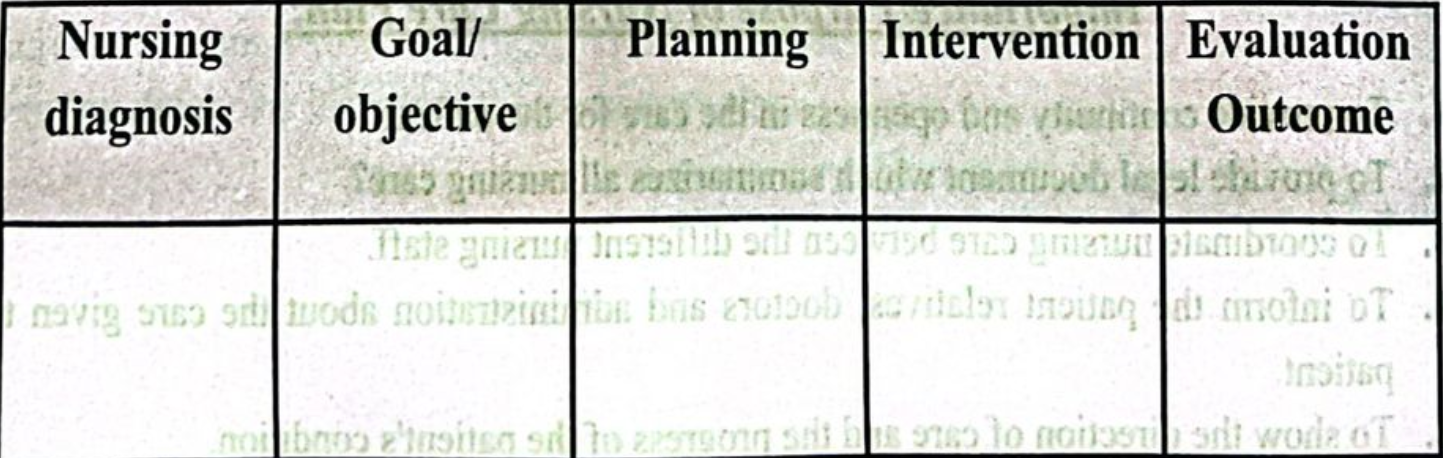
1. To provide continuity and openness in the care for the patient.
2. To provide legal document which summarizes all nursing care?
3. To coordinate nursing care between the different nursing staff.
4. To inform the patient relatives, doctors and administration about the care given to the patient.
Characteristics of Nursing Care Plan:
1. Nursing care plan should be written by a qualified nurse.
2. Nursing care plan is most effective when it is initiated after nurses’ first contact with patient / clients.
3. Nursing care plan should be readily available to all personnel involved in the care of the patients/ clients.
4. Nursing care plans should contains all current information.
5. It focuses on actions which are designed to solve or minimize the existing problem.
6. It is a product of a deliberate systematic process.
7. It relates to the future.
8. It is based upon identifiable health and nursing problem.
Components/Elements of Nursing Care Plan:
1. Nursing diagnosis.
2. Goal/objective.
3. Planning.
4. Implementation/intervention.
5. Evaluation.
Format of Nursing Care Plan
Make The Planning More Effective:
Effective planning depends on the quality and comprehensiveness of the assessment.
1. Determine the problems.
2. Establish the risks and priorities. How ill are they?
3. Can they breathe adequately (Safe airway).
4. Are they in pain? (Physical /psychological).
5. Can they maintain a safe environment? If not why not? (Drugs, drink, mental or psychological problem?).
6. Non-compliance with medical advice.
Evaluation
Evaluation is a concurrent and a terminal process. It is concurrent in that the nurse normally evaluates during the implementing phase of the process.
Purposes of Evaluation:
➤ To determine the extent to which goals of nursing care have been achieved.
Steps of Evaluating Process:
The evaluation process determines the success of nursing care and the need to alter the care plan.
The evaluation includes six steps-
➤ Identifying the outcome criteria (standards of measuring success) that will be used to and measure achievement of the goals.
➤ Collecting data related to the identified criteria.
➤ Comparing the data collected with the identified criteria and judging whether the goals have been attained criteria.
➤ Relating nursing actions to client outcomes.
➤ Reexamining the clients care plan.
➤ Modifying the care plan.
Types of Evaluation:
➤ According to criteria (structure, process and outcomes): Structure, process and outcomes all works together affect care. However each requires different criteria and methods of evaluation.
- Structural evaluation: Focuses on the setting in which care is provided. It explores the effect of organizational characteristics and the quality of care. It requires data about policies, procedures, fiscal resources, physical facilities and equipment and number and qualification of personnel.
- Process evaluation: Focus on the manner in which care is given the activities performed by nurse and other personnel. It explore whether the care was relevant to the patient needs, appropriate, complete and timely.
- Outcome evaluation: Focuses on demonstrable or measurable changes in the patient health status than result from the care given.
➤ According to frequency and time (ongoing, intermittent and terminal):
- Ongoing evaluation: It will be performed while implementing, immediately after an evaluation or at each patient contact.
- Intermittent evaluation: It is performed at specific times, which enables nurse to mmnan judge the progress towards goal achievement and to modify the care plan as needed.
